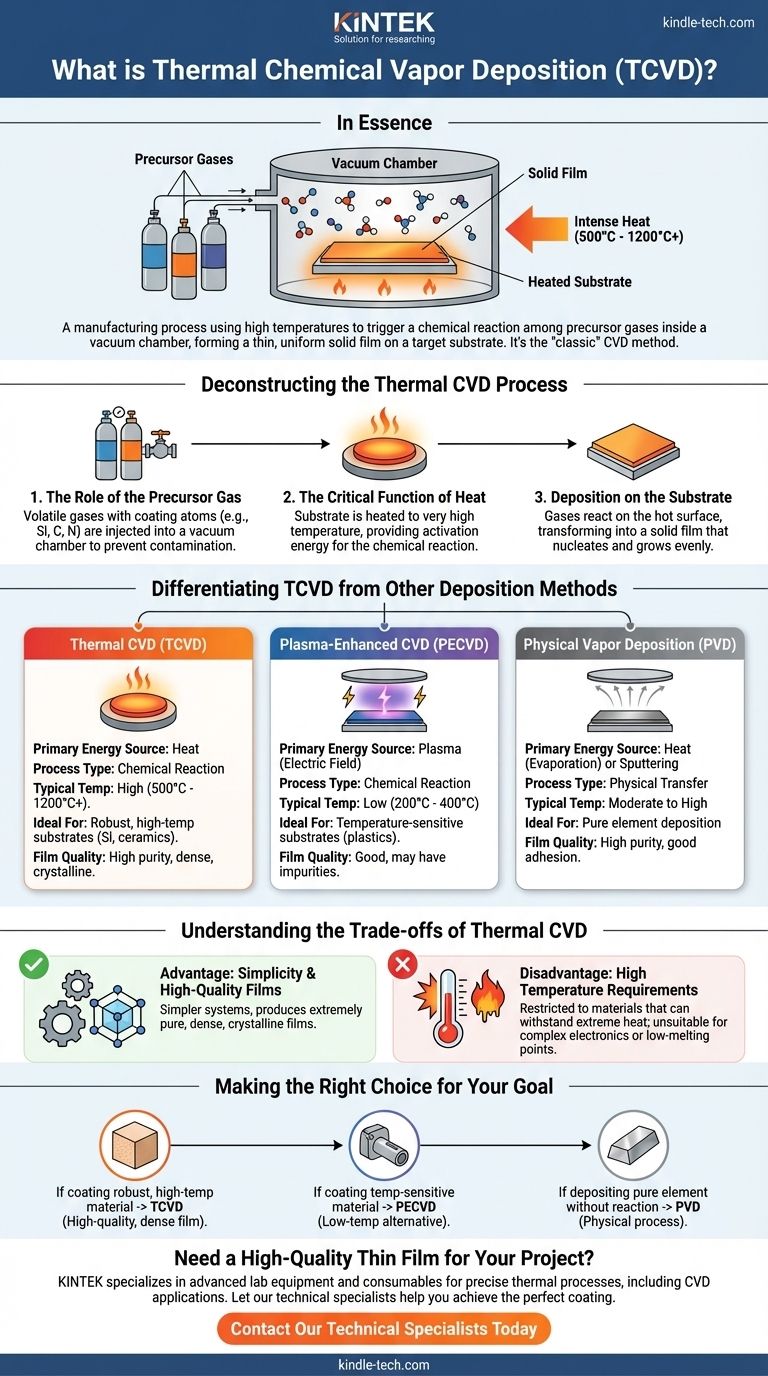
In essence, Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition (TCVD) is a manufacturing process that uses high temperatures to trigger a chemical reaction among precursor gases inside a vacuum chamber. This reaction forms a solid material that deposits as a thin, uniform film onto a target object, known as a substrate. It is considered the conventional or "classic" form of the broader Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) family of technologies.
The central concept to grasp is that Thermal CVD is a process of chemical transformation, not physical transfer. It fundamentally relies on heat as the sole energy source to break down gases and create an entirely new solid coating on a surface, a method whose simplicity is balanced by its restrictive high-temperature requirements.

Deconstructing the Thermal CVD Process
To understand TCVD, it's best to break it down into its core operational steps. Each stage is critical for forming a high-quality, adherent film.
