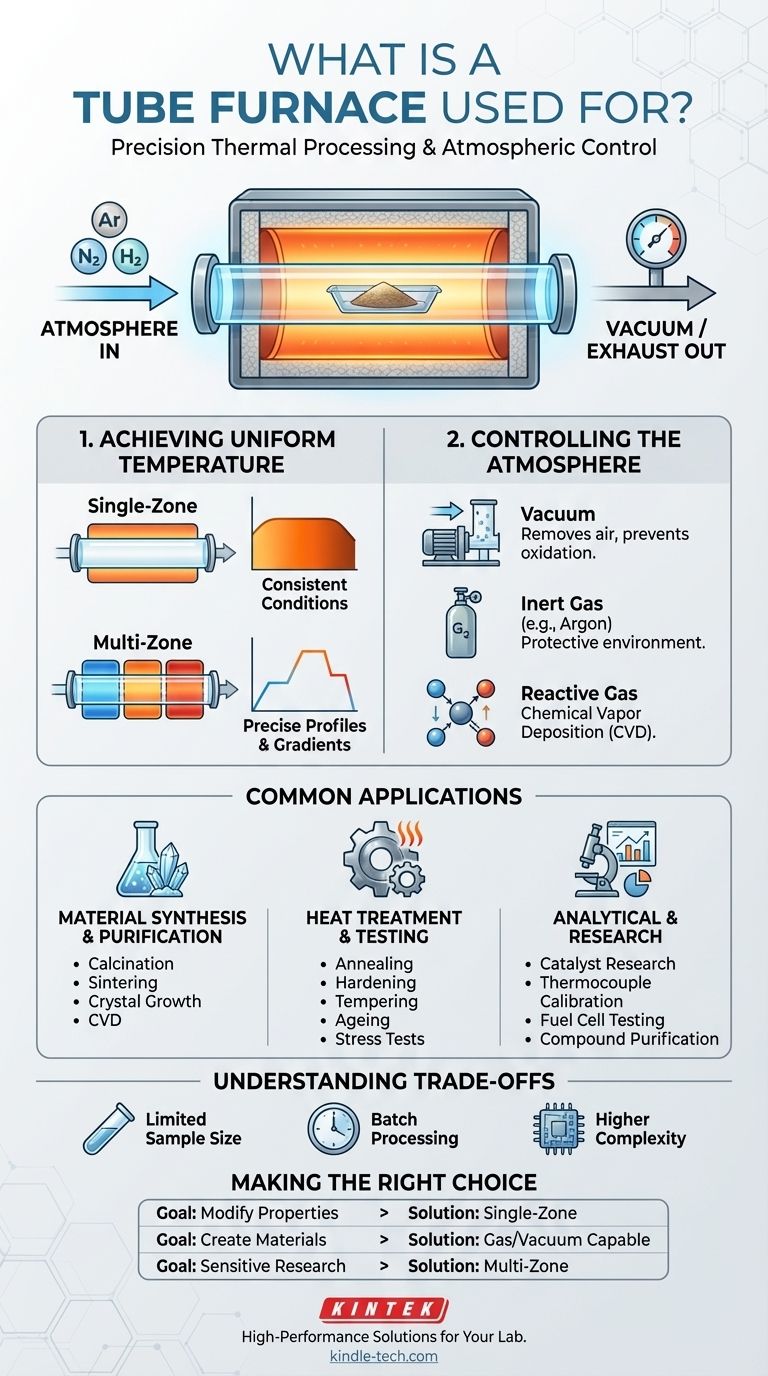
In essence, a tube furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven designed for processing materials with exceptional precision and atmospheric control. It is used across research and industrial settings for a vast range of thermal processes, including synthesizing new materials, heat-treating metals, purifying chemical compounds, and conducting advanced catalyst research.
The defining feature of a tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its ability to create a highly uniform and controllable environment. Its cylindrical chamber is the key to achieving precise temperature profiles and isolating the sample from the outside air, which is critical for sensitive processes.
