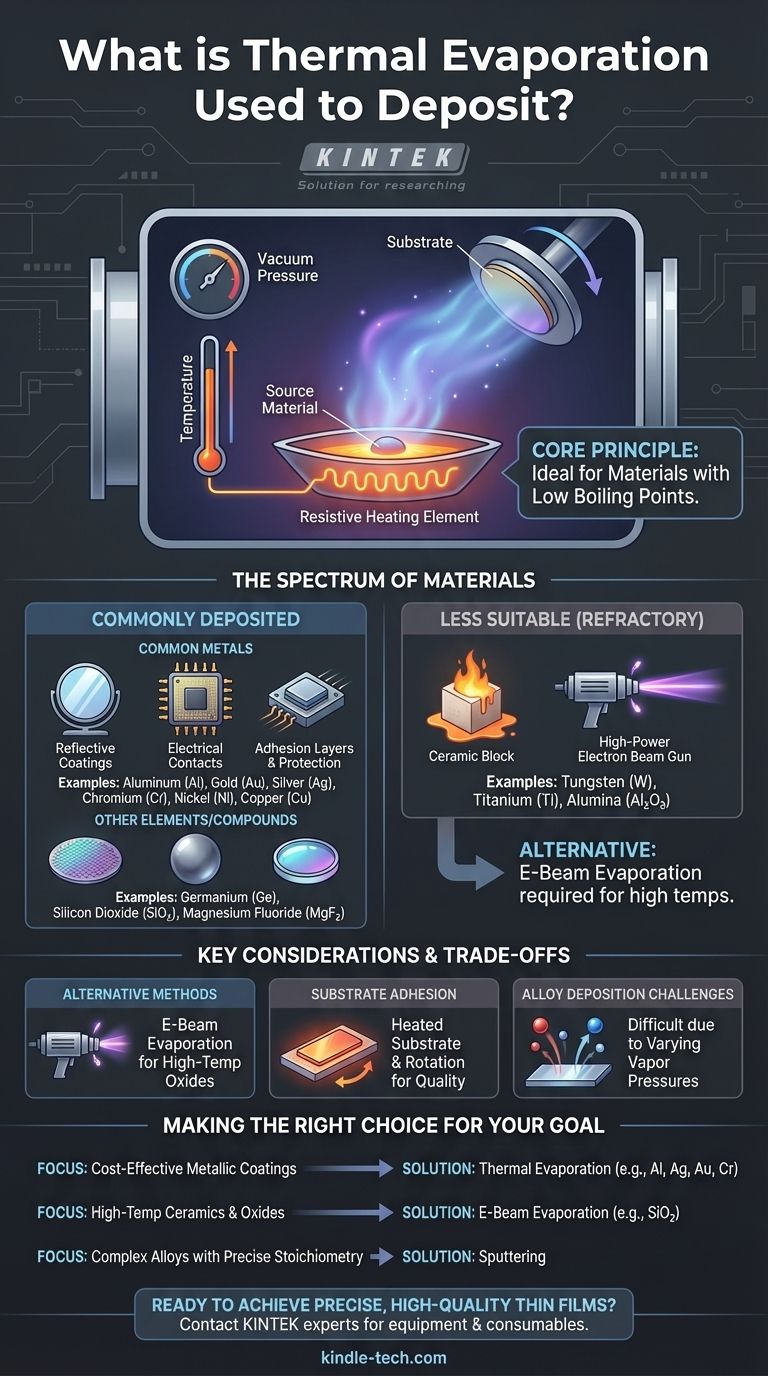
In short, thermal evaporation is used to deposit a wide range of materials, particularly metals with relatively low boiling points. Common examples include aluminum, silver, gold, chromium, nickel, and copper, as well as some non-metals and organic compounds.
The central takeaway is that thermal evaporation is a versatile technique, but its suitability is fundamentally dictated by the material's vapor pressure. It excels with materials that can be easily evaporated through resistive heating in a vacuum, making it ideal for many common metals but less effective for high-temperature ceramics or refractory metals.
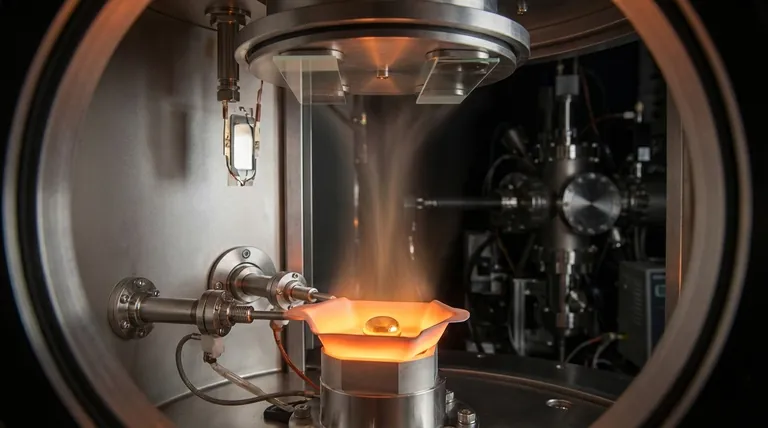

The Spectrum of Materials for Thermal Evaporation
Thermal evaporation is a workhorse process in thin-film deposition, capable of handling a variety of material categories. The choice of material is directly linked to the desired properties of the final thin film, such as electrical conductivity, reflectivity, or adhesion.
