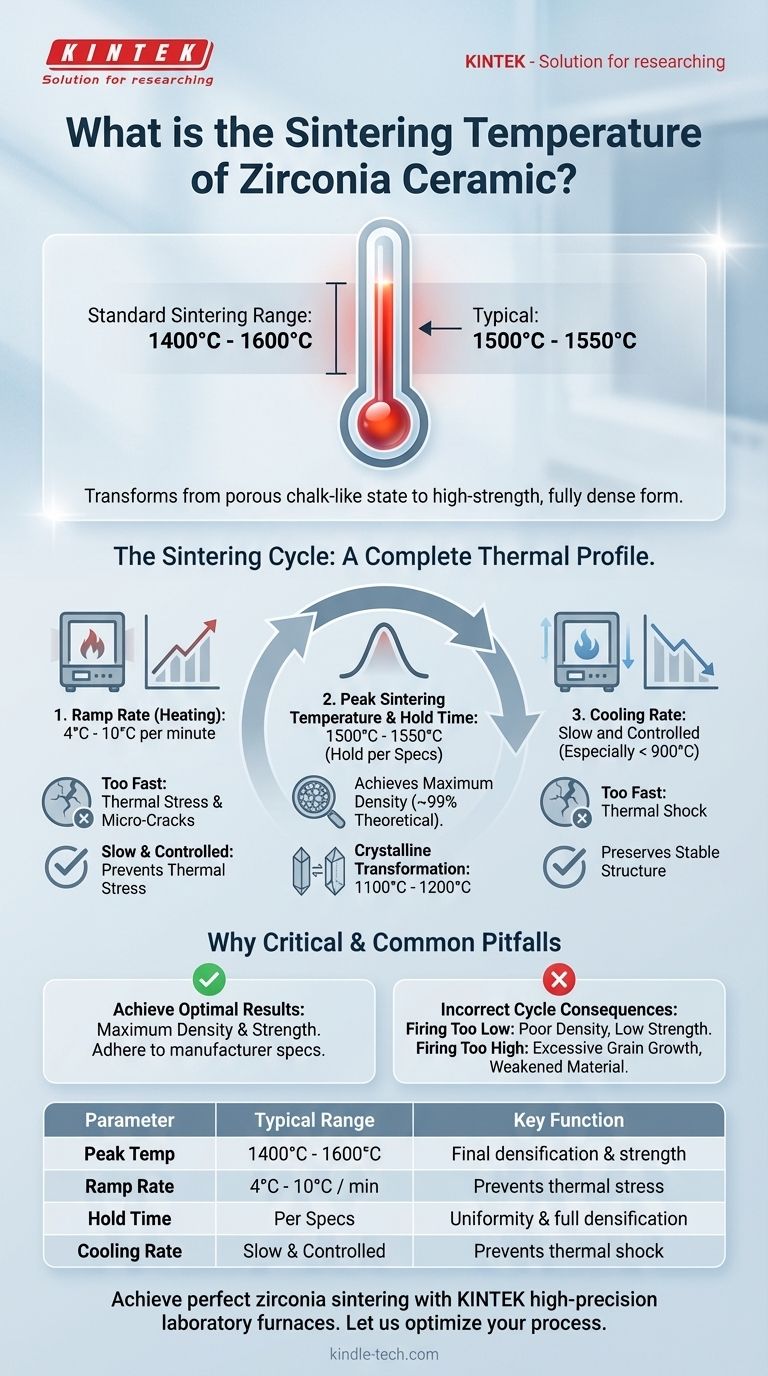
The standard sintering temperature for zirconia ceramic falls within a range of 1400°C to 1600°C, with most materials being fired at approximately 1500°C to 1550°C. This specific thermal process is not just about reaching a peak temperature; it is essential for transforming the material from a porous, chalk-like state into its final, high-strength and fully dense form.
The final sintering temperature is only one part of a precise process. Achieving optimal strength, density, and aesthetics in zirconia depends equally on controlling the entire thermal cycle, including the rate of heating and cooling.

