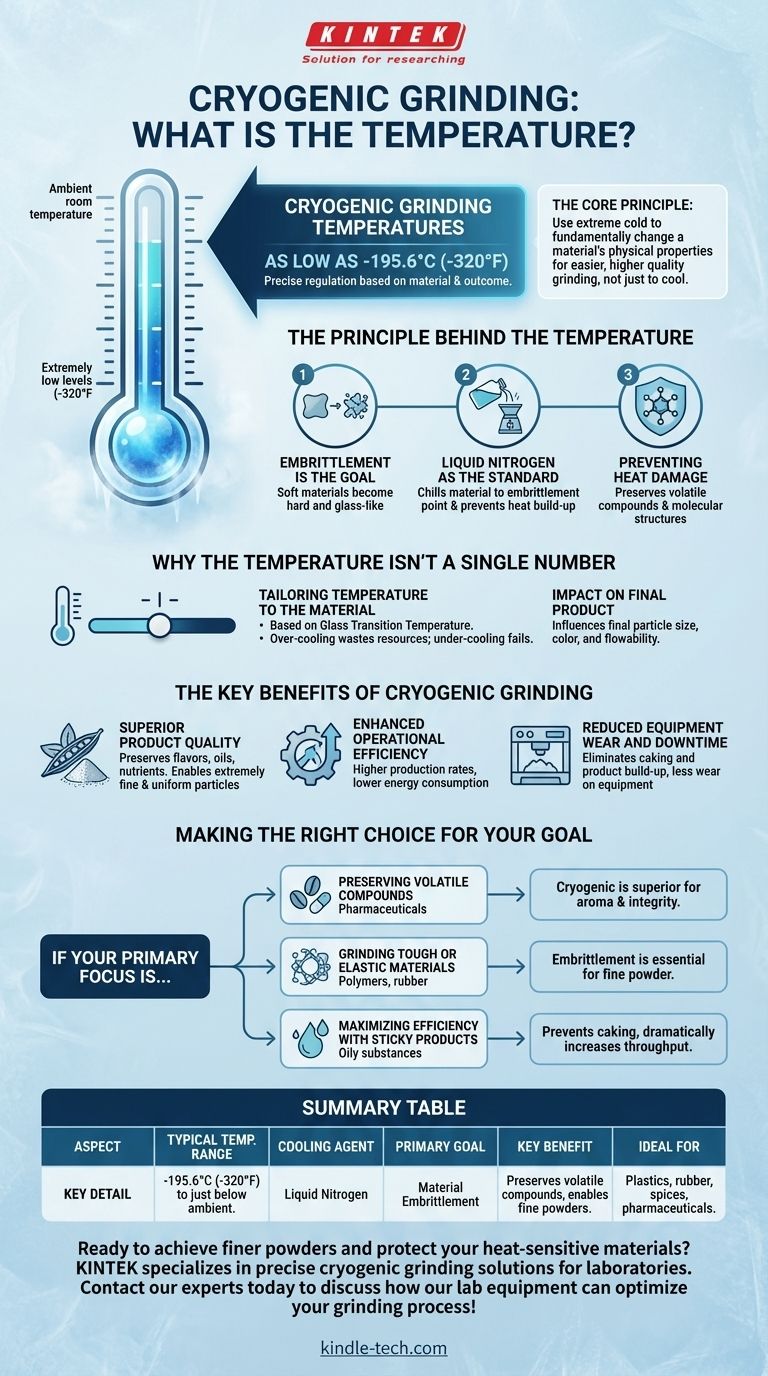
In short, cryogenic grinding temperatures can be as low as −195.6°C (−320°F), the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. However, this extreme cold is not always necessary. The actual operating temperature is precisely regulated based on the specific material being processed and the desired outcome, and can be set anywhere from that low point up to just a few degrees below ambient temperature.
The core principle of cryogenic grinding is not simply to make something cold, but to use extreme cold to fundamentally change a material's physical properties. By making a material brittle, it shatters more easily and predictably, resulting in a higher quality final product while protecting its heat-sensitive components.

The Principle Behind the Temperature
Cryogenic grinding leverages extreme cold to overcome common milling challenges. The process is far more sophisticated than just cooling a material down before grinding it.
