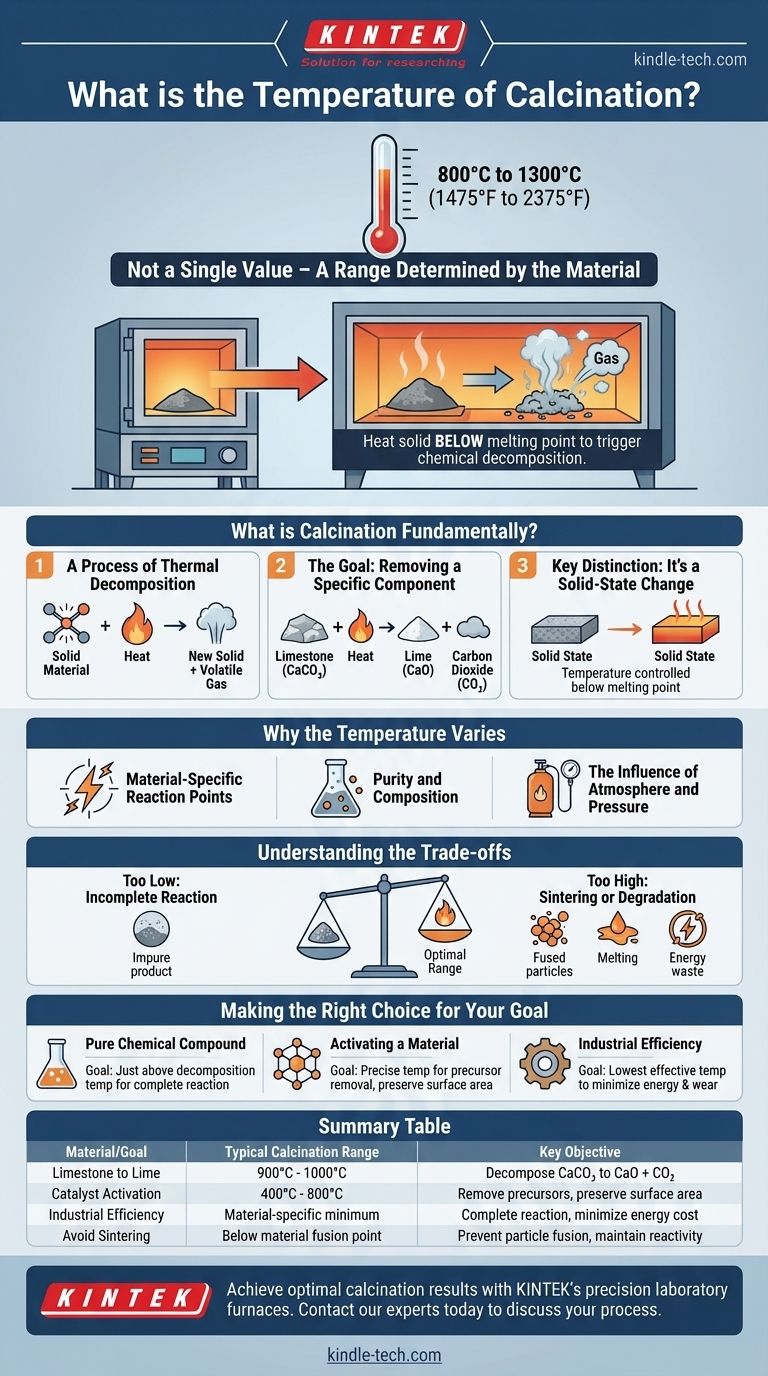
The temperature of calcination is not a single value but a specific range determined by the material being processed. For most industrial applications, calcination furnaces operate between 800°C and 1300°C (1475°F to 2375°F) to induce a fundamental chemical change in the material.
The core principle of calcination is to heat a solid material to a high temperature below its melting point. The goal isn't to melt it, but to trigger a specific chemical decomposition, typically to drive off a volatile component like carbon dioxide or water.

What is Calcination Fundamentally?
A Process of Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a thermal treatment process that brings about a chemical change in a material. This is distinct from simply drying, which only removes absorbed water.
