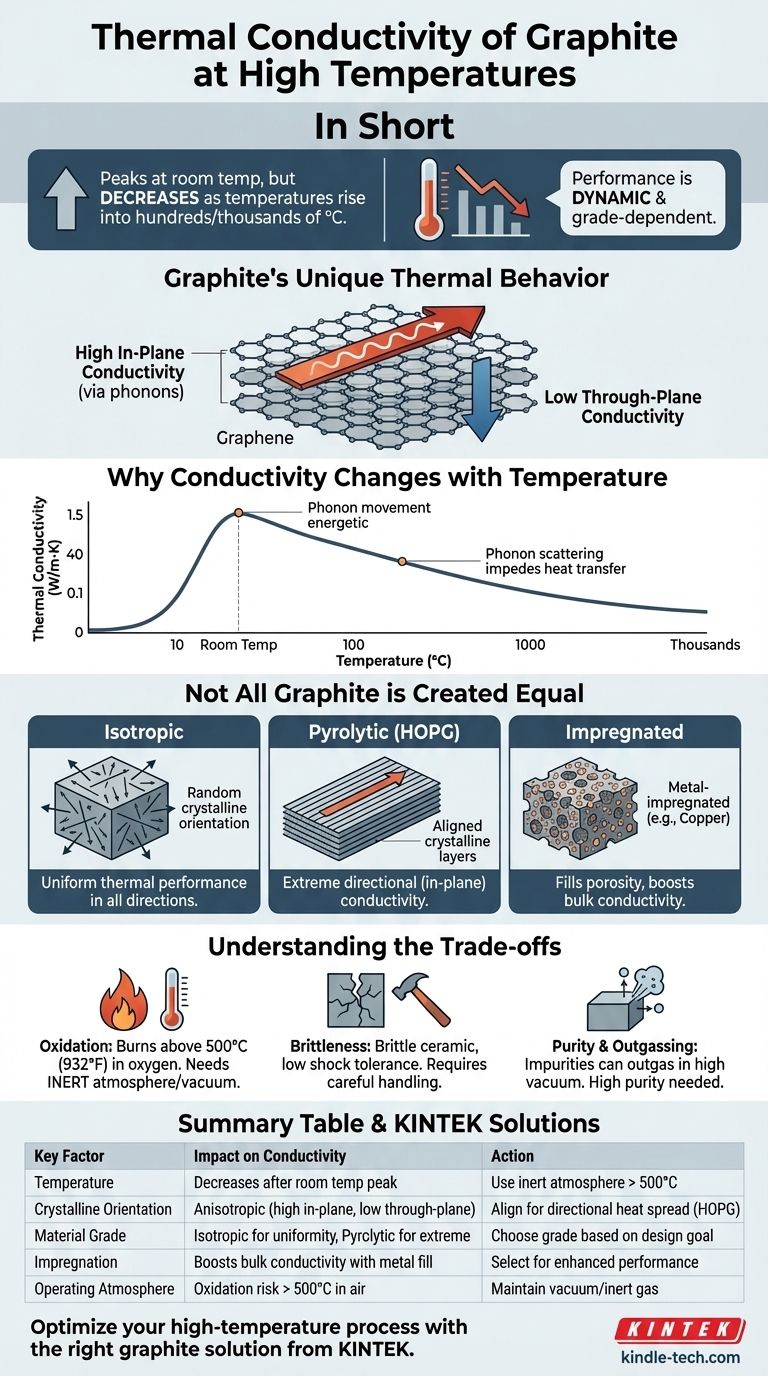
In short, the thermal conductivity of most crystalline graphite grades is very high at room temperature—often exceeding that of metals like steel and iron—but it typically decreases as temperatures rise into the hundreds or thousands of degrees Celsius. This counter-intuitive behavior is a critical design consideration, as the specific grade of graphite and its crystalline orientation are the most important factors determining its actual performance.
The central takeaway is that "graphite" is not a single material with one thermal value. Its performance is dynamic: conductivity peaks near room temperature and then falls, and the choice between different grades, such as isotropic, pyrolytic, or impregnated graphite, will have a far greater impact on thermal management than temperature alone.

Understanding Graphite's Unique Thermal Behavior
To use graphite effectively in high-temperature environments, you must understand the physics of how it transfers heat. Its performance is directly tied to its unique atomic structure.
The Role of Crystalline Structure
Graphite consists of stacked layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, much like sheets of chicken wire. This is often referred to as a graphene layer.
Heat travels very efficiently along these flat layers (in-plane) via lattice vibrations, known as phonons. This is what gives graphite its exceptionally high thermal conductivity in that direction.
Why Conductivity Changes with Temperature
The relationship between temperature and thermal conductivity in graphite is not linear.