Embrittlement is the Goal
The primary reason for using such low temperatures is to induce embrittlement. Many materials that are soft, elastic, or gummy at room temperature (like plastics, rubber, or oily spices) become hard and glass-like when cooled.
This physical change allows the material to be shattered cleanly and efficiently into a fine powder, rather than being smeared, melted, or torn by the grinding mechanism.
Liquid Nitrogen as the Standard
The process almost universally uses liquid nitrogen as the cooling agent. As the material is fed into the mill, it is sprayed with or immersed in liquid nitrogen.
This not only chills the material to its embrittlement point but also blankets the entire grinding chamber, preventing heat build-up from friction.
Preventing Heat Damage
Conventional grinding generates significant heat, which can destroy volatile compounds like flavors and aromas in spices, or degrade the molecular structure of polymers and pharmaceuticals.
By keeping the entire process at cryogenic temperatures, these heat-sensitive components are fully protected, preserving the original quality of the material.
Why the Temperature Isn't a Single Number
The exact temperature required is not a fixed value; it is a carefully controlled variable determined by the material's properties and the end-product specifications.
Tailoring Temperature to the Material
Different materials have a different glass transition temperature—the point at which they shift from a tough or rubbery state to a brittle, glassy one.
The goal is to cool the material just below this specific temperature. Over-cooling is inefficient and wastes liquid nitrogen, while under-cooling will fail to achieve the necessary brittleness for effective grinding.
Impact on Final Product
The final temperature setting is also influenced by the desired characteristics of the end product. Factors like final particle size, color requirements, and flowability all depend on precise temperature control during the milling process.
The Key Benefits of Cryogenic Grinding
The use of extreme cold delivers several distinct advantages over traditional ambient-temperature grinding, impacting both product quality and operational efficiency.
Superior Product Quality
By preventing heat damage, the process preserves volatile oils, flavors, and nutrients. It also enables the creation of extremely fine and uniform particles, which can improve texture, dispersal, and pouring properties.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Brittle materials shatter with less energy. This results in higher production rates (throughput) and lower overall energy consumption per pound of product.
Reduced Equipment Wear and Downtime
Grinding soft, sticky materials at room temperature often leads to caking and product build-up inside the mill, requiring frequent and difficult cleaning. Cryogenic grinding eliminates this issue entirely, which also leads to less wear and tear on the grinding equipment itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Cryogenic grinding is a specialized technique, not a universal solution. Its value is determined entirely by the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is preserving volatile compounds: For spices, coffee, or pharmaceuticals where aroma and molecular integrity are critical, cryogenic grinding is the superior choice to prevent heat degradation.
- If your primary focus is grinding tough or elastic materials: For polymers, rubbers, or certain composites, the embrittlement from cryogenic temperatures is often the only way to achieve a fine, uniform powder.
- If your primary focus is maximizing efficiency with sticky products: For materials high in oil or fat that would otherwise clog a mill, this process prevents caking and dramatically increases throughput.
Ultimately, choosing cryogenic grinding is about controlling a material's physical state to achieve a level of quality and efficiency that traditional methods cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Typical Temperature Range | -195.6°C (-320°F) to just below ambient |
| Cooling Agent | Liquid Nitrogen |
| Primary Goal | Material Embrittlement |
| Key Benefit | Preserves volatile compounds, enables fine powders |
| Ideal For | Plastics, rubber, spices, pharmaceuticals |
Ready to achieve finer powders and protect your heat-sensitive materials?
KINTEK specializes in cryogenic grinding solutions for laboratories. Our equipment ensures precise temperature control to embrittle your toughest materials—from polymers and composites to spices and pharmaceuticals—preserving their quality and boosting your milling efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can optimize your grinding process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
People Also Ask
- Why is a cryogenic grinder required for cured alkyd resin HRMAS NMR? Ensure Structural Integrity & Sample Precision
- What is the mechanism of a cryogenic grinder? Master Polymer Powder Preparation for Additive Manufacturing
- How do crushing and grinding systems improve microalgae gas production? Optimize Biomass Pretreatment for Higher Yields
- What is the process of cold grinding? Achieve Superior Powder Quality for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What was the cryogenic grinding process compared against in the study? Cryogenic vs. Dry Grinding Analysis



















