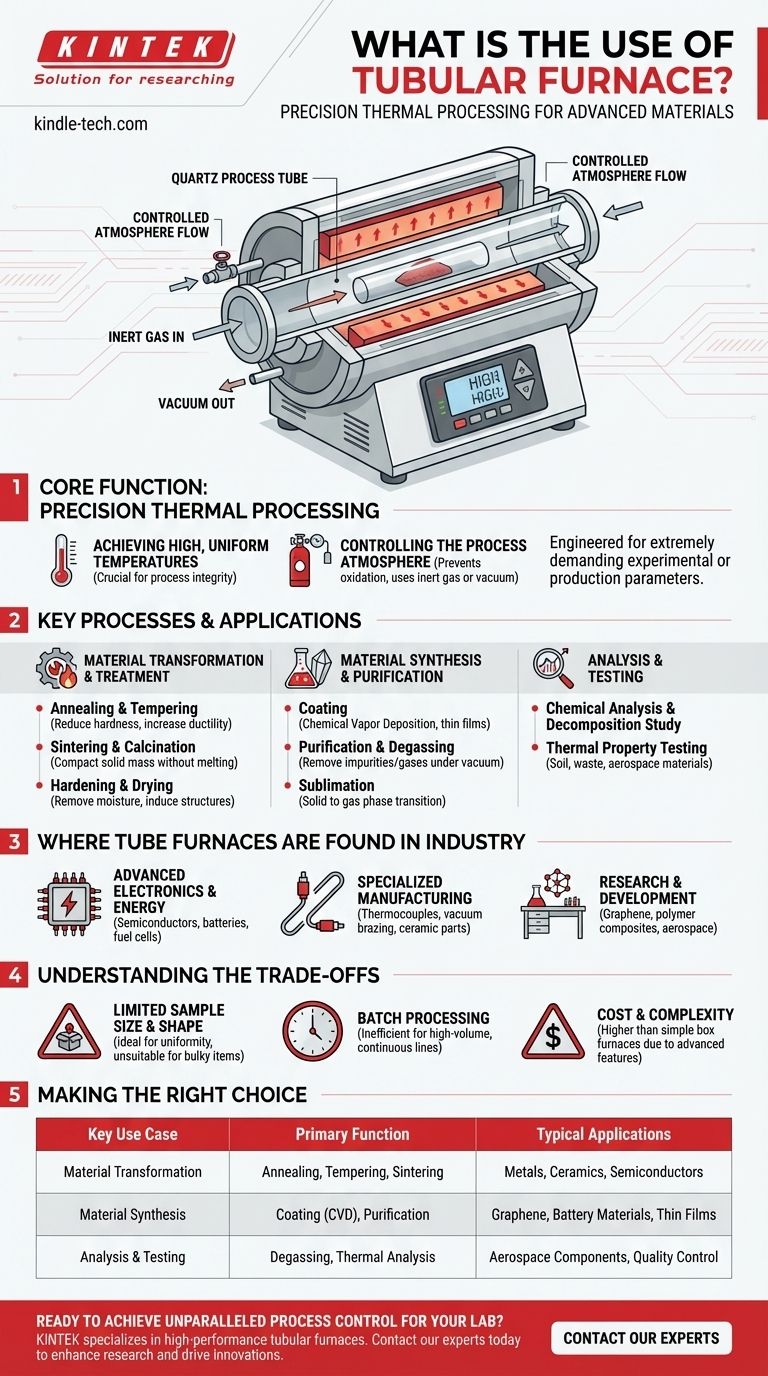
At its core, a tubular furnace is a high-temperature electric furnace used to process small samples of materials with exceptional precision. Its primary purpose is to perform a wide variety of thermal processes—such as annealing, sintering, and chemical analysis—on materials placed within a cylindrical tube, often under a tightly controlled atmosphere or vacuum.
The defining use of a tubular furnace is not just to generate high heat, but to do so with superior temperature uniformity and strict atmospheric control. This makes it indispensable for advanced materials research and specialized industrial production where process integrity is paramount.

The Core Function: Precision Thermal Processing
A tube furnace is chosen over other heating equipment when the experimental or production parameters are extremely demanding. Its design is engineered to solve specific challenges related to heat and environmental exposure.
Achieving High, Uniform Temperatures
The cylindrical heating chamber, which surrounds the process tube, is designed to deliver exceptionally uniform heat to the sample inside. This uniformity is critical for processes where even minor temperature variations could ruin the outcome.