Why Sintering Temperature is Critical
Sintering is a thermal process that fuses ceramic particles together, eliminating the voids between them to create a solid, coherent mass. For zirconia, this process is fundamental to developing its renowned mechanical properties.
The Goal: Achieving Maximum Density
The primary objective of sintering is to achieve maximum material density. A properly executed cycle brings zirconia to nearly 99% of its theoretical maximum density.
This densification directly correlates to the material's final strength and hardness. Incomplete sintering results in a weaker, more porous structure that is unfit for its intended application.
The Crystalline Transformation Point
Zirconia undergoes a critical phase transformation from a monoclinic to a tetragonal crystalline state at temperatures between 1100°C and 1200°C.
However, simply reaching this transformation temperature is not enough. The much higher sintering temperatures of 1500°C and above are required to complete the densification process and create a stable, robust final structure.
Deconstructing the Sintering Cycle
Focusing only on the peak temperature is a common mistake. The entire temperature curve—the ramp up, hold, and cool down—is critical for success.
The Ramp Rate (Rate of Heating)
The rate at which the furnace temperature increases is a crucial parameter. Most zirconia manufacturers recommend a slow heat rise, typically between 4°C and 10°C per minute.
A ramp rate that is too fast can induce thermal stress in the material, leading to micro-cracks and compromising the integrity of the final part.
The Hold Time at Peak Temperature
Once the target sintering temperature is reached, it must be held consistently for a specified duration. This "hold time" ensures that the entire component reaches a uniform temperature and that full densification can occur throughout the material's volume.
The Cooling Rate
Just as with heating, the rate of cooling is also carefully controlled. A slow, managed cooling process, especially as the material passes back through the 900°C range, is essential to prevent thermal shock and preserve the stable crystalline structure achieved during sintering.
Understanding the Variables and Pitfalls
While general guidelines exist, the exact parameters for sintering zirconia are not universal. Several factors can influence the ideal process, and deviation can lead to suboptimal results.
Manufacturer Specifications are Key
Different formulations of zirconia, such as those with varying translucency for dental applications, may require slightly different sintering temperatures and cycles. Always defer to the manufacturer's specific instructions for the material you are using.
The Impact of an Incorrect Cycle
Firing zirconia outside of its recommended parameters can have significant consequences.
Firing too low or for too short a time results in incomplete sintering, leading to poor density, low strength, and unacceptable porosity.
Firing too high or with improper ramp rates can cause excessive grain growth, which can paradoxically weaken the material or negatively affect its aesthetic properties.
How to Achieve Optimal Zirconia Sintering
To ensure consistent and reliable results, approach sintering as a complete, controlled process rather than a single temperature setting.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer's recommended peak temperature, typically around 1500-1550°C, and ensure a slow, controlled ramp rate.
- If you are troubleshooting poor results (e.g., fractures or low strength): Verify not only the peak temperature but the entire heating and cooling cycle, as incorrect ramp rates are a common source of error.
- If you are working with a new zirconia material: Never assume a standard cycle will suffice; always begin with the specific instructions provided for that particular formulation.
Ultimately, mastering zirconia sintering requires treating it as a complete thermal profile, not just a target number.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Sintering Temperature | 1400°C - 1600°C (commonly 1500°C-1550°C) | Drives final densification and strength |
| Ramp Rate (Heating) | 4°C - 10°C per minute | Prevents thermal stress and micro-cracks |
| Hold Time | As per manufacturer specifications | Ensures uniform temperature and full densification |
| Cooling Rate | Slow and controlled, especially below 900°C | Prevents thermal shock and preserves structure |
Achieve perfect zirconia sintering results every time with KINTEK.
Our high-precision laboratory furnaces are engineered to deliver the exact temperature control and uniform heating required for the critical zirconia sintering cycle (1400°C-1600°C). Whether you are in dental ceramics, industrial components, or advanced materials research, KINTEK's reliable equipment ensures maximum density and strength for your zirconia parts.
Let us help you optimize your process. Contact our sintering experts today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference in lab performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















