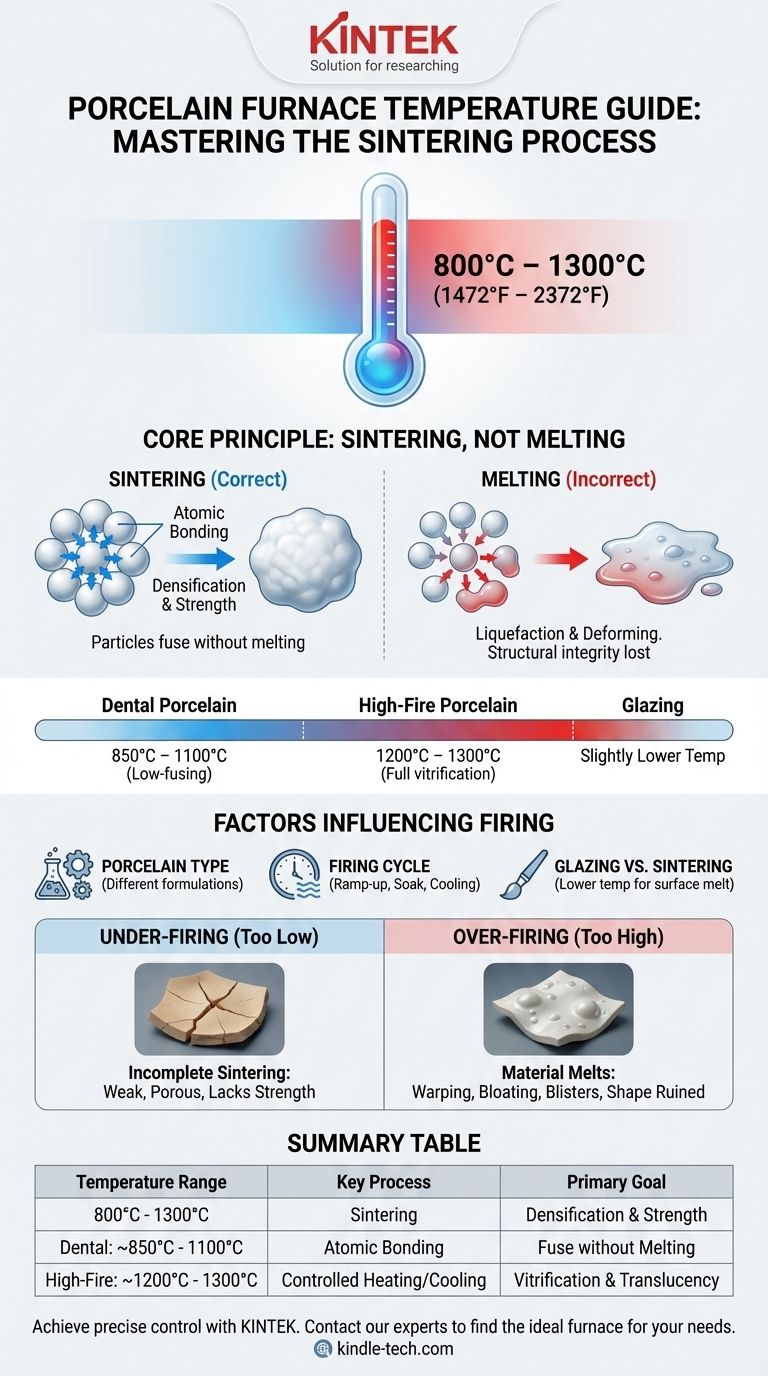
The temperature of a porcelain furnace typically ranges from 800°C to 1300°C (1472°F to 2372°F). This wide range exists because the precise temperature required depends entirely on the specific type of porcelain being fired and the intended outcome of the process, which is known as sintering.
The core principle is that the furnace temperature must be high enough to fuse the ceramic particles together, but must remain strictly below the material’s melting point. The goal is to create a dense, solid mass without ever liquefying and deforming the object.
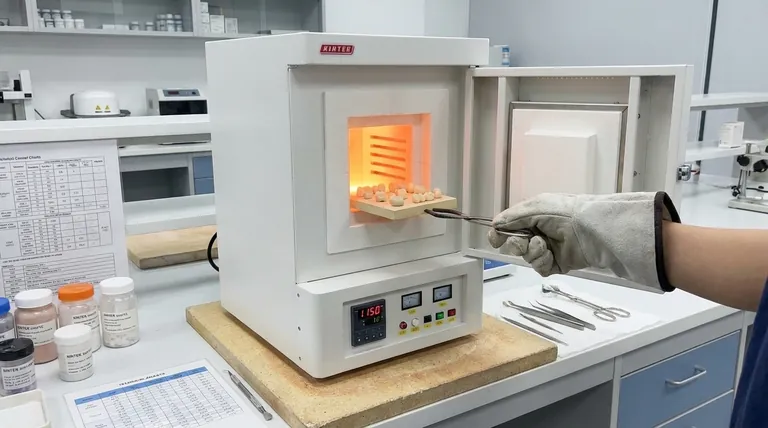

The Principle of Sintering, Not Melting
Understanding the "why" behind the temperature is more critical than memorizing a single number. Porcelain furnaces are designed for a process called sintering, a fundamentally different concept from melting.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal process where individual particles in a powdered material bond together at a high temperature.
