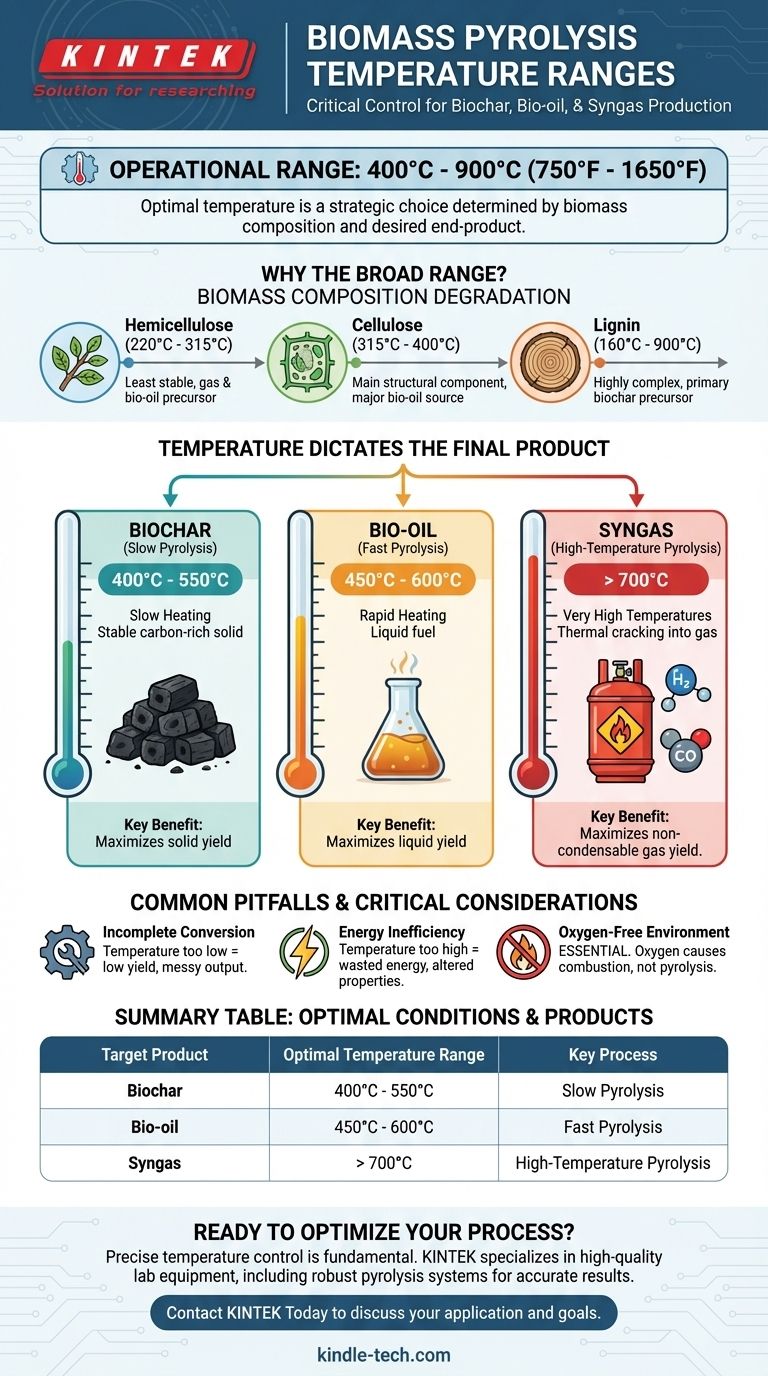
In short, the operational temperature for biomass pyrolysis is a broad range, typically falling between 400°C and 900°C (approximately 750°F to 1650°F). The precise temperature used within this range is not arbitrary; it is the most critical factor determining the final products of the process.
The core principle to understand is that there is no single "correct" temperature for pyrolysis. Instead, the optimal temperature is a strategic choice dictated by the chemical makeup of the specific biomass feedstock and, most importantly, which primary end-product—biochar, bio-oil, or syngas—you intend to produce.

Why Such a Broad Temperature Range?
The wide temperature spectrum exists because biomass is not a single chemical but a complex composite material. Its thermal decomposition occurs in stages as its primary components break down.
The Role of Biomass Composition
Biomass is primarily composed of three polymers: hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin. Each of these components decomposes at a different temperature range, influencing the overall process.
