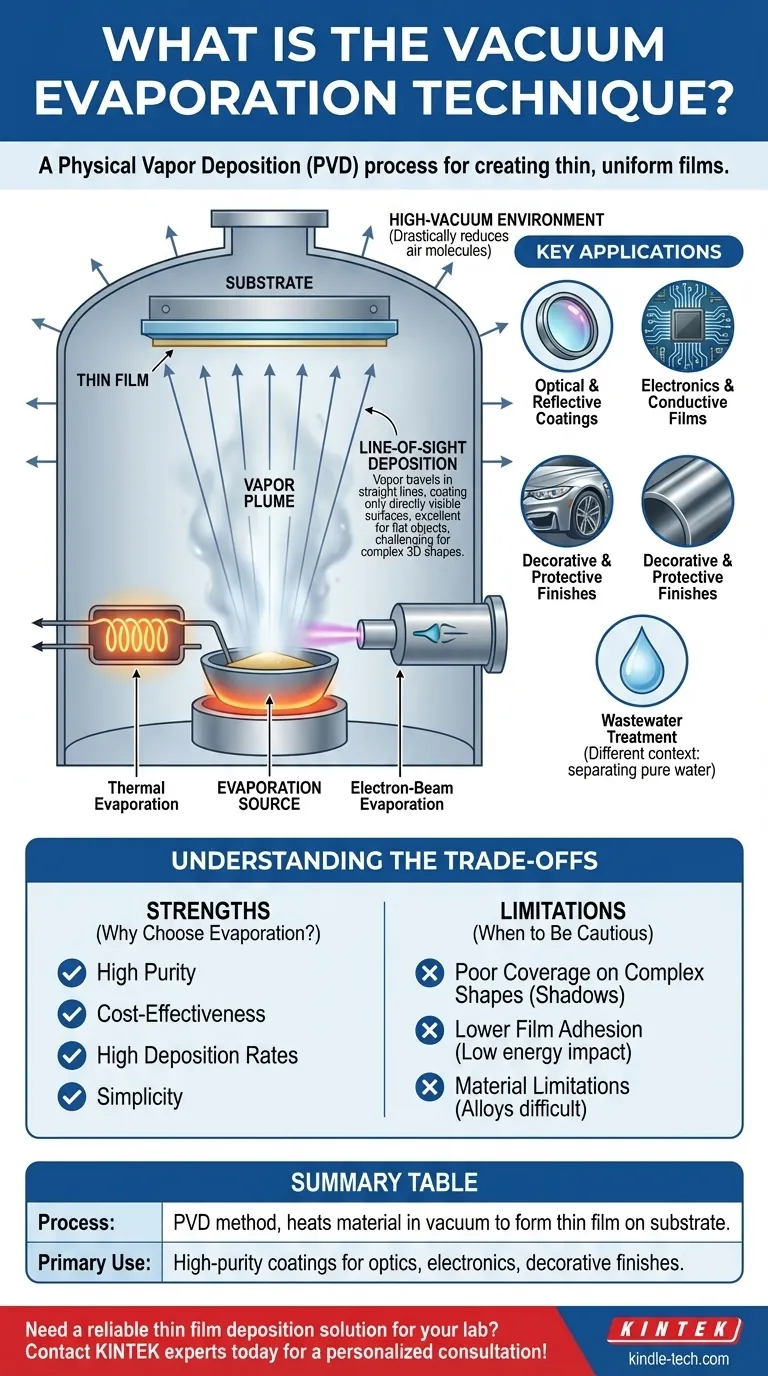
In essence, vacuum evaporation is a method for depositing a thin, uniform film of material onto a surface. It is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process where a source material, such as a metal or a compound, is heated in a high-vacuum chamber until it evaporates. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler target surface (the substrate), forming a solid, high-purity layer.
Vacuum evaporation is fundamentally a process of phase change: a solid is heated to become a gas, which then cools back into a solid on a target. Its primary value lies in its simplicity and cost-effectiveness for creating high-quality films on simple surfaces, but this simplicity comes with important trade-offs in adhesion and coverage.

How Vacuum Evaporation Works: The Core Principles
To understand its applications, you must first grasp the three critical components of the process: the vacuum, the heat source, and the path of the vapor.