Controlling the Process Atmosphere
The most significant advantage of a tube furnace is the ability to control the atmosphere around the sample. The process tube can be sealed and then purged with inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) or put under a vacuum to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation.
Key Processes and Applications
The combination of precise temperature and atmospheric control makes the tube furnace a versatile tool for a wide range of specific thermal processes.
Material Transformation and Treatment
Many applications involve changing the physical properties of a material. This includes processes like:
- Annealing & Tempering: Heating and slow cooling to reduce hardness and increase ductility.
- Sintering & Calcination: Using heat to compact and form a solid mass of material without melting it.
- Hardening & Drying: Removing moisture or inducing specific crystalline structures through heat.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Tube furnaces are also critical for creating new materials or refining existing ones.
- Coating: Applying thin films to substrates through processes like chemical vapor deposition.
- Purification & Degassing: Removing impurities or trapped gases from a material under vacuum.
- Sublimation: Transitioning a substance directly from a solid to a gas phase for purification.
Analysis and Testing
In research and quality control, these furnaces are used to analyze material behavior under heat. This includes chemical analysis, studying physical decomposition, and testing the thermal properties of materials for soil, waste, or aerospace applications.
Where Tube Furnaces Are Found in Industry
This versatility makes tube furnaces essential in numerous high-tech and research fields.
Advanced Electronics and Energy
They are fundamental tools for producing semiconductors, batteries, and solid oxide fuel cells, where material purity and structural integrity are non-negotiable.
Specialized Manufacturing
Tube furnaces are used in the fabrication of thermocouples and mineral-insulated cables. They are also used for high-integrity joining processes like vacuum brazing and for general heat treatment of specialized metal and ceramic parts.
Research and Development
In both academic and commercial labs, tube furnaces are workhorses for developing next-generation materials like graphene and polymer composites. They are also used extensively for oil and gas analysis and testing advanced aerospace components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the tube furnace is not the right tool for every heating task. Its specialized nature comes with inherent limitations.
Sample Size and Shape
The primary drawback is the limited sample size. The cylindrical chamber is ideal for uniformity but restricts the dimensions and shape of the material being processed, making it unsuitable for large or bulky components.
Batch Processing
A standard tube furnace operates as a batch process, meaning samples are loaded, processed, and then unloaded one at a time. This is inefficient for high-volume, continuous manufacturing lines, which may require a different furnace design.
Cost and Complexity
The features that make a tube furnace so valuable—especially its atmospheric control systems—also add to its cost and operational complexity compared to a simpler box or muffle furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating equipment depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research: A tube furnace is essential for its unparalleled control over atmosphere and temperature, enabling work with sensitive materials like semiconductors or graphene.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical heat treatment: A tube furnace is ideal for annealing, sintering, or tempering small, high-value parts where uniformity is critical to performance.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating or ashing large samples: A simpler and larger box or muffle furnace would likely be a more practical and cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, a tube furnace is the instrument of choice when your process integrity depends on absolute control over temperature and atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Key Use Case | Primary Function | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transformation | Annealing, Tempering, Sintering | Metals, Ceramics, Semiconductors |
| Material Synthesis | Coating (CVD), Purification | Graphene, Battery Materials, Thin Films |
| Analysis & Testing | Degassing, Thermal Analysis | Aerospace Components, Quality Control |
Ready to achieve unparalleled process control for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance tubular furnaces designed for the precise thermal processing needs of research and industrial laboratories. Our equipment delivers the superior temperature uniformity and atmospheric control required for advanced work in semiconductors, battery development, and materials science.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK tubular furnace can enhance your research, improve your yields, and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency
- How does a tube resistance furnace contribute to the preparation of carbon-based sulfonated solid acid catalysts?
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces contribute to the precursor preparation stage of Na1-xZrxLa1-xCl4 electrolytes?
- What are the two types of biomass conversion? Harness Heat or Biology for Renewable Energy
- What process is controlled by a tube furnace during RP/C pretreatment? Optimize Your Anode Material Synthesis
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace required for preparing noble metal catalysts? Unlock Sensor Sensitivity
- What is the function of a tube resistance furnace and nitrogen system in wool biochar? Optimize Controlled Pyrolysis
- What protections do high vacuum tube furnaces offer for DMR? Ensure Precise Atmosphere Control & Catalyst Purity



















