In the context of thin-film deposition, the "sputtering process of gas" refers to the critical role a gas, typically an inert one like argon, plays as the primary agent for the physical ejection of atoms from a source material. The gas itself is not the material being deposited; instead, it is ionized and accelerated to become a high-energy projectile that bombards a target, knocking loose the atoms that will form a new coating on a substrate.
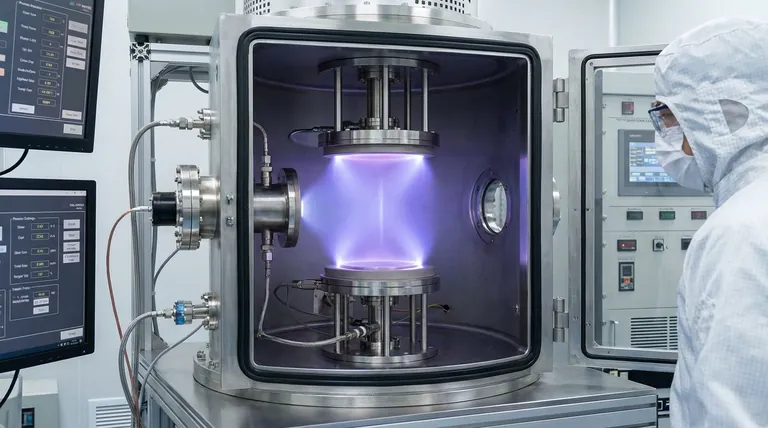
Sputtering is a vacuum-based process where a gas is transformed into a plasma. The ions from this gas act like a subatomic sandblaster, dislodging particles from a source material (the target) which then deposit as a highly uniform, ultra-thin film onto another object (the substrate).
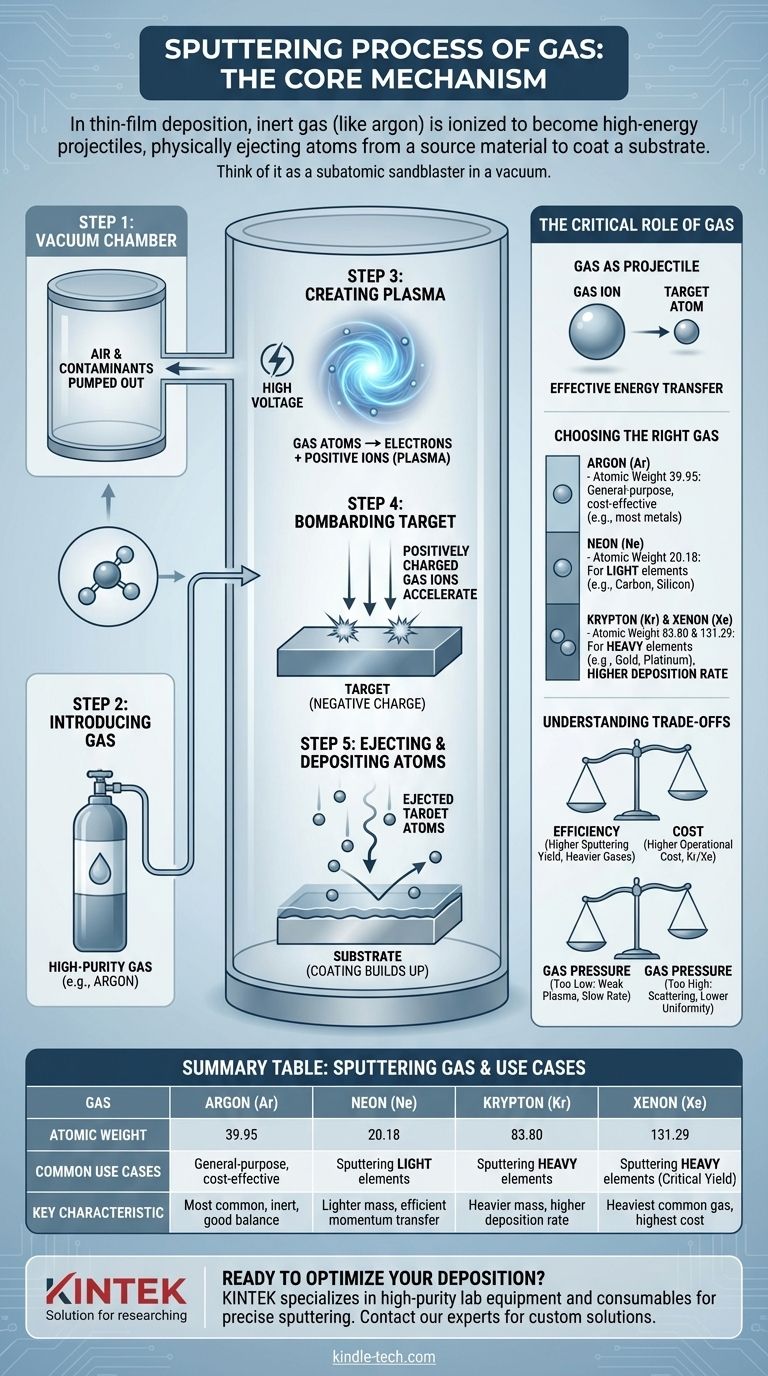
The Core Mechanism: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Sputtering physically transfers material from a source to a destination. The gas is the medium that makes this physical transfer possible at an atomic level. The entire process takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber.