The heat acts as the energy source to break chemical bonds within the substance, causing it to decompose into a new solid material and a volatile gas.
The Goal: Removing a Specific Component
The most common application is to remove a specific part of a compound. A classic example is the production of lime from limestone.
Limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is heated to drive off carbon dioxide (CO₂). This leaves behind lime (calcium oxide, CaO), a new substance with different properties.
Key Distinction: It's a Solid-State Change
A critical aspect of calcination is that the material remains in a solid state. The temperature is carefully controlled to be high enough for the chemical reaction to occur but low enough to prevent the material from melting or fusing.
Why the Temperature Varies
Material-Specific Reaction Points
Every chemical reaction requires a specific amount of energy, known as the enthalpy of reaction. The temperature needed for calcination is dictated by the energy required to break the specific chemical bonds in the starting material.
For example, the bonds in limestone require a different amount of energy to break than the bonds in hydrated alumina or other minerals.
Purity and Composition
The exact composition of the raw material affects the necessary temperature. Impurities within a mineral can either lower or raise the temperature needed for a complete reaction.
The Influence of Atmosphere and Pressure
The atmosphere inside the furnace plays a role. The partial pressure of the gas being released (like CO₂) can influence the equilibrium of the reaction. Operating under a vacuum or in a controlled atmosphere can sometimes lower the required calcination temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Too Low: Incomplete Reaction
If the temperature is too low, the decomposition reaction will not complete. The final product will be impure, containing a mixture of the original material and the desired product, which usually makes it unsuitable for its intended application.
Too High: Sintering or Degradation
Exceeding the necessary temperature is often more damaging than under-heating. It can cause the solid particles to fuse together, a process called sintering. This reduces the surface area and reactivity of the final product.
In some cases, excessive heat can cause undesirable phase changes or even begin to melt the material, destroying its intended structure and properties entirely.
Energy Waste and Cost
From a practical standpoint, overheating is a significant waste of energy. Maintaining furnace temperatures of 1200°C when 950°C would suffice leads to drastically higher fuel consumption and operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct temperature is a matter of understanding your material and your desired final product.
- If your primary focus is creating a pure chemical compound (like lime): You must heat the material just above its known decomposition temperature to ensure a complete reaction without causing sintering.
- If your primary focus is activating a material (like a catalyst): You need the precise temperature that drives off precursors without reducing the material's active surface area through sintering.
- If your primary focus is industrial efficiency: The goal is to identify the lowest possible temperature that achieves complete calcination in a reasonable amount of time to minimize energy costs and mechanical wear.
Ultimately, the correct calcination temperature is a carefully balanced parameter specific to each material and process objective.
Summary Table:
| Material/Goal | Typical Calcination Range | Key Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone to Lime | 900°C - 1000°C | Decompose CaCO₃ to CaO + CO₂ |
| Catalyst Activation | 400°C - 800°C | Remove precursors, preserve surface area |
| Industrial Efficiency | Material-specific minimum | Complete reaction, minimize energy cost |
| Avoid Sintering | Below material fusion point | Prevent particle fusion, maintain reactivity |
Achieve optimal calcination results with KINTEK's precision laboratory furnaces. Our equipment delivers the exact temperature control and uniform heating your materials require for complete decomposition, maximum purity, and energy efficiency. Whether you're processing limestone, activating catalysts, or developing new materials, KINTEK's solutions are designed for your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your calcination process and find the perfect furnace for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of pyrolysis? Transforming Waste into High-Value Biofuels and Biochar
- What is the output of the pyrolysis plant? A Flexible Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the reaction of pyrolysis? Unlock Value from Waste with Thermal Decomposition
- What are the components of a pyrolysis plant? Unlock the 4 Key Systems for Waste-to-Energy
- What is the difference between roasting and calcination? A Guide to Metallurgical Ore Processing
- What are the advantages of using a rotary reactor for ALD on copper powders? Superior Coating for Cohesive Materials
- What are the examples of the products of pyrolysis? Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Explained
- What are the advantages of flash pyrolysis? Maximize Liquid Bio-Oil Yield & Efficiency



















