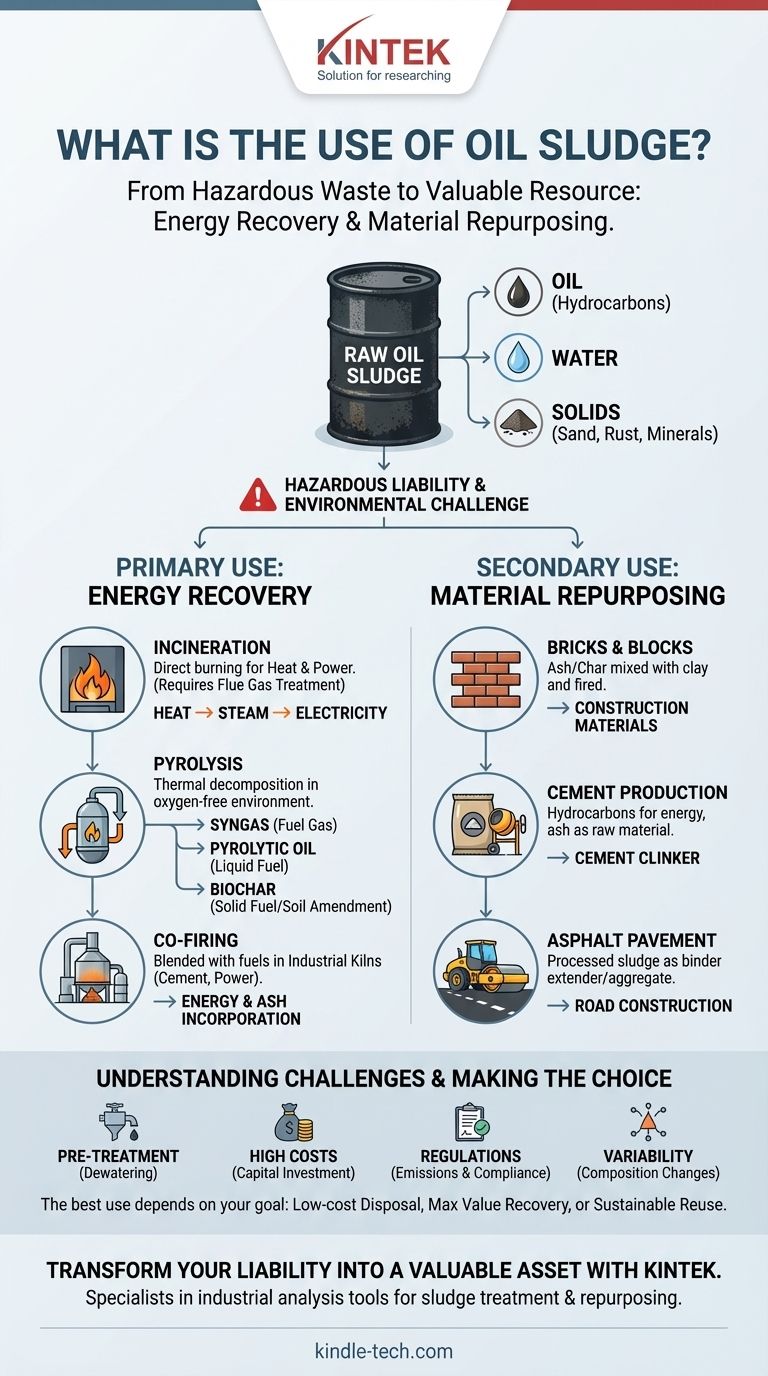
Far from being a simple waste product, oil sludge is increasingly seen as a valuable secondary resource. Its primary uses are centered on energy recovery through processes like incineration and pyrolysis, or as a raw material in the manufacturing of construction materials such as bricks, cement, and asphalt after it has been properly treated.
Oil sludge is a hazardous liability that requires costly disposal. However, its high hydrocarbon and mineral content means that with the right technology, it can be transformed from a waste stream into a source of energy and valuable materials.

What Defines Oil Sludge?
The Three Core Components
Oil sludge is an emulsion, a complex mixture of three main things: oil (hydrocarbons), water, and solids. These solids include sand, rust, and various mineral and metal particles.
An Inevitable Byproduct
This sludge forms naturally during the extraction, transportation, and refining of crude oil. It settles at the bottom of storage tanks, separators, and pipelines, accumulating over time.
