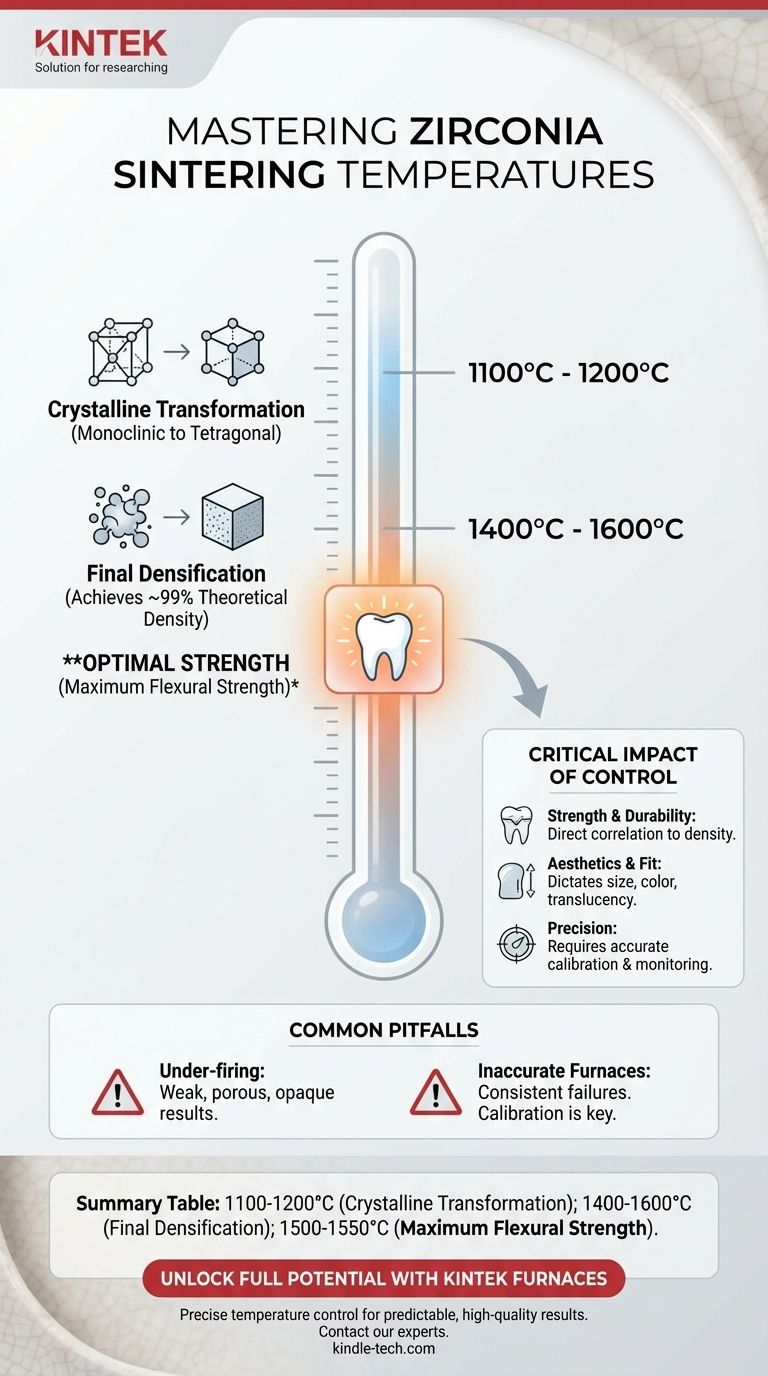
The typical sintering temperature for dental zirconia is between 1400°C and 1600°C. While the material begins its crucial crystalline transformation around 1100°C, this higher temperature range is required to achieve the final density and strength needed for clinical use. For maximum mechanical strength, studies indicate an optimal range between 1500°C and 1550°C.
The specific sintering temperature is not a single universal number but a critical process parameter. The precise temperature directly dictates the final strength, density, size, and color of the zirconia restoration, making strict adherence to the manufacturer's protocol essential for predictable, high-quality results.