As heat is applied, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them into a solid, coherent piece. This reduces porosity and increases the density and strength of the final object.
Why Temperature Control is Critical
The success of the entire process hinges on maintaining the temperature below the porcelain's melting point.
If the temperature gets too high, the material will begin to liquefy, slump under its own weight, and lose its precisely crafted shape. Sintering achieves structural integrity; melting destroys it.
The Goal: Densification and Strength
The target temperature is the sweet spot that maximizes atomic bonding and minimizes internal voids.
Proper sintering transforms a fragile, chalky "greenware" object into a hard, non-porous, and durable ceramic product with the desired mechanical and aesthetic properties.
Factors Influencing Firing Temperature
The exact temperature isn't a universal constant. It is dictated by the composition of the porcelain and the specific stage of the manufacturing process.
Type of Porcelain
Different porcelain formulations have different sintering temperatures. For example, dental porcelains are often "low-fusing," firing at temperatures between 850°C and 1100°C.
In contrast, high-fire artistic or industrial porcelains require much higher temperatures, often approaching 1300°C, to achieve full vitrification and translucency.
The Firing Cycle
A complete firing process is a "schedule," not a single temperature. It involves a controlled ramp-up phase to prevent thermal shock, a "soak" or hold at the peak sintering temperature, and a controlled cooling phase. Each stage is crucial for the final quality.
Glazing vs. Sintering
After an initial sintering fire (the "bisque" fire in artistic ceramics), a glaze may be applied. The subsequent glaze firing is often done at a slightly lower temperature, designed only to melt the glassy glaze layer onto the already-sintered ceramic body.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Deviating from the ideal temperature and schedule leads to predictable failures. This precision is why professional-grade furnaces with programmable digital controllers are essential.
Firing Too Low (Under-firing)
If the peak temperature isn't reached, the sintering process will be incomplete. The resulting product will be weak, porous, and lack the desired strength because the ceramic particles have not fully bonded.
Firing Too High (Over-firing)
Exceeding the correct temperature is often catastrophic. The porcelain will begin to warp, bloat, or even melt into an unrecognizable shape. The surface may become overly glassy or develop blisters, ruining the piece.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving a successful outcome requires matching the furnace's temperature profile to the material's specific needs.
- If your primary focus is dental ceramics: You will work with low-fusing porcelains and must follow the manufacturer's specific firing schedule with absolute precision.
- If your primary focus is high-fire artistic porcelain: You will need a furnace capable of reaching temperatures of 1200°C to 1300°C to achieve full vitrification and strength.
- If you are diagnosing a firing problem: Always analyze the entire firing schedule—not just the peak temperature—as issues like cracking or poor density can stem from incorrect heating or cooling rates.
Ultimately, mastering the porcelain furnace is about precisely controlling temperature to manage a material's transformation, not just applying heat.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Process | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 800°C - 1300°C (1472°F - 2372°F) | Sintering | Densification & Strength |
| Dental Porcelain: ~850°C - 1100°C | Atomic Bonding | Fuse particles without melting |
| High-Fire Porcelain: ~1200°C - 1300°C | Controlled Heating/Cooling | Achieve vitrification & translucency |
Achieve precise temperature control and perfect sintering results with KINTEK.
Whether you are working with dental ceramics or high-fire artistic porcelain, the right laboratory furnace is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces designed for exacting thermal processes, helping you avoid under-firing and over-firing to produce strong, durable, and consistent results every time.
Ready to enhance your ceramic production? Contact our experts today to find the ideal furnace for your specific porcelain and temperature requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What are the strongest and toughest ceramic materials currently used in dentistry? Zirconia vs. Lithium Disilicate
- What are some common features of modern Dental Press Furnaces? Boost Lab Efficiency with Smart Technology
- What are the disadvantages of all-ceramic restorations? Key Limitations for Long-Term Success
- How strong are ceramic implants? Discover the Power of Zirconia for a Metal-Free Smile
- What is the function of a high-vacuum sintering furnace in 3Y-TZP? Enhance Dental Restoration Quality
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is an economical method for purging a porcelain furnace muffle? A Simple, High-Heat Cycle for Cleaner Dental Restorations



















