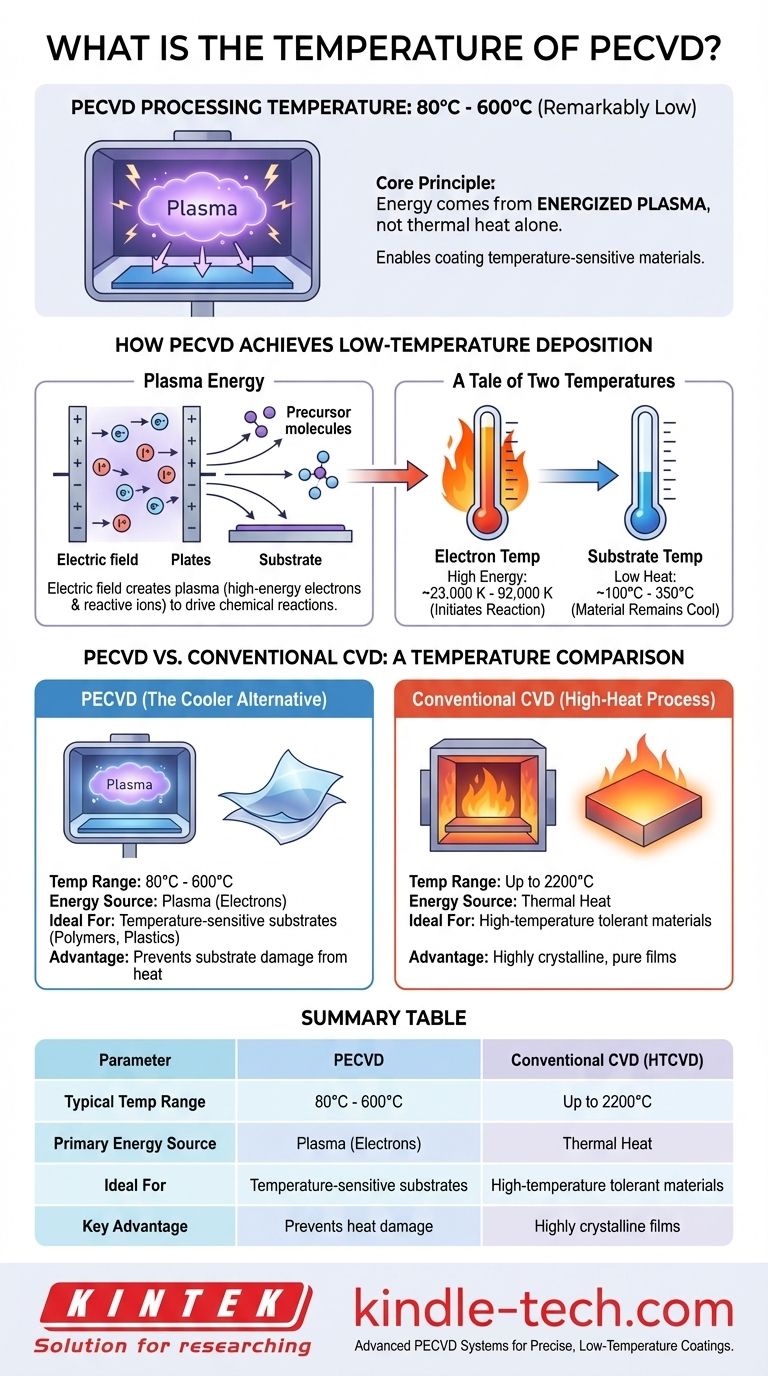
In short, the processing temperature for Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is remarkably low, typically ranging from 80°C to 600°C. This low temperature is the defining characteristic of the process, enabling a wide range of applications that are impossible with traditional high-temperature methods. The energy required for the chemical reaction comes from an energized plasma rather than thermal heat alone.
The core principle to understand is that PECVD separates the energy source from the substrate temperature. While the electrons in the plasma are incredibly hot (tens of thousands of degrees), the substrate and surrounding gas remain cool, making it ideal for temperature-sensitive materials.

How PECVD Achieves Low-Temperature Deposition
The fundamental advantage of PECVD is its ability to drive chemical reactions without extreme heat. This is accomplished by creating a non-thermal equilibrium system inside the reactor.
The Critical Role of Plasma Energy
In a PECVD reactor, an electrical field is used to ionize a gas, creating a plasma. This plasma is a sea of high-energy electrons and reactive ions.
These energetic electrons collide with the precursor gas molecules, breaking them down into highly reactive chemical species. This dissociation step is what allows the deposition reaction to occur on the substrate surface.
A Tale of Two Temperatures
The "temperature" in a PECVD system is not a single number. There are two vastly different thermal environments coexisting.
The electron temperature is extraordinarily high, with mean electron energies of 2 to 8 eV, equivalent to temperatures from 23,000 K to over 92,000 K. These electrons possess the energy needed to initiate the chemical reaction.
In contrast, the substrate temperature—the actual physical heat of the material being coated—remains very low, often between 100°C and 350°C. This is possible because the heavier ions and neutral gas atoms do not heat up to the same degree as the lightweight electrons.
PECVD vs. Conventional CVD: A Temperature Comparison
Understanding the temperature difference between PECVD and conventional high-temperature CVD (HTCVD) clarifies its unique value proposition.
Conventional CVD: A High-Heat Process
Traditional CVD methods rely entirely on thermal energy to break down precursor gases.
To achieve this, these furnaces must operate at extremely high temperatures, often reaching up to 2200°C. This severely limits the types of materials that can be used as substrates.
PECVD: The Cooler Alternative
By using plasma as the primary energy source, PECVD bypasses the need for extreme heat.
This process allows for high-quality film deposition on materials that would melt, deform, or be destroyed in a conventional CVD furnace, such as polymers, plastics, and complex semiconductor devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its low temperature is a significant advantage, PECVD is not without its considerations. It's crucial to understand the trade-offs involved.
Film Quality and Composition
Because the deposition occurs at lower temperatures, the resulting films may not be as dense or have the same crystalline structure as those grown at very high temperatures.
Films deposited via PECVD can also have higher concentrations of incorporated elements, like hydrogen, which may affect the material's final optical or electrical properties.
Potential for Plasma-Induced Damage
The high-energy ions within the plasma, while necessary for the reaction, can sometimes physically bombard the substrate surface.
For extremely sensitive electronic components, this can introduce surface defects or damage that must be carefully managed through process parameter optimization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting between PECVD and other methods depends entirely on your material constraints and desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is almost always the superior or only viable choice due to its low operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity or a specific crystal structure: High-temperature CVD may be necessary, but only if your substrate can tolerate the extreme thermal conditions.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental temperature distinction is the key to leveraging PECVD for depositing advanced materials on thermally sensitive platforms.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | PECVD | Conventional CVD (HTCVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Temperature Range | 80°C - 600°C | Up to 2200°C |
| Primary Energy Source | Plasma (Electrons) | Thermal Heat |
| Ideal For | Temperature-sensitive substrates (polymers, plastics) | High-temperature tolerant materials |
| Key Advantage | Prevents substrate damage from heat | Can produce highly crystalline, pure films |
Need to deposit high-quality thin films on temperature-sensitive materials? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including PECVD systems, to help you achieve precise, low-temperature coatings without compromising your substrates. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your specific application, from R&D to production. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PECVD technology can benefit your laboratory's workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