The Environmental Challenge
Raw oil sludge is classified as hazardous waste. It contains toxic compounds that can contaminate soil and groundwater, making its disposal a significant environmental and regulatory challenge for the petroleum industry.
Primary Use: Energy Recovery
The most common application for oil sludge is to harness its significant energy content, which comes from its trapped hydrocarbons.
Incineration for Heat and Power
The most direct method is incineration. The sludge is burned in a controlled furnace to generate heat. This heat can be used to produce steam, which in turn can drive turbines to generate electricity or be used for industrial processes.
Effective incineration requires flue gas treatment systems to capture pollutants, but it provides a definitive way to destroy the hazardous components while recovering energy.
Pyrolysis for Higher-Value Fuels
A more advanced thermal process is pyrolysis. Instead of burning, the sludge is heated to high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment.
This process breaks down the complex hydrocarbons into simpler, more valuable products:
- Syngas: A fuel gas that can be used to generate power.
- Pyrolytic Oil: A liquid fuel similar to diesel that can be refined further or used directly.
- Biochar: A solid, carbon-rich material that can be used as fuel or a soil amendment.
Co-firing in Industrial Kilns
Oil sludge can be blended with other fuels, such as coal or petcoke, and co-fired in large industrial furnaces. Cement kilns and power plants are ideal candidates.
This approach reduces the consumption of primary fossil fuels and allows the mineral content (ash) of the sludge to be incorporated directly into the final product, such as cement clinker.
Secondary Use: Material Repurposing
Once the organic components are either removed or stabilized, the remaining solid inorganic matter can be repurposed, primarily in construction.
Manufacturing Bricks and Blocks
The ash produced from sludge incineration or the solid char from pyrolysis can be mixed with clay and fired to create bricks and construction blocks. The residual hydrocarbons can even contribute to the fuel needed for the firing process.
A Component in Cement Production
Treated sludge can be used in cement kilns in two ways. Its hydrocarbon content provides energy for the high-temperature process, and its mineral ash (containing silica, alumina, and iron) becomes part of the raw material feed for producing cement clinker.
Additive for Asphalt Pavement
Processed oil sludge can also be incorporated into asphalt mixtures used for road construction. It can act as a binder extender or part of the aggregate, reducing the need for virgin materials and providing a durable, long-term disposal solution.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The Critical Need for Pre-Treatment
Raw, wet sludge cannot be used directly. It must first be dewatered to reduce its volume and improve its handling and caloric value. This is a crucial and often energy-intensive first step.
High Technology and Capital Costs
The technologies for effective recovery, especially pyrolysis and compliant incineration, require significant capital investment. The cost of equipment, installation, and operation is a major barrier to adoption.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Using or processing oil sludge is heavily regulated. Any energy recovery process must include systems to control emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and heavy metals to meet strict environmental standards. The final solid byproducts must also be tested to ensure they are non-hazardous.
Variability of Sludge Composition
The exact chemical and physical makeup of sludge can vary dramatically depending on the source of the crude oil and the specific process that created it. This variability makes it challenging to design a one-size-fits-all recovery system, often requiring bespoke solutions for different sludge streams.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best use for oil sludge depends entirely on its specific composition, available technology, local regulations, and your primary economic objective.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-volume disposal: Co-firing in a local cement kiln or power plant is often the most direct and economically viable path.
- If your primary focus is maximizing value recovery: Pyrolysis offers the greatest potential, converting the waste into marketable oil and gas products.
- If your primary focus is sustainable material reuse: Incorporating treated sludge or ash into bricks and asphalt for local construction projects provides a durable, long-term solution.
By treating oil sludge as a raw material instead of a waste, you can effectively turn a significant environmental liability into a tangible asset.
Summary Table:
| Use Case | Process | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Recovery | Incineration, Pyrolysis, Co-firing | Heat, Electricity, Syngas, Pyrolytic Oil |
| Material Repurposing | Brick/Block Manufacturing, Cement Production, Asphalt Additive | Construction Bricks, Cement Clinker, Road Pavement |
Transform your oil sludge liability into a valuable asset with KINTEK.
As specialists in lab equipment and consumables for industrial analysis, KINTEK provides the precise tools and technology needed to analyze, treat, and repurpose oil sludge effectively. Whether your goal is energy recovery or material reuse, our solutions help you meet regulatory standards and maximize value from your waste stream.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific oil sludge management needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















