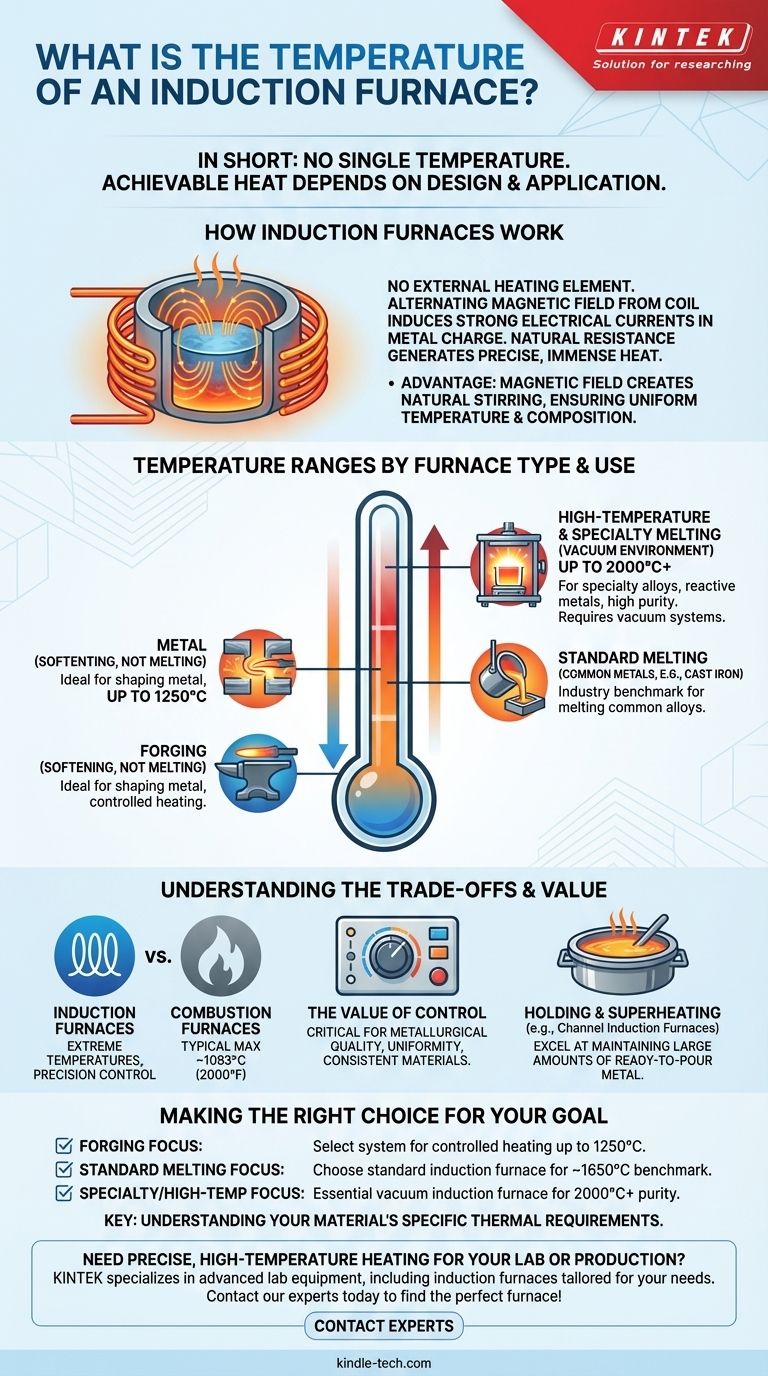
In short, there is no single temperature for an induction furnace. The achievable temperature depends entirely on the furnace's design and its specific application, ranging from 1250°C for forging to over 2000°C for melting specialty alloys in a vacuum environment.
An induction furnace's temperature is not a fixed property but a capability defined by its purpose. Standard furnaces typically reach 1650°C for melting, while specialized vacuum models can exceed 2000°C for advanced materials processing.

How Induction Furnaces Work
The Principle of Induction Heating
An induction furnace does not use an external heating element. Instead, it uses a powerful alternating magnetic field generated by a copper coil.
This magnetic field induces strong electrical currents directly within the metal (the "charge") placed inside the furnace. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates immense, rapid, and precise heat.
The Stirring Effect
A key advantage of this process is the natural stirring action created by the magnetic field. This ensures the molten metal has a highly uniform temperature and composition throughout the bath.
Precision and Control
This method allows for extremely high temperature control accuracy. There is often a very small temperature difference between the core of the material and its surface, which is critical for metallurgical quality.
Temperature Ranges by Furnace Type and Use
The maximum temperature of an induction furnace is dictated by its intended function. Different tasks require different thermal capabilities.
Forging Temperatures
For applications like forging, where metal needs to be softened but not melted, an induction furnace typically operates at temperatures up to 1250°C.
Standard Melting Temperatures
For melting most common metals and alloys like cast iron, a standard or small induction furnace will reach temperatures between 1600°C and 1650°C.
High-Temperature and Specialty Melting
When dealing with specialty alloys, reactive metals, or materials requiring extreme purity, a vacuum induction melting furnace is used. These specialized systems can reach a maximum temperature of 2000°C or even higher.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating technology is about more than just maximum temperature. The context of the application is critical.
Induction vs. Combustion Furnaces
An induction furnace's capabilities far exceed those of many traditional furnaces. For example, a typical natural gas furnace may only reach temperatures around 1093°C (2000°F).
The Value of Control
While the high temperatures are impressive, the primary advantage of induction is often the precision. The ability to control temperature accurately and maintain uniformity is essential for producing high-quality, consistent materials.
Holding and Superheating
Some designs, like the channel induction furnace, are not built for maximum temperature. They excel at holding large amounts of molten metal at a specific temperature or for superheating, making them ideal for foundries that need a consistent supply of ready-to-pour metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select the furnace technology based on the specific thermal requirements of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is forging: You need a system designed for controlled heating up to 1250°C.
- If your primary focus is melting standard alloys like cast iron: A standard induction furnace capable of reaching 1650°C is the industry benchmark.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or high-temperature alloys: A vacuum induction furnace capable of 2000°C is essential for maintaining purity and achieving the necessary melt.
Ultimately, understanding your material's specific needs is the key to selecting the correct heating technology.
Summary Table:
| Application | Typical Temperature Range | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Forging | Up to 1250°C | Heats metal without melting, ideal for softening before shaping. |
| Standard Melting (e.g., Cast Iron) | 1600°C – 1650°C | Industry standard for melting common metals and alloys. |
| Vacuum Melting (Specialty Alloys) | Up to 2000°C+ | Used for reactive metals, high-purity applications in a controlled environment. |
Need precise, high-temperature heating for your lab or production process? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction furnaces tailored for forging, standard melting, or high-temperature vacuum applications. Our solutions ensure uniform heating, exact temperature control, and reliability for your specific material needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