Step 1: Achieving a Vacuum
Before the process begins, air and other contaminants are pumped out of the chamber. This is critical because it prevents unwanted particles from reacting with the coating and ensures the sputtered atoms have a clear path to the substrate.
Step 2: Introducing the Sputtering Gas
A small, precisely controlled amount of a high-purity gas is introduced into the chamber. The most common choice is Argon because it is chemically inert and relatively heavy, but other gases can be used for specific applications.
Step 3: Creating a Plasma
A high voltage is applied within the chamber, creating a strong electric field. This field energizes free electrons, which then collide with the gas atoms. These collisions have enough force to knock electrons off the gas atoms, creating positively charged gas ions and more free electrons. This super-heated, ionized gas is known as a plasma.
Step 4: Bombarding the Target
The source material to be deposited, known as the target, is given a negative electrical charge. This causes it to strongly attract the positively charged gas ions from the plasma. These ions accelerate and slam into the surface of the target with tremendous kinetic energy.
Step 5: Ejecting and Depositing Atoms
This high-energy bombardment is a pure momentum transfer, like a cue ball breaking a rack of billiard balls. The impact has enough force to dislodge, or "sputter," individual atoms from the target material. These ejected atoms travel through the vacuum and land on the substrate, gradually building up a thin film atom by atom.
The Critical Role of the Gas
The choice and condition of the sputtering gas directly influence the efficiency and quality of the final film. It is not a passive component but an active tool.
The Gas as a Projectile
The fundamental purpose of the gas is to become an ion that can transfer momentum. The effectiveness of this transfer depends heavily on the relative masses of the gas ion and the target atom.
Choosing the Right Gas for the Job
For the most efficient energy transfer, the atomic weight of the sputtering gas should be close to that of the target material.
- Argon (Ar): The most common and cost-effective choice for a wide range of materials.
- Neon (Ne): Preferred for sputtering very light elements, as its lower mass is a better match.
- Krypton (Kr) or Xenon (Xe): Used for sputtering heavy elements. Their greater mass provides a more powerful impact, increasing the rate of deposition.
The Importance of Purity
The sputtering gas must be exceptionally pure and dry. Any contaminants, like oxygen or water vapor, can get incorporated into the plasma and chemically react with the target material, altering the composition and properties of the final film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the physics are straightforward, process optimization involves balancing competing factors.
Efficiency vs. Cost
Heavier gases like Krypton and Xenon provide a higher sputtering yield (more atoms ejected per ion), which speeds up the process. However, these gases are significantly more expensive than Argon, creating a direct trade-off between process speed and operational cost.
The Impact of Gas Pressure
Gas pressure inside the chamber is a critical parameter.
- Too Low: Insufficient gas pressure results in a weak plasma with too few ions to sustain an effective sputtering rate.
- Too High: Excessive pressure means the sputtered atoms are more likely to collide with gas atoms on their way to the substrate. This can scatter them, reducing deposition rate and film uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a sputtering gas is driven by the specific material you are depositing and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose coating: Use Argon, as it provides a good balance of performance and economy for a vast range of target materials.
- If you are sputtering a light element target (e.g., carbon, silicon): Consider Neon to achieve a more efficient momentum transfer and potentially a higher-quality film.
- If you need the highest possible deposition rate for a heavy element (e.g., gold, platinum): Use Krypton or Xenon to maximize the sputtering yield, accepting the higher gas cost as a trade-off for speed.
Ultimately, mastering the sputtering process begins with understanding that the gas is the engine that drives the entire system.
Summary Table:
| Sputtering Gas | Atomic Weight | Common Use Cases | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | 39.95 | General-purpose, cost-effective coating | Most common, inert, good balance |
| Neon (Ne) | 20.18 | Sputtering light elements (e.g., carbon, silicon) | Lighter mass for efficient momentum transfer |
| Krypton (Kr) | 83.80 | Sputtering heavy elements (e.g., gold, platinum) | Heavier mass for higher deposition rate |
| Xenon (Xe) | 131.29 | Sputtering heavy elements where highest yield is critical | Heaviest common gas, highest cost |
Ready to Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process?
Understanding the role of sputtering gas is just the first step. Selecting the right equipment and consumables is crucial for achieving high-quality, uniform coatings. KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including vacuum chambers, targets, and gas handling systems designed for precise sputtering applications.
Let our experts help you configure the ideal setup for your specific material and deposition goals. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How difficult is it to grow a diamond? The Immense Challenge of Atomic-Level Precision
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- How does chemical vapor deposition work for diamonds? Grow Lab-Created Diamonds Layer by Layer
- How does MPCVD work? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition



