The Role of the Precursor Gas
The process begins with one or more volatile precursor gases. These are carefully selected chemicals that contain the atoms of the desired coating material (e.g., silicon, carbon, nitrogen).
These gases are injected into a sealed, low-pressure chamber. The vacuum environment is essential to prevent contamination from air and to ensure the precursor molecules can travel freely to the target surface.
The Critical Function of Heat
This is the defining characteristic of TCVD. The substrate is heated to a very high temperature, often ranging from several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius.
This intense heat provides the activation energy needed for the precursor gases to react or decompose when they come into contact with the hot surface. Without sufficient thermal energy, the chemical reaction will not occur.
Deposition on the Substrate
As the precursor gases react on the heated substrate, they transform from a gaseous state into a solid. This solid material nucleates and grows on the surface, gradually building up a thin film.
Because the reaction is driven by the surface temperature, the coating forms evenly across all exposed areas of the substrate, creating a highly uniform and conforming layer.
Differentiating TCVD from Other Deposition Methods
The term "CVD" covers a family of processes. Understanding how TCVD differs from other methods is key to appreciating its specific applications.
Thermal CVD vs. Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
The most common alternative is Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD). Instead of relying solely on high heat, PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma (an energized, ionized gas).
This plasma provides the energy to drive the chemical reaction at much lower temperatures than TCVD. This makes PECVD suitable for coating materials, like plastics or certain metals, that cannot withstand extreme heat.
A Critical Distinction: CVD vs. PVD
A common point of confusion is the difference between Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
TCVD is a chemical process; the precursor gases react to form a new compound on the substrate. In contrast, PVD is a physical process. It involves heating a solid source material until it evaporates and then letting this vapor condense onto the substrate. No chemical reaction occurs.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Thermal CVD
Like any engineering process, TCVD has distinct advantages and disadvantages that dictate its use.
Advantage: Simplicity and High-Quality Films
Because it relies only on heat, a TCVD system can be relatively simpler and more robust than plasma-based systems.
The process is capable of producing extremely pure, dense, and high-quality crystalline films, which are often superior to those made at lower temperatures.
Disadvantage: High Temperature Requirements
The primary limitation of TCVD is its dependence on high heat. This severely restricts the types of substrates that can be coated.
Materials with low melting points or those that might be damaged by thermal stress (like complex electronic components) are not suitable for this process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition technology depends entirely on your material constraints and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is coating a robust, high-temperature material (like silicon, ceramics, or refractory metals): TCVD is often the most direct and effective choice for producing a high-quality, dense film.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material (like polymers, plastics, or certain alloys): You must use a low-temperature alternative like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) to avoid damaging the substrate.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure element (like titanium or aluminum) without a chemical reaction: A physical process like PVD is the more appropriate technology.
By understanding the fundamental role of thermal energy in driving deposition, you can confidently select the right manufacturing process for your specific material and goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Thermal CVD | PECVD | PVD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Energy Source | Heat | Plasma (Electric Field) | Heat (Evaporation) or Sputtering |
| Process Type | Chemical Reaction | Chemical Reaction | Physical Transfer |
| Typical Temperature | High (500°C - 1200°C+) | Low (200°C - 400°C) | Moderate to High |
| Ideal For | Robust, high-temp substrates (e.g., Si, ceramics) | Temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., plastics) | Pure element deposition |
| Film Quality | High purity, dense, crystalline | Good, but may contain impurities | High purity, good adhesion |
Need a High-Quality Thin Film for Your Project?
Choosing the right deposition technology is critical for your material's performance. The experts at KINTEK can help you navigate these choices. We specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processes, including materials suited for CVD applications.
Let us help you achieve the perfect coating for your substrate. Contact our technical specialists today to discuss your specific requirements and discover the right solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is physical Vapour deposition process? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Coatings
- What is the temperature of LPCVD polysilicon? Master the Critical 580°C to 650°C Range
- How does the hydrogen and nitrogen mixed atmosphere influence graphene morphology? Master CVD Synthesis Control
- What is the principle of MOCVD? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of thin film deposition? A Guide to PVD, CVD, and Coating Techniques
- Is CVD costly? Unlocking the True Investment in Superior Coating Performance
- What is a CVD reactor? The Engine for Atomic-Level Material Creation
- How does the two-cycle process of RF sputtering work? Master Thin Film Deposition with Precision



