At very low temperatures, conductivity is low. As temperature increases towards ambient, conductivity rises sharply as phonon movement becomes more energetic.
However, above a peak (often near room temperature), the thermal conductivity begins to decrease. At these higher temperatures, the atomic lattice is vibrating so violently that the phonons begin to collide with and scatter each other, creating a "traffic jam" that impedes the efficient transfer of heat.
The Critical Importance of Anisotropy
Because of its layered structure, graphite is highly anisotropic, meaning its properties are direction-dependent.
The thermal conductivity in-plane (along the layers) can be hundreds of times higher than the conductivity through-plane (across the layers). This is a crucial detail for designing components like heat sinks or spreaders, where the orientation of the graphite is paramount.
Not All Graphite is Created Equal
The term "graphite" covers a wide range of materials. The manufacturing process and final form dictate its thermal performance, especially at high temperatures.
Synthetic vs. Natural Graphite
Synthetic graphite is produced by heat-treating carbon precursors at very high temperatures. This process yields high purity and allows for controlled crystalline structures, making it the preferred choice for predictable, high-performance applications like furnace elements or semiconductor manufacturing.
Isotropic vs. Pyrolytic Grades
Isotropic graphite is engineered to have a more random crystal orientation. While its peak conductivity is lower than highly oriented grades, it offers more uniform thermal performance in all directions, which is ideal for applications like molds or heating elements requiring even heat distribution.
Highly Oriented Pyrolytic Graphite (HOPG) is a specialized form where the layers are almost perfectly aligned. It offers some of the highest in-plane thermal conductivity of any material at room temperature, making it a superhighway for heat in one plane but an insulator in the other.
High-Performance Impregnated Grades
As noted in the references, graphite can be impregnated with metals like copper or silver. This process fills the material's natural porosity, boosting its bulk thermal and electrical conductivity even further for the most demanding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While graphite is an exceptional thermal material, it comes with practical limitations that are critical to acknowledge in any design.
Oxidation at High Temperatures
This is graphite's primary weakness. In the presence of oxygen, graphite will begin to oxidize (effectively, burn) at temperatures around 500°C (932°F). Therefore, for high-temperature use, it must be operated in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent degradation.
Mechanical Brittleness
Unlike metals, graphite is a brittle ceramic material. It has low tensile strength and cannot tolerate shock or high-impact loads. Designs must account for this by avoiding sharp corners and providing proper mechanical support.
Purity and Outgassing
For applications in high-vacuum or clean environments (like in the semiconductor industry), the purity of the graphite is critical. Lower-grade graphite can contain impurities that will outgas at high temperatures, potentially contaminating the process or chamber.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct graphite grade is essential for project success. Your decision should be based on your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum, directional heat spreading: Use a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) and ensure it is aligned to move heat along the desired path.
- If your primary focus is uniform, multi-directional heat management: Choose a high-purity, isotropic graphite grade for predictable performance in all directions.
- If you are designing a high-temperature furnace element: Select a dense, synthetic graphite grade and operate it in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
- If cost is a major driver for a less demanding application: A standard molded or extruded synthetic graphite may suffice, but be sure to verify its properties with the supplier.
By understanding these principles, you can leverage graphite not just as a material, but as a precise thermal engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Thermal Conductivity at High Temperatures |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Decreases significantly after a peak near room temperature due to phonon scattering. |
| Crystalline Orientation | In-plane (along layers) is very high; through-plane (across layers) is much lower (anisotropic). |
| Material Grade | Isotropic graphite offers uniform performance; Pyrolytic (HOPG) offers extreme directional conductivity. |
| Impregnation | Impregnation with metals (e.g., copper) can increase bulk thermal conductivity. |
| Operating Atmosphere | Must be used in a vacuum or inert gas to prevent oxidation above ~500°C (932°F). |
Optimize your high-temperature process with the right graphite solution from KINTEK.
Graphite's thermal performance is complex and grade-dependent. Choosing incorrectly can lead to inefficiency or failure. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of synthetic, isotropic, and specialty graphites for demanding thermal applications.
Our experts can help you select the ideal material to ensure superior heat management, longevity, and process reliability in your furnace, semiconductor, or research application.
Contact us today to discuss your specific thermal challenges and how our graphite materials can provide the solution. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal limit of graphite? Unlock Extreme Heat Performance in Your Lab
- How does graphite react to heat? Unlocking Its Unique High-Temperature Strengths
- At what temperature does graphite thermal decompose? The Critical Role of Atmosphere
- Is a graphite melting point high or low? Discover Its Extreme Thermal Resilience
- Is graphite good in high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential



















