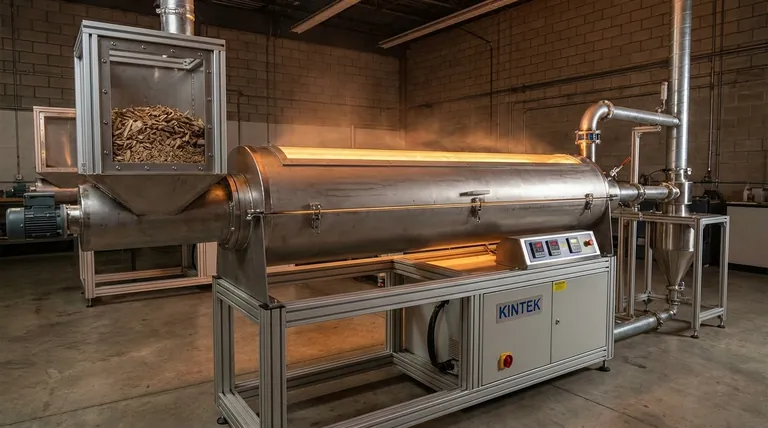
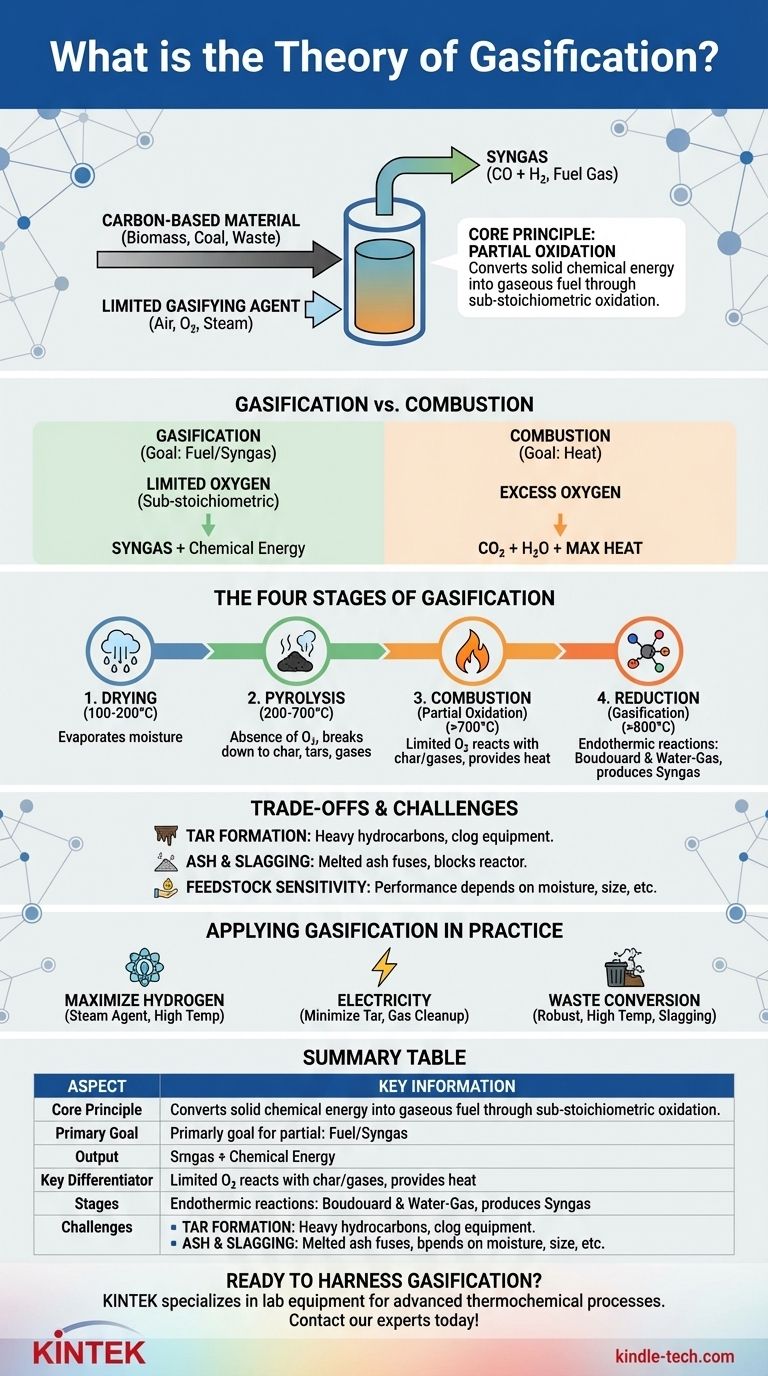
In essence, the theory of gasification describes a thermochemical process that converts carbon-based materials like biomass, coal, or waste into a valuable fuel gas called syngas. It achieves this by heating the material in a controlled environment with a limited amount of a "gasifying agent" (such as oxygen, air, or steam), deliberately starving it of enough oxygen for full combustion.
