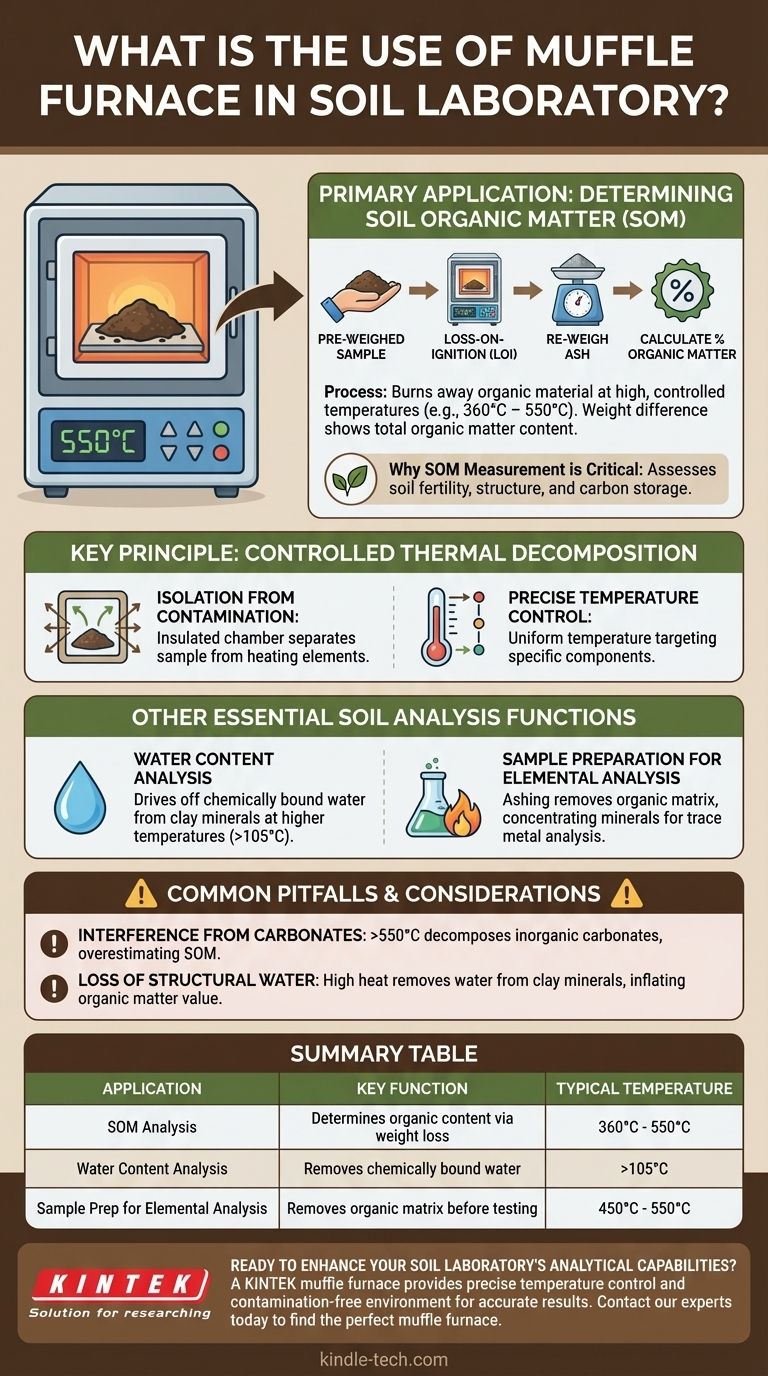
In a soil laboratory, a muffle furnace is primarily used to determine the organic matter content of a sample through a process called "loss-on-ignition." By subjecting a pre-weighed soil sample to extremely high, controlled temperatures, the furnace burns away all organic material, leaving only the mineral components behind. This allows technicians to calculate the percentage of organic matter by measuring the weight difference before and after heating.
The core function of a muffle furnace is not just heating, but controlled thermal decomposition. It uses precise, high temperatures in a clean environment to isolate and quantify specific components of a soil sample, revealing critical information about its composition and health.