Common Metals
Many of the most frequently deposited materials are metals. Their high electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as their optical properties, make them essential for countless applications.
Examples include:
- Aluminum (Al): Widely used for creating reflective coatings (like in mirrors) and for electrical contacts in microelectronics.
- Gold (Au) & Silver (Ag): Valued for their high conductivity and resistance to oxidation. They are used in electronics, sensors, and specialized optical coatings.
- Chromium (Cr) & Nickel (Ni): Often used as adhesion layers between a substrate and another metal (like gold) or for creating hard, protective coatings.
- Copper (Cu): A primary material for creating conductive pathways in electronic devices.
Other Elements and Compounds
Beyond pure metals, thermal evaporation can also deposit other types of materials, expanding its use into semiconductor and optical applications.
- Semiconductors: Elements like Germanium (Ge) can be deposited to create specific electronic device layers.
- Dielectrics/Insulators: Certain compounds like Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) or Magnesium Fluoride (MgF2) can be evaporated. These are crucial for creating insulating layers or anti-reflection coatings on lenses.
Understanding the Core Limitation: Boiling Point
The effectiveness of thermal evaporation is governed by a simple physical principle: heating a material in a high vacuum until it turns into a vapor that coats a substrate. This directly ties the process to the material's boiling point and vapor pressure.
The Principle of Vapor Pressure
In a vacuum chamber, the source material (e.g., a pellet of aluminum) is heated in a small crucible or "boat." As its temperature rises, its vapor pressure increases until atoms begin to sublimate or evaporate, traveling in a straight line to coat anything in their path, including the target substrate.
Why Low Boiling Points are Ideal
Materials like aluminum, silver, and gold have relatively low boiling points. This means they can be evaporated efficiently using standard resistive heating sources without requiring extreme temperatures that could damage the equipment or introduce impurities.
The Challenge with Refractory Materials
Materials with very high boiling points, such as tungsten, titanium, or ceramics like Alumina (Al2O3), are known as refractory materials. They require immense energy to evaporate. Standard thermal evaporation often cannot reach these temperatures effectively, making it an unsuitable method.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
Choosing thermal evaporation involves more than just selecting a material; the process itself has inherent characteristics that you must account for.
Alternative Deposition Methods
For high-temperature source materials like SiO2 or transition metal oxides, electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation is often a better choice. E-beam uses a focused beam of electrons to heat the source material, achieving much higher temperatures than standard thermal boats can.
Substrate Adhesion
The quality of the final film depends heavily on how well it sticks to the substrate. To promote better adhesion and film quality, the substrate is often heated during deposition. The substrate holder can also be rotated to ensure the coating is deposited evenly across the entire surface.
Alloy Deposition Challenges
Depositing alloys with a precise composition is very difficult with thermal evaporation. This is because the different elements in the alloy will have different vapor pressures and will evaporate at different rates, leading to a film whose composition does not match the source material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material and process requires aligning them with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective metallic coatings: Thermal evaporation is an excellent choice for common metals like Aluminum, Silver, Gold, and Chromium for applications in electronics or optics.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-temperature ceramics or oxides: You should strongly consider E-Beam Evaporation, which is designed to handle the extreme temperatures these materials require.
- If your primary focus is depositing complex alloys with precise stoichiometry: You should explore an alternative process like sputtering, as thermal evaporation is poorly suited for maintaining alloy compositions.
Ultimately, understanding a material's physical properties is the key to selecting the most effective deposition technology for your project.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Common Metals | Aluminum (Al), Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Chromium (Cr) | Electrical contacts, reflective coatings, adhesion layers |
| Other Elements/Compounds | Germanium (Ge), Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | Semiconductor layers, optical coatings, insulation |
| Less Suitable (Refractory) | Tungsten (W), Titanium (Ti), Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Requires alternative methods like E-beam evaporation |
Ready to achieve precise, high-quality thin films for your research or production?
The right deposition method is critical to your project's success. KINTEK specializes in providing the ideal lab equipment and expert consumables for thermal evaporation and other thin-film processes. Whether you're working with common metals or exploring more complex materials, we can help you select the perfect solution to enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the right equipment for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab



















