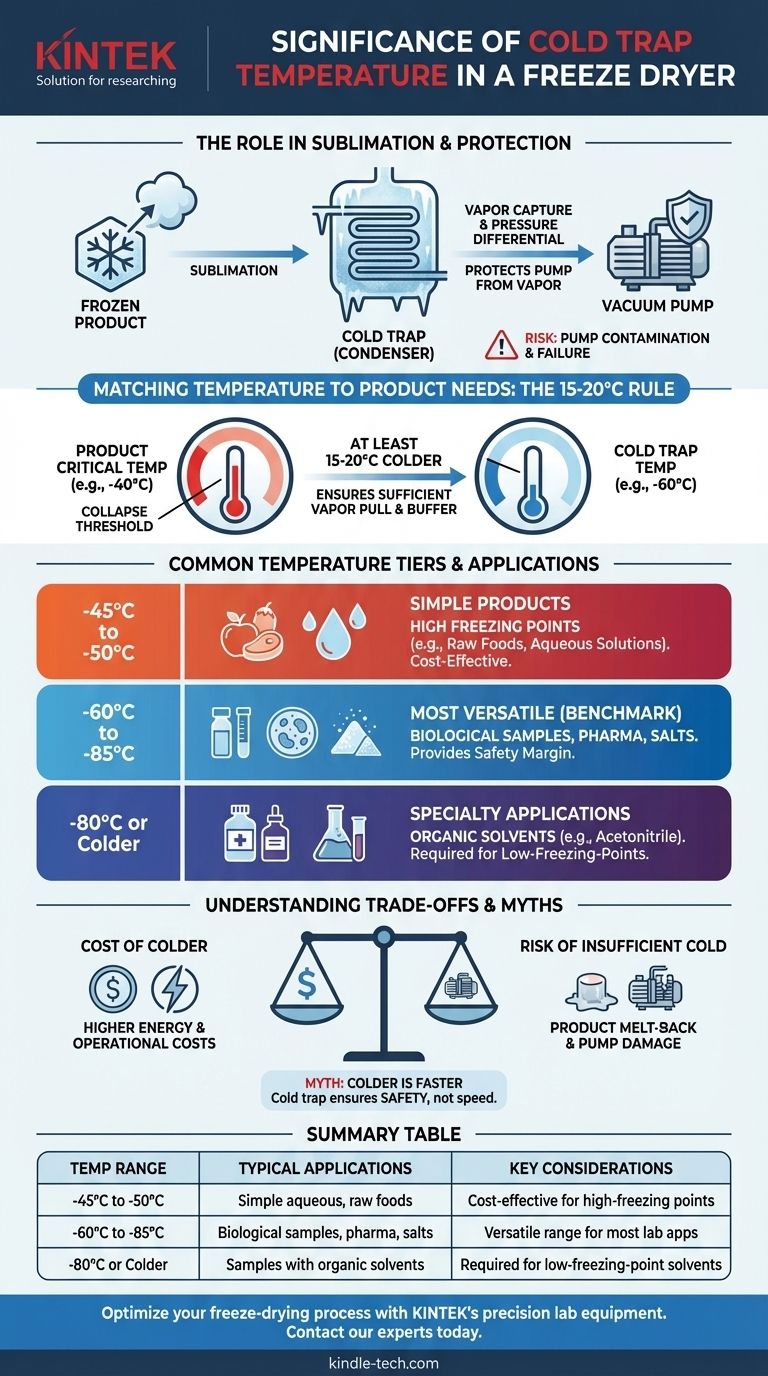
In freeze-drying, the cold trap temperature dictates the efficiency and safety of the entire process. Its primary significance is its ability to capture water vapor sublimating from your product. A lower temperature creates a more effective trap, ensuring vapor turns back into ice on the condenser coils instead of damaging the vacuum pump. Standard temperatures range from -45°C for simple products to -80°C for those containing solvents, with -60°C serving as a versatile benchmark for most applications.
The core principle is that your cold trap must be significantly colder than your product to create the necessary pressure differential for sublimation. The right temperature is a critical balance between protecting your sample's integrity, ensuring process efficiency, and managing operational costs.

The Role of the Cold Trap in Sublimation
To understand the cold trap's importance, you must first understand its role in the physics of freeze-drying. The goal is to gently remove water from a frozen product without passing through a liquid phase.
The Sublimation Engine
Freeze-drying works by first freezing the product, then applying a deep vacuum. Under this vacuum, the frozen water (ice) transitions directly into a gas (water vapor) in a process called sublimation.
The cold trap, also known as the condenser, is the destination for this water vapor.