The Primary Application: Determining Soil Organic Matter (SOM)
The most common and vital use of a muffle furnace in soil science is to measure Soil Organic Matter (SOM). This is a cornerstone metric for assessing soil fertility, structure, and carbon storage capacity.
The "Loss-on-Ignition" (LOI) Method
The process is straightforward but requires precision. First, a soil sample is dried to remove all water and then carefully weighed. It is then placed in the muffle furnace and heated to a specific temperature, typically between 360°C and 550°C, for several hours.
This intense heat causes the complete combustion of the organic components (carbon, plant residues, microbial biomass). After cooling, the remaining ash is weighed again. The difference in weight represents the total organic matter that was burned off.
Why SOM Measurement is Critical
Knowing the SOM percentage is fundamental to agriculture and environmental science. It directly relates to a soil's ability to hold water and nutrients, support plant life, and sequester atmospheric carbon.
Other Essential Soil Analysis Functions
Beyond determining organic matter, a muffle furnace serves other important preparatory and analytical roles in a soil lab.
Water Content Analysis
While a standard drying oven is used for simple moisture content (at ~105°C), a muffle furnace can be used at higher temperatures to drive off water that is chemically bound within the structure of certain clay minerals.
Sample Preparation for Elemental Analysis
For analyzing the concentration of specific trace metals or other inorganic elements, the organic portion of the soil can interfere with the results.
Ashing the sample in a muffle furnace effectively removes this organic matrix. This leaves a concentrated mineral sample that is easier to process for analysis by methods like atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) or inductively coupled plasma (ICP) mass spectrometry.
Understanding the Key Principle: Controlled Thermal Decomposition
A muffle furnace is superior to a simple high-temperature oven because it is designed for analytical precision, which relies on two key features.
Isolation from Contamination
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that separates the sample from the heating elements. This design prevents byproducts of combustion from the heat source from contaminating the sample, ensuring that the weight loss is due only to changes within the soil itself.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern furnaces allow for precise and uniform temperature control. This is critical because different soil components decompose at different temperatures. Researchers can set specific temperature profiles to target organic matter while minimizing the decomposition of other minerals.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, the loss-on-ignition method has limitations that a skilled analyst must consider for accurate interpretation.
Interference from Carbonates
At temperatures above 550°C, inorganic materials like calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) can begin to decompose, releasing carbon dioxide. This weight loss can be mistakenly attributed to organic matter, leading to an overestimation.
Loss of Structural Water
Some clay minerals contain water molecules within their crystalline structure. The high temperatures in a muffle furnace can drive this structural water off, which also contributes to weight loss and can slightly inflate the final organic matter value.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The muffle furnace is a versatile tool, but its application should be tailored to your specific analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is soil fertility and carbon content: The loss-on-ignition method for quantifying organic matter is your key application.
- If your primary focus is preparing samples for heavy metal analysis: Use the furnace for ashing to remove the organic matrix prior to instrumental analysis.
- If your primary focus is the detailed mineralogical composition: Be aware that the furnace can alter clay structures and decompose carbonates, requiring careful temperature control and data interpretation.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace allows you to break a soil sample down to its fundamental components, revealing the essential building blocks of its health and history.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Typical Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Organic Matter (SOM) Analysis | Determines organic content via weight loss | 360°C - 550°C |
| Water Content Analysis | Removes chemically bound water from clay minerals | >105°C |
| Sample Preparation for Elemental Analysis | Removes organic matrix before metal testing | 450°C - 550°C |
Ready to enhance your soil laboratory's analytical capabilities? A KINTEK muffle furnace provides the precise temperature control and contamination-free environment essential for accurate loss-on-ignition testing, water content analysis, and sample preparation. Our lab equipment is designed specifically for soil scientists and agricultural laboratories who demand reliable, repeatable results for soil health assessment.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your soil analysis needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the operating temperature of the muffle furnace? Find Your Ideal Range for Lab Success
- Why do we use muffle furnace? For Unmatched Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What are the acceptance criteria for muffle furnace? Ensure Safety, Performance & Success
- What is the significance of the muffle furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace used for in pharma? Ensuring Purity and Regulatory Compliance



