The core principle differentiating gasification from simple burning is partial oxidation. Instead of completely burning the fuel to release heat, gasification strategically uses just enough oxidation to power a series of chemical reactions that break down the feedstock into a combustible gas mixture rich in hydrogen and carbon monoxide.

Gasification vs. Combustion: The Critical Difference
To understand gasification, you must first distinguish it from combustion (burning). They are two fundamentally different goals achieved through similar means.
The Role of the Gasifying Agent
Combustion aims for complete oxidation by supplying excess oxygen, ensuring all the fuel burns to produce mainly carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and maximum heat.
Gasification, however, uses a sub-stoichiometric amount of a gasifying agent. This means there isn't enough oxygen to complete the combustion process, forcing different chemical pathways to occur. Common agents include air, pure oxygen, steam, or CO2.
The Key Distinction: Fuel vs. Heat
The ultimate output is the main difference. The goal of combustion is to release thermal energy (heat) directly from the fuel.
The goal of gasification is to convert the solid fuel's chemical energy into a gaseous fuel (syngas). This syngas can then be burned elsewhere to produce electricity, or used as a chemical building block to produce hydrogen, methanol, and other valuable products.
The Four Stages of the Gasification Process
Gasification is not a single reaction but a sequence of four distinct thermal processes that occur in different zones within a gasifier.
Stage 1: Drying
As the feedstock enters the gasifier, the initial heat (typically 100-200°C) drives off any moisture. This is a simple evaporation phase that prepares the material for the next stage.
Stage 2: Pyrolysis
Around 200-700°C, in the absence of oxygen, pyrolysis begins. The heat breaks down the complex hydrocarbon structures of the feedstock into three primary products: a solid carbon char, condensable vapors (tars and oils), and non-condensable volatile gases.
Stage 3: Combustion (Partial Oxidation)
In this zone, the gasifying agent is introduced. A portion of the char and volatile products from pyrolysis react with the limited oxygen in an exothermic reaction (releasing heat). This combustion step is vital as it produces the high temperatures (over 700°C) needed to drive the final, all-important reduction stage.
Stage 4: Reduction (Gasification)
This is the primary gas-making stage, occurring at the highest temperatures (typically >800°C). In this oxygen-poor, high-heat environment, the remaining char and gases undergo several endothermic (heat-absorbing) reactions with steam and carbon dioxide produced during combustion.
Key reactions include the Boudouard reaction (C + CO2 → 2CO) and the water-gas reaction (C + H2O → CO + H2), which convert solid carbon and intermediate gases into the final, energy-rich components of syngas.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, gasification is a complex process with inherent difficulties that must be managed for successful operation.
The Problem of Tar Formation
Tars are complex, heavy hydrocarbons produced during pyrolysis that fail to break down in the reduction zone. If they exit the gasifier, they can cool, condense, and clog downstream equipment like engines and turbines, causing significant operational problems.
Ash and Slagging Issues
All feedstocks contain inorganic, non-combustible material that becomes ash. At the high temperatures inside a gasifier, this ash can melt and fuse into a glassy slag, which can block passages and damage the reactor's lining.
Feedstock Sensitivity
Gasification performance is highly dependent on the feedstock's characteristics, including its moisture content, ash content, and physical size. This means that materials often require significant pre-processing (drying, shredding) to be used effectively.
Applying Gasification Theory in Practice
Understanding the core principles allows you to align technology choices with your specific objectives. The theory dictates the practical outcomes.
- If your primary focus is maximizing hydrogen production: You should prioritize steam as the gasifying agent and operate at high temperatures to favor the water-gas reaction.
- If your primary focus is generating electricity with an engine: Your priority must be minimizing tar content through reactor design (e.g., downdraft gasifiers) and effective gas cleanup systems.
- If your primary focus is converting municipal solid waste: You need a robust, high-temperature gasifier (like a plasma gasifier) that can handle diverse, inconsistent feedstock and melt the ash into a non-hazardous, inert slag.
Ultimately, gasification is the controlled art of transforming solid matter into a versatile gaseous chemical feedstock.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Partial oxidation (sub-stoichiometric oxygen) |
| Primary Goal | Convert solid fuel into a gaseous fuel (syngas) |
| Main Output | Syngas (rich in CO and H2) |
| Key Differentiator | Produces a fuel gas, not just heat (like combustion) |
| Process Stages | 1. Drying, 2. Pyrolysis, 3. Combustion, 4. Reduction |
| Common Challenges | Tar formation, ash/slagging, feedstock sensitivity |
Ready to harness the power of gasification in your lab or pilot project?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced thermochemical processes like gasification. Whether you are researching feedstock efficiency, optimizing syngas production, or developing new clean energy solutions, our reliable reactors, temperature control systems, and gas analysis tools are designed to support your innovation.
Let's build your ideal gasification setup together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