Creating the Necessary Pressure Differential
Water vapor, like any gas, naturally moves from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure. The surface of your frozen product has a certain vapor pressure, while the intensely cold surface of the trap has a much lower vapor pressure.
This difference in pressure is the driving force of freeze-drying. A sufficiently cold trap ensures a constant, powerful "pull" that continuously draws vapor away from the product.
Protecting the Vacuum Pump
The vacuum pump is essential for creating the low-pressure environment, but it is not designed to handle large amounts of water vapor. Any vapor that bypasses the cold trap can contaminate the pump's oil, drastically reducing its performance and leading to costly repairs.
A correctly specified cold trap is the system's ultimate gatekeeper, protecting the pump and ensuring a stable vacuum throughout the process.
Matching Temperature to Your Product's Needs
The ideal cold trap temperature is not a single value; it is dictated entirely by the composition of the product being dried.
The Product's Critical Temperature
Every product has a critical temperature—the maximum temperature it can withstand during primary drying before its structure softens and collapses. This is often referred to as the eutectic point or collapse temperature.
Exceeding this temperature causes irreversible damage, resulting in a failed batch. The goal is to keep the product temperature safely below this threshold.
The 15-20°C Rule of Thumb
As a guiding principle, your cold trap temperature should be at least 15°C to 20°C colder than your product's critical temperature.
This margin ensures a sufficient vapor pressure differential to drive efficient sublimation and provides a buffer for process fluctuations.
Common Temperature Tiers Explained
Freeze dryer systems are typically offered in distinct temperature ranges, each suited for different applications.
- -45°C to -50°C: This range is effective for products with high freezing points, such as raw foods or simple aqueous solutions without salts or solvents.
- -60°C to -85°C: This is the most versatile and common range. It provides the necessary safety margin for most biological samples, pharmaceuticals, and products containing salts, which significantly depress the sample's freezing point.
- -80°C or Colder: This is required for specialty applications involving samples that contain low concentrations of certain organic solvents (like acetonitrile) which have very low freezing points.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a temperature is an engineering decision with clear trade-offs. Colder is more effective, but not always better or necessary.
The Cost of Colder Temperatures
Achieving and maintaining lower temperatures requires more energy and more complex, expensive refrigeration systems. Running a -80°C system for a product that only requires -50°C is inefficient and increases operational costs without adding value.
The Risk of an Insufficiently Cold Trap
This is the most significant risk. If the trap is not cold enough, the pressure differential weakens. This leads to longer processing times and, more critically, risks the product temperature rising above its critical point, causing melt-back.
It also increases the amount of vapor bypassing the trap, leading to certain vacuum pump contamination.
The Myth of "Colder is Faster"
While a colder trap is more efficient at capturing vapor, it does not necessarily shorten the drying cycle. The primary bottleneck for drying speed is often the rate of heat transfer to the product. The cold trap's main job is to ensure process safety and stability, not to accelerate it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Base your decision on a clear understanding of your product's characteristics and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is routine drying of simple aqueous products: A -45°C or -50°C trap is often sufficient, energy-efficient, and cost-effective.
- If you are working with a wide variety of biological or research samples: A system rated for -60°C to -85°C provides the necessary versatility and safety margin for most applications.
- If your product contains low-freezing-point solvents: You must select a system rated for -80°C or colder to ensure effective capture and prevent system damage.
Ultimately, selecting the correct cold trap temperature is the foundation for a successful, repeatable, and safe freeze-drying process.
Summary Table:
| Cold Trap Temperature | Typical Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| -45°C to -50°C | Simple aqueous solutions, raw foods | Cost-effective for high-freezing-point products |
| -60°C to -85°C | Biological samples, pharmaceuticals, salts | Versatile range for most lab applications |
| -80°C or colder | Samples with organic solvents | Required for low-freezing-point solvents |
Optimize your freeze-drying process with KINTEK's precision lab equipment. Whether you're processing pharmaceuticals, biological samples, or complex solvent-based materials, our freeze dryers with precisely calibrated cold traps ensure efficient sublimation and complete sample protection. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and discover how KINTEK's reliable laboratory solutions can enhance your results and safeguard your valuable samples.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- What is the function of efficient cooling systems and cold traps in plastic pyrolysis? Maximize Yield and Purity
- What role does a laboratory cold trap play in high-temperature corrosion experiments? Mastering Phase Control
- Why is it necessary to configure efficient cold traps in membrane distillation? Ensure Flux Stability & Data Accuracy
- What is the mechanism of a high-efficiency cold trap in pervaporation? Optimize Your Vapor Capture Efficiency
- Why are cold traps considered essential auxiliary equipment in laboratory-scale plastic pyrolysis research? | KINTEK












