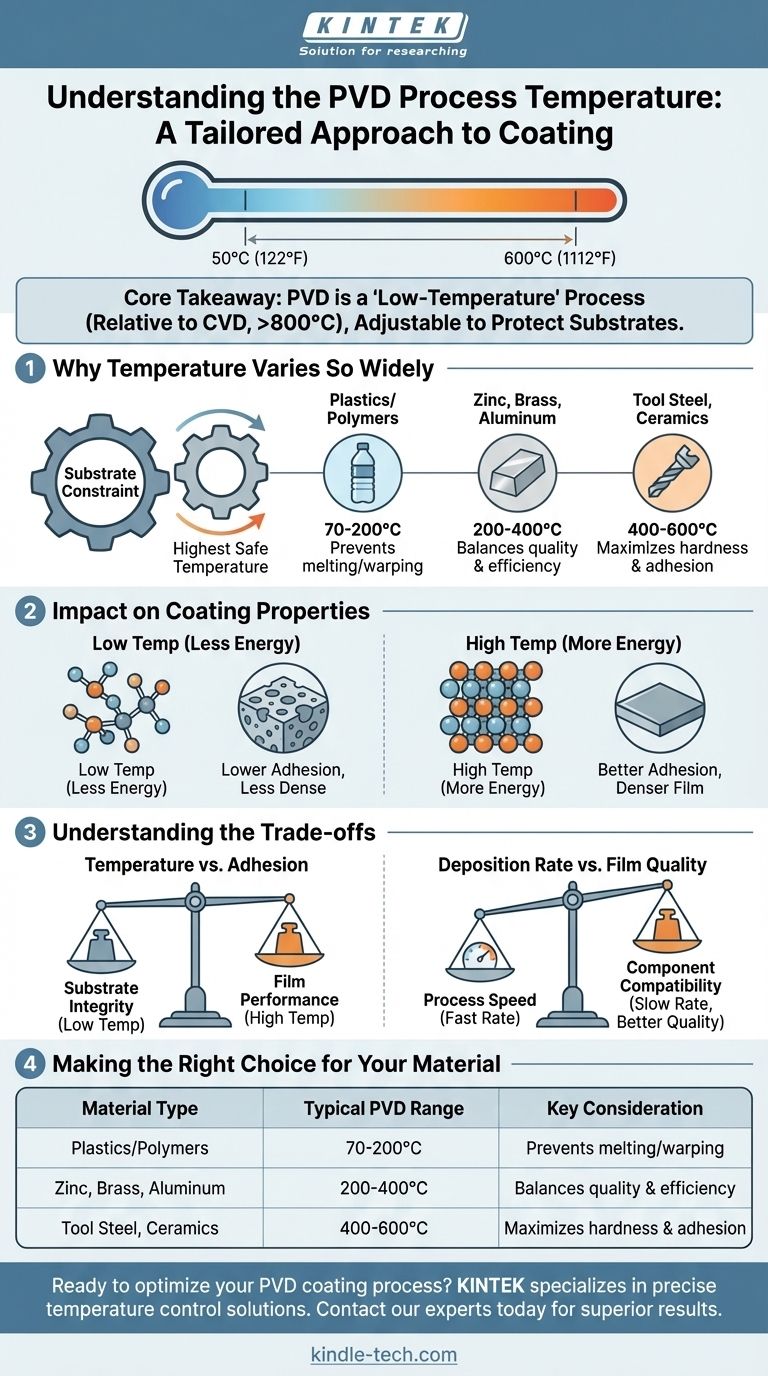
The temperature of a PVD process is not a single value but a highly controlled variable that depends on the material being coated and the desired film properties. While typical PVD processes operate in a broad range from 50°C to 600°C (122°F to 1112°F), the specific temperature is chosen to match the heat tolerance of the substrate, making it one of the most versatile coating methods available.
The core takeaway is that Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is fundamentally a "low-temperature" process relative to other methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Its key advantage is the ability to adjust the process temperature to protect the underlying part, from sensitive plastics to robust tool steels.

Why PVD Temperature Varies So Widely
The temperature is not an arbitrary setting; it is a critical parameter engineered to achieve a successful coating on a specific part. The variation seen in reported temperature ranges stems from two primary factors: the substrate material and the desired outcome.
The Substrate Material is the Primary Constraint
The single most important factor determining the process temperature is the heat tolerance of the substrate, which is the object being coated.
Heat-sensitive materials like plastics or polymers require very low temperatures, often between 70°C and 200°C (158°F and 392°F), to prevent them from melting, warping, or deforming.
More robust materials like zinc, brass, or aluminum can handle a moderate temperature range, typically from 200°C to 400°C (392°F to 752°F).
For applications requiring maximum hardness and adhesion on durable substrates like steel or ceramics, the process may run at the higher end of the PVD spectrum, from 400°C to 600°C (752°F to 1112°F).
The Impact on Coating Properties
Temperature directly influences the final quality of the coating. Generally, higher process temperatures provide more thermal energy to the depositing atoms.
This increased energy promotes better adhesion to the substrate and can result in a denser, less porous, and more durable film structure. This is why a manufacturer will use the highest temperature the substrate can safely tolerate.
A Key Advantage Over Other Methods
PVD's ability to operate at these relatively low temperatures is its defining advantage over older technologies like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which often requires temperatures in excess of 800°C (1472°F).
This makes PVD the ideal choice for coating precision components, electronics, or any part with critical dimensional tolerances that cannot withstand the extreme heat of CVD.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right temperature involves balancing the needs of the substrate with the goals for the coating. This balance introduces practical trade-offs that are critical to understand.
Temperature vs. Adhesion
Forcing a process to run at a very low temperature to protect a plastic substrate may compromise the ultimate adhesion or density of the film compared to what could be achieved on a steel part at a higher temperature. This is a fundamental compromise between substrate integrity and film performance.
Deposition Rate vs. Film Quality
At lower temperatures, deposition rates may need to be slowed to ensure the atoms arrange themselves into a quality film. This can increase cycle time and affect manufacturing throughput, representing a trade-off between process speed and component compatibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your material dictates the available process window. Use the following guidelines to understand what to expect from PVD for your specific application.
- If you are coating heat-sensitive materials (like plastics or polymers): PVD is one of the few viable options, operating below 200°C to protect your part's integrity.
- If you are coating standard metals (like aluminum or zinc): A moderate temperature range of 200-400°C is common to achieve an excellent balance of coating quality and process efficiency.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability on robust substrates (like tool steel): The process will be optimized at higher temperatures (400°C+) to produce the hardest and most adherent coating possible.
Ultimately, PVD's strength lies in its adaptability, allowing for the creation of high-performance coatings on an exceptionally wide range of materials.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical PVD Temperature Range | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics/Polymers | 70°C - 200°C (158°F - 392°F) | Prevents melting/warping |
| Zinc, Brass, Aluminum | 200°C - 400°C (392°F - 752°F) | Balances quality & efficiency |
| Tool Steel, Ceramics | 400°C - 600°C (752°F - 1112°F) | Maximizes hardness & adhesion |
Ready to optimize your PVD coating process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise temperature control in PVD applications. Whether you're coating heat-sensitive plastics or high-performance tool steels, our solutions ensure optimal adhesion and film quality while protecting your substrates. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's coating capabilities and achieve superior results for your specific materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