Hemicellulose Degradation
Hemicellulose is the least stable component. Its thermal breakdown begins at lower temperatures, typically between 220°C and 315°C, contributing significantly to the initial production of gases and bio-oil.
Cellulose Degradation
Cellulose, the main structural component of plant cells, decomposes in a relatively narrow and higher temperature band, usually between 315°C and 400°C. This rapid decomposition is a major source of the condensable vapors that form bio-oil.
Lignin Degradation
Lignin is a highly complex and stable polymer that provides rigidity to plants. It decomposes very slowly across a wide range of temperatures, from 160°C up to 900°C. Lignin is the primary precursor to the solid biochar residue.
How Temperature Dictates the Final Product
Choosing a temperature target is directly linked to the desired output. Different process conditions, such as "slow" or "fast" pyrolysis, use temperature to favor one product over another.
Lower Temperatures for Biochar (Slow Pyrolysis)
To maximize the yield of biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid, a process called slow pyrolysis is used. This involves a slow heating rate at relatively low temperatures, typically 400°C to 550°C. This allows the lignin to convert to char without being broken down into liquids and gases.
Moderate Temperatures for Bio-oil (Fast Pyrolysis)
To maximize the yield of bio-oil, a liquid fuel, fast pyrolysis is necessary. This process uses moderate temperatures, around 450°C to 600°C, but with an extremely rapid heating rate. This quickly breaks down cellulose and hemicellulose into vapors that are then rapidly cooled and condensed into liquid.
Higher Temperatures for Syngas
To maximize the yield of non-condensable gases, known as syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide), very high temperatures are required, often above 700°C. At these temperatures, the hydrocarbon chains from the bio-oil vapors are "cracked" into smaller, permanent gas molecules.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Selecting the right temperature involves critical trade-offs. Misunderstanding these can lead to inefficient or failed outcomes.
Incomplete Conversion
Operating at a temperature too low for the desired process will result in incomplete decomposition of the feedstock. This leads to low yields of your target product and a messy, inconsistent mixture of outputs.
Energy Inefficiency
Using a higher temperature than necessary is a common mistake. For example, producing biochar at 700°C instead of 500°C wastes significant energy and can unfavorably alter the char's properties by driving off valuable volatile matter.
The Oxygen-Free Environment
Regardless of the temperature, pyrolysis must occur in an oxygen-limited or oxygen-free environment. The introduction of oxygen will cause the biomass to combust (burn) rather than pyrolyze, completely altering the chemical pathways and final products.
Selecting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
Your target temperature is a direct function of your primary objective. Use these guidelines to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is maximizing biochar yield: Target a lower temperature range (400-550°C) with a slow heating rate to preserve the solid carbon structure.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil production: Target a moderate temperature range (450-600°C) coupled with a very high heating rate to rapidly vaporize and then condense the liquids.
- If your primary focus is producing syngas: Target a high temperature range (above 700°C) to ensure the thermal cracking of all heavier molecules into gas.
Ultimately, temperature is the most powerful lever you have to control the outcome of biomass pyrolysis.
Summary Table:
| Target Product | Optimal Temperature Range | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar | 400°C - 550°C | Slow Pyrolysis |
| Bio-oil | 450°C - 600°C | Fast Pyrolysis |
| Syngas | > 700°C | High-Temperature Pyrolysis |
Ready to optimize your biomass pyrolysis process?
The precise temperature control of your pyrolysis system is fundamental to achieving your target yields of biochar, bio-oil, or syngas. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your laboratory needs, including robust pyrolysis systems designed for accurate and repeatable results.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment to master your process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of carbon regeneration? Restore Spent Carbon for Cost-Effective, Sustainable Use
- What is pyrolytic decomposition? Transform Waste into Valuable Resources with Pyrolysis
- What are the basics of a rotary kiln? A Guide to Industrial-Scale Material Processing
- What is pyrolysis of lignocellulosic materials? Converting Biomass into Bio-oil, Bio-char, and Syngas
- What are the problems of rotary kiln of cement and their remedies? Achieve Long-Term Reliability and Efficiency
- What are the different types of pyrolysis oil? Choosing the Right Process for Your Fuel or Chemical Needs
- Can you regenerate activated charcoal? The Truth About Reusing Spent Carbon Filters
- What are the problems in a rotary kiln? Avoid Costly Downtime and Failures

