Why Temperature is More Than Just a Number
Understanding the sintering process reveals why precise temperature control is fundamental to the final quality of any zirconia component. It's a multi-stage process where heat drives critical physical changes.
The Crystalline Transformation
Zirconia undergoes a phase transformation from a monoclinic to a tetragonal crystalline structure at approximately 1100°C to 1200°C. This change is the first step in developing its desirable mechanical properties.
Achieving Maximum Density
The primary goal of sintering at higher temperatures—between 1400°C and 1600°C—is densification. At this stage, the individual zirconia particles fuse together, eliminating the pores between them and shrinking the component to its final, highly dense state.
Proper sintering can achieve a density close to 99% of the theoretical maximum, which is the foundation of zirconia's exceptional strength.
Optimizing for Mechanical Strength
While the broad range is effective, research shows that firing within a narrower window of 1500°C to 1550°C often produces the absolute maximum flexural strength. This is the target for high-stress applications where performance is the top priority.
The Critical Impact of Temperature Control
Minor deviations from the ideal sintering cycle can have significant consequences. The detail and workmanship invested in crafting a restoration can be ruined by a poorly controlled furnace.
The Effect on Strength and Durability
Temperature directly correlates to density. If the furnace temperature is too low or the time is too short, the sintering will be incomplete, resulting in a porous, weaker material that is prone to premature failure.
The Effect on Aesthetics and Fit
Sintering temperature also dictates the final size, color, and translucency of the restoration. Inconsistent heating can lead to restorations that do not match the desired shade or that have an improper fit due to incorrect shrinkage.
The Role of Precise Measurement
Professional sintering furnaces use a combination of electronic temperature controllers and thermocouples to ensure accuracy. Regular calibration is critical to guarantee that the temperature displayed is the true temperature inside the chamber.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Achieving a successful outcome requires avoiding common errors related to temperature management. The difference between a perfect restoration and a failure is often just a few degrees.
The Problem with Under-firing
This is the most common pitfall. An insufficient temperature fails to achieve full densification, leaving the zirconia weak, porous, and opaque. The material simply will not have the physical properties required for its intended function.
The Risk of Inaccurate Furnaces
A furnace that is not properly calibrated is a primary source of error. A furnace reporting 1530°C but actually operating at 1480°C will consistently produce weaker-than-expected results, leading to frustrating and costly failures.
The Manufacturer's Protocol is Paramount
Different zirconia formulations (e.g., high-strength vs. high-translucency) have unique sintering protocols specified by the manufacturer. There is no one-size-fits-all temperature. Using a generic cycle for a specialized material is a guaranteed way to compromise its quality.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your ideal temperature target depends on your specific goals for the restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability: Target the 1500°C to 1550°C range, but only if this aligns with the specific instructions for the zirconia puck you are using.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic consistency: Prioritize the exact duplication of the manufacturer's recommended temperature cycle every single time, as this ensures predictable color, translucency, and shrinkage.
- If your primary focus is reliable and repeatable results: Make furnace calibration and strict adherence to the material-specific instructions your highest priorities.
Mastering the sintering temperature is the key to unlocking zirconia's full potential for both performance and aesthetics.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Primary Outcome | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 1100°C - 1200°C | Crystalline Transformation | Initial phase change to tetragonal structure. |
| 1400°C - 1600°C | Final Densification | Achieves near 99% theoretical density. |
| 1500°C - 1550°C | Maximum Flexural Strength | Optimal range for high-stress applications. |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Zirconia Restorations
Precise temperature control is non-negotiable for achieving the strength, fit, and aesthetics your patients deserve. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab sintering furnaces, offering the accuracy and reliability that dental labs need for predictable, high-quality results every time.
Ready to achieve perfect sintering? Contact our experts today to find the ideal furnace for your specific zirconia materials and workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag



