The High-Vacuum Environment
The entire process occurs in a chamber where the air has been pumped out to create a high vacuum. This is not simply a detail; it is essential for success.
A vacuum drastically reduces the number of air molecules present. This ensures that the evaporated material atoms can travel directly to the substrate without colliding with other particles, which would otherwise contaminate the film or scatter the vapor.
The Evaporation Source
The source material is heated until its atoms or molecules gain enough energy to escape into a gaseous state. This is typically achieved in one of two ways:
- Thermal Evaporation: The material is placed in a small, electrically resistive boat or crucible, which is heated by passing a high current through it. This is the simplest and least expensive method.
- Electron-Beam Evaporation: A high-energy electron beam is aimed at the source material, heating a localized spot to a very high temperature. This allows for the evaporation of materials with very high melting points.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
Once evaporated, the material vapor travels in straight lines away from the source. This is known as line-of-sight deposition.
The vapor will only coat surfaces that have an uninterrupted path from the source. This is excellent for creating precise patterns with masks or for coating flat surfaces, but it poses a significant challenge for coating complex, three-dimensional objects.
Key Applications and Industries
The combination of high purity, simplicity, and line-of-sight deposition makes vacuum evaporation suitable for a specific range of applications.
Optical and Reflective Coatings
This technique is widely used to create mirror coatings (like aluminum on glass) and sophisticated optical interference coatings. The high purity of the deposited film ensures excellent reflective or anti-reflective properties.
Electronics and Conductive Films
Vacuum evaporation can deposit thin, electrically conducting films of metal onto circuits or other components. The ability to precisely control the film's thickness is critical for achieving the desired electrical resistance.
Decorative and Protective Finishes
When used to deposit metals, the process is often called vacuum metallization. It is a common way to give plastics a metallic finish for decorative purposes or to apply corrosion-protective coatings on various parts.
A Note on Wastewater Treatment
The term "vacuum evaporation" is also used in a completely different context: wastewater treatment. The principle is similar—lowering pressure reduces a liquid's boiling point—but the goal is to separate pure water from contaminants, not to deposit a thin film.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strengths and Limitations
No single technique is perfect for every job. Understanding the trade-offs of vacuum evaporation is key to using it effectively.
The Advantages: Why Choose Evaporation?
- High Purity: Because the process occurs in a vacuum and the source material can be highly pure, the resulting films are exceptionally clean.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It is generally the least expensive P_V_D process, making it highly accessible.
- High Deposition Rates: Compared to some other methods, it can deposit material relatively quickly.
- Simplicity: The equipment and process are straightforward, with easy monitoring and control of the deposition rate.
The Limitations: When to Be Cautious
- Poor Coverage on Complex Shapes: The line-of-sight nature means that any area not directly visible from the source will not be coated, creating "shadows."
- Lower Film Adhesion: The evaporated atoms arrive at the substrate with relatively low energy. This can result in weaker adhesion compared to other PVD techniques like sputtering, where atoms impact the substrate with much higher force.
- Material Limitations: It can be difficult to evaporate alloys while maintaining their exact composition, as the constituent elements may have different evaporation rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct deposition method requires matching the technique's characteristics to your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-purity coatings on flat or simple surfaces: Vacuum evaporation is an excellent and highly capable choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability or coating complex 3D shapes: You should investigate sputtering, as it provides superior film adhesion and better coverage on non-flat surfaces.
- If your primary focus is processing materials with very high melting points or complex alloys: Electron-beam evaporation is a more suitable variant, though other methods may still be superior.
By understanding these fundamental principles and trade-offs, you are empowered to determine if this foundational technique is the right tool for your engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | A Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) method where a material is heated in a vacuum to form a thin film on a substrate. |
| Primary Use | Creating high-purity coatings for optical mirrors, conductive films in electronics, and decorative finishes. |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effectiveness and high purity, ideal for coating flat or simple surfaces. |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight deposition results in poor coverage on complex, 3D shapes. |
Need a reliable thin film deposition solution for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including vacuum evaporation systems. Whether you're working on optical coatings, electronic components, or protective finishes, our expertise ensures you get the right tool for precise, cost-effective results.
Let's discuss your project requirements and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab



