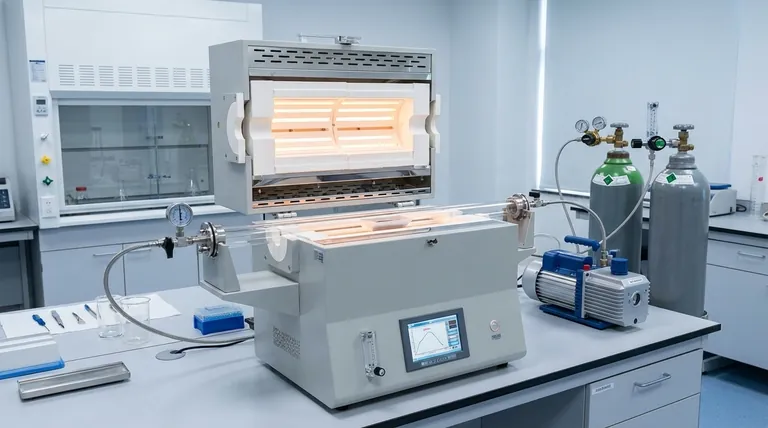

The Core Function: Precise Environmental Control
While many furnaces provide heat, a tube furnace is selected when the conditions of that heating are paramount. This control is achieved through two primary mechanisms.
Achieving Uniform Temperature
The cylindrical geometry of a tube furnace is inherently better at distributing heat evenly around a sample compared to a rectangular box furnace. This ensures the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions.
For even greater precision, multi-zone tube furnaces use multiple, independently controlled heating elements along the length of the tube. This allows operators to create a perfectly flat temperature profile or a specific, stable temperature gradient.
Controlling the Atmosphere
The most significant advantage of a tube furnace is its ability to control the gaseous environment around the sample. The processing tube can be sealed and connected to gas handling systems.
This allows processes to be run under a vacuum, in an inert atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, or with reactive gases for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or other synthesis methods.
Common Applications by Process Type
The combination of uniform heating and atmospheric control makes tube furnaces indispensable for a wide variety of applications. These can be grouped into three main categories.
Material Synthesis and Purification
These processes involve creating new materials or removing impurities, often requiring the exclusion of air or the introduction of specific gases.
Key examples include calcination (heating to high temperatures in air or a controlled atmosphere), sintering (fusing powders together), crystal growth, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where gases react to form a solid coating on a substrate.
Heat Treatment and Material Testing
This category focuses on modifying the physical properties of existing materials. The precise, repeatable heating of a tube furnace is essential for achieving consistent results.
Common processes include annealing (softening metals), hardening, tempering, ageing, and subjecting materials to accelerated stress tests at high temperatures.
Analytical and Research Processes
In a laboratory setting, repeatability is everything. Tube furnaces provide the stable and isolated environment needed for sensitive experiments.
Applications include fundamental catalyst research, high-accuracy thermocouple calibration, testing fuel cell components, and the purification of organic and inorganic compounds for analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a tube furnace is not the right tool for every job. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Limited Sample Size
The most obvious constraint is the diameter of the tube. This restricts the size and volume of the material that can be processed at one time, making it less suitable for large-scale production compared to box or belt furnaces.
Batch Processing
Tube furnaces are inherently batch-processing instruments. Loading, sealing, processing, cooling, and unloading a sample takes time. This limits throughput for applications that require continuous operation.
Higher Complexity
Systems that incorporate multi-zone heating or advanced gas handling and vacuum capabilities are more complex and costly to purchase, operate, and maintain than simpler oven designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties (Heat Treatment): A single-zone tube furnace provides the stable, uniform temperature needed for reliable annealing or tempering.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials or removing impurities (Synthesis & Purification): A tube furnace with gas and vacuum capabilities is essential for controlling the chemical environment during processes like CVD or calcination.
- If your primary focus is highly sensitive research: A multi-zone tube furnace offers the ultimate control over temperature gradients, ensuring the most precise and repeatable experimental conditions possible.
Ultimately, choosing a tube furnace is a decision to prioritize control and precision over sample volume and throughput.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Uniform Heating & Single Zone | Heat Treatment (Annealing, Tempering) | Consistent material properties |
| Gas/Vacuum Capability | Material Synthesis (CVD, Calcination) | Controlled chemical reactions |
| Multi-Zone Heating | Advanced Research & Crystal Growth | Precise temperature gradients |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance tube furnaces designed for research and industrial applications. Whether you need a standard single-zone model for reliable heat treatment or a sophisticated multi-zone system with gas handling for advanced material synthesis, our solutions deliver the control and repeatability your work demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your material synthesis, purification, and testing processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















