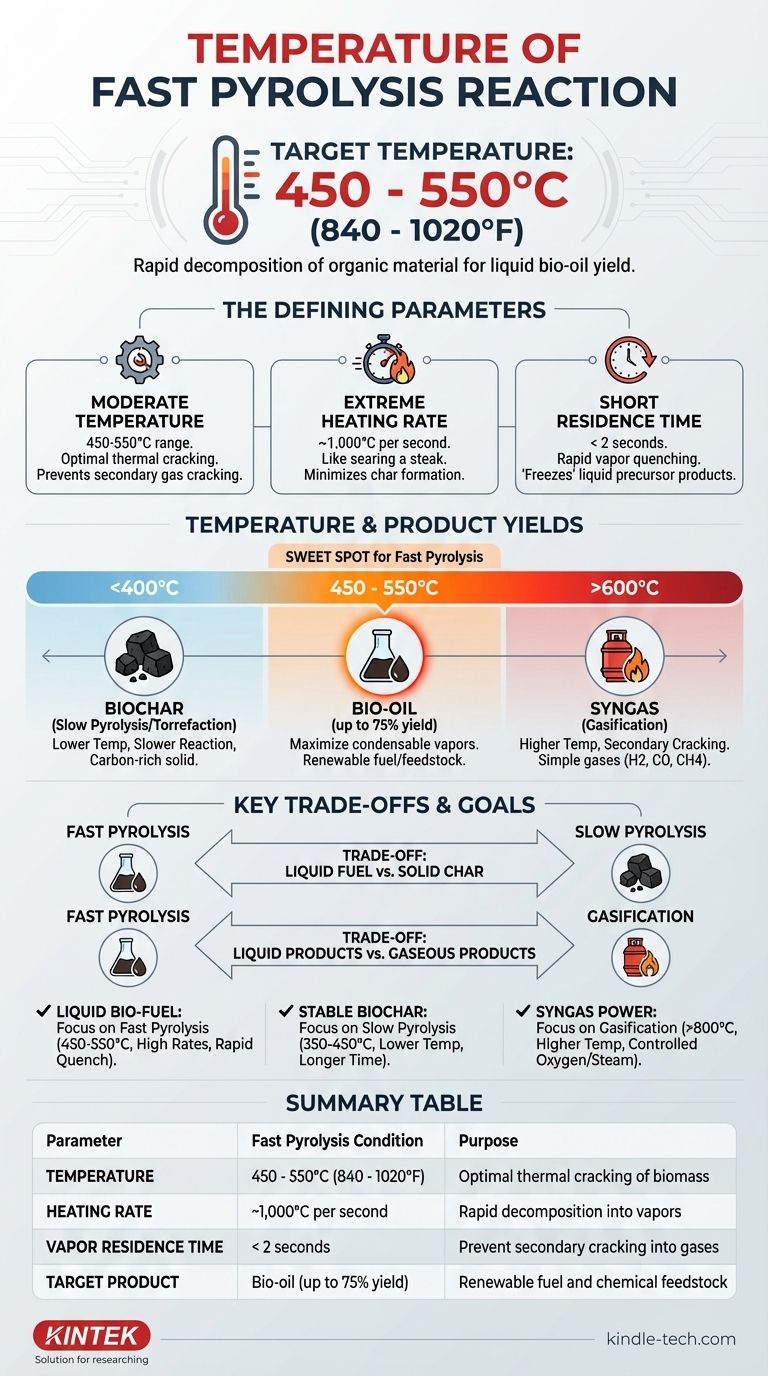
For a fast pyrolysis reaction, the target temperature is typically in the range of 450 to 550°C (840 to 1020°F). This specific temperature is a critical component of a process designed to rapidly decompose organic material, such as biomass, in the absence of oxygen.
The core principle of fast pyrolysis is not just achieving a specific temperature, but controlling a trio of conditions: a moderate temperature, an extremely high heating rate, and a very short vapor residence time. This precise combination is engineered to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.

The Defining Parameters of Fast Pyrolysis
To fully understand the process, we must look beyond a single temperature value. Fast pyrolysis is a carefully balanced act between three interconnected variables.
### The Role of Temperature
The 450-550°C range is the optimal window for the initial thermal cracking of biomass. In this range, long-chain biopolymers like cellulose and lignin break down into smaller, vaporized organic molecules.
This temperature is high enough to ensure rapid decomposition but not so high that it favors the secondary cracking of those valuable vapors into non-condensable gases.
### The Critical Impact of Heating Rate
Fast pyrolysis requires extremely high heating rates, often in the order of 1,000°C per second. This rapid energy transfer is arguably more important than the final temperature itself.
Think of it like searing a steak. High, fast heat creates a specific chemical reaction on the surface. Similarly, rapid heating in pyrolysis ensures the biomass particles decompose directly into vapors and aerosols, minimizing the formation of solid char.
### The Necessity of Short Residence Time
The hot vapors and gases produced must be removed from the reactor almost instantly, typically in less than two seconds. This is known as a short vapor residence time.
This rapid quenching is essential to "freeze" the reaction products in their liquid precursor state. If left in the hot reactor, these vapors would continue to react and break down into lower-value permanent gases (like carbon monoxide and methane) and more char.
How Temperature Influences Product Yields
Slight deviations from the optimal temperature window can dramatically alter the final products.
### Below the Optimal Range (<400°C)
At lower temperatures, the reactions are much slower. This condition favors the production of biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid. This process is known as slow pyrolysis or torrefaction.
### Within the Optimal Range (450-550°C)
This is the "sweet spot" for fast pyrolysis, designed to maximize the yield of condensable vapors. When cooled, these vapors form bio-oil, a dark, viscous liquid that can be used as a renewable fuel or chemical feedstock. Yields can reach up to 75% by weight.
### Above the Optimal Range (>600°C)
As temperatures increase well beyond the fast pyrolysis window, the process shifts toward gasification. The desirable organic vapors undergo secondary thermal cracking, breaking them down further into simple, non-condensable molecules like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This maximizes the yield of syngas.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The choice of thermal conversion technology is entirely dependent on the desired end product.
### Fast Pyrolysis vs. Slow Pyrolysis
The primary trade-off is between liquid fuel and solid charcoal. Fast pyrolysis sacrifices char production to maximize bio-oil. Slow pyrolysis operates for hours at lower temperatures to maximize the output of biochar.
### Fast Pyrolysis vs. Gasification
This is a choice between liquid products and gaseous products. Fast pyrolysis aims to preserve complex organic molecules as a liquid, while gasification uses much higher temperatures (often >800°C) to completely break them down into a combustible syngas.
### The Engineering Challenge
Achieving the high heating rates and short residence times for fast pyrolysis is technically challenging. It requires specialized reactors, such as fluidized beds or ablative reactors, that can ensure rapid and efficient heat transfer to the feedstock particles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your target temperature is dictated by the product you want to create.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid bio-fuel: Your goal is true fast pyrolysis, targeting a temperature of 450-550°C with very high heating rates and rapid vapor quenching.
- If your primary focus is producing stable biochar for agriculture or carbon sequestration: You should use slow pyrolysis, with much lower temperatures (350-450°C) and significantly longer processing times.
- If your primary focus is producing syngas for power generation: You need to operate in the gasification regime, which requires much higher temperatures (>800°C) and often the introduction of a controlled amount of oxygen or steam.
Ultimately, selecting the correct temperature is the first step in aligning the process chemistry with your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Fast Pyrolysis Condition | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 450 - 550°C (840 - 1020°F) | Optimal thermal cracking of biomass |
| Heating Rate | ~1,000°C per second | Rapid decomposition into vapors |
| Vapor Residence Time | < 2 seconds | Prevent secondary cracking into gases |
| Target Product | Bio-oil (up to 75% yield) | Renewable fuel and chemical feedstock |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum bio-oil yield? The precise control of temperature, heating rate, and residence time is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for thermal conversion research. Our experts can help you select the right reactor system to achieve your specific product goals. Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your research efficiency and outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















