At its core, sintering uses fine powder, immense pressure, and intense heat to transform loose material into a solid, unified mass. This process is not limited to a single substance; it is a versatile manufacturing technique that works with a wide range of materials, most notably powdered metals and ceramics, which are heated to a point just below their melting temperature to fuse them together.
Sintering is fundamentally a thermal process that bonds particles of a material together, creating a solid object without melting it. This allows for the creation of complex parts from materials like metal alloys and high-performance ceramics that can be difficult to shape using traditional methods.

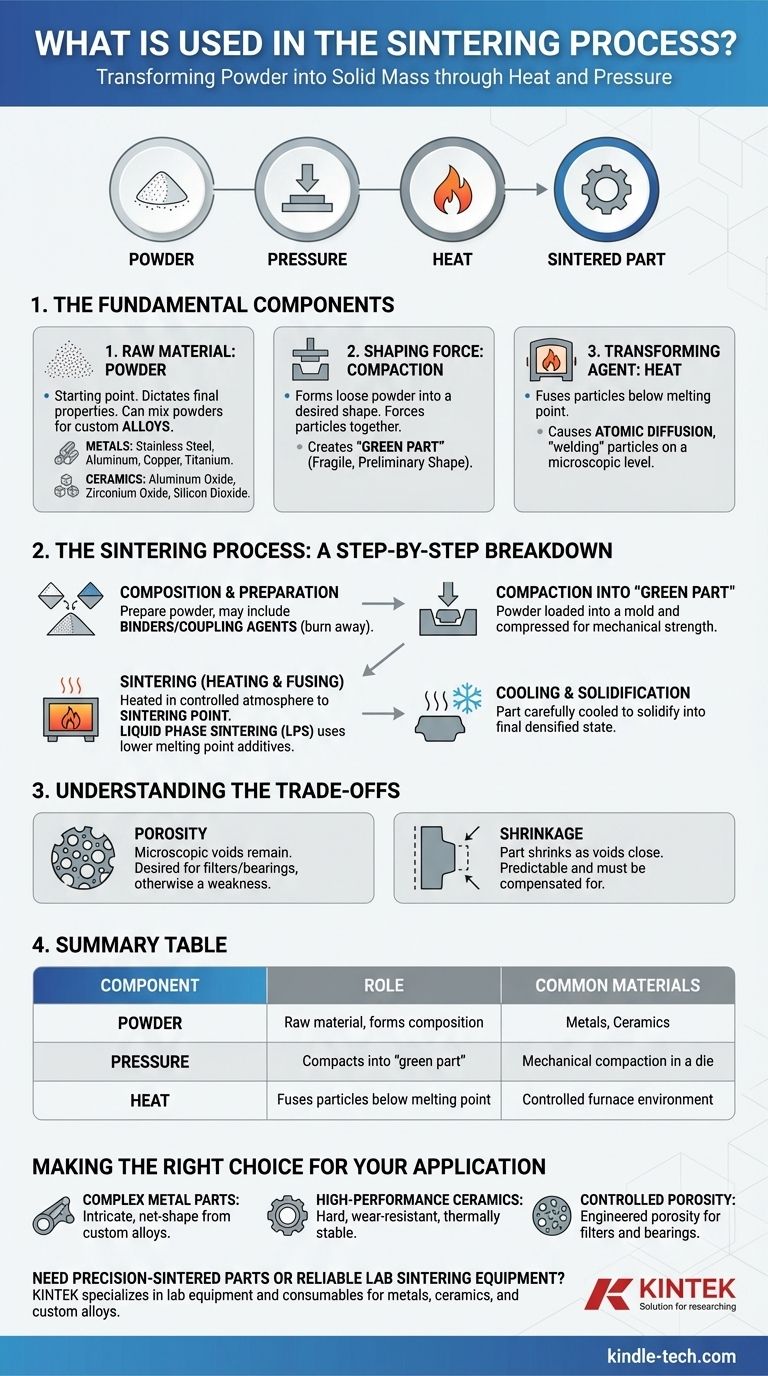
The Fundamental Components of Sintering
Sintering is best understood as a system with three primary components: the raw material, the shaping force, and the transforming agent.
The Raw Material: Powder
The starting point for any sintering process is a fine powder. The choice of powder dictates the final properties of the object.
Common materials include metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, copper, nickel, and titanium alloys. A key advantage of sintering is the ability to mix different metal powders to create custom alloys with unique characteristics.
The process is also widely used for ceramics, employing materials like aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, silicon dioxide, and iron oxide to create hard, heat-resistant components.
The Shaping Force: Compaction
Before heating, the loose powder must be formed into the desired shape. This is achieved through mechanical compaction.
The powder is placed into a die or mold and subjected to high pressure. This process, often called cold or hot mold pressing, forces the particles into close contact, creating a fragile, preliminary shape known as a "green part."
The Transforming Agent: Heat
Heat is the critical agent that transforms the compressed powder into a dense, solid object.
The green part is heated in a controlled environment, such as a kiln or furnace, to a temperature below the material's melting point. This heat provides the energy for atoms to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, effectively welding them together on a microscopic level.
The Sintering Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
While the components are simple, the process itself is a sequence of carefully controlled stages.
Stage 1: Composition and Preparation
This initial step involves preparing the raw powder. It may be a single material or a precise mixture of different powders to form an alloy.
Often, organic additives like binders or coupling agents are mixed in. These additives help the particles hold their shape during compaction and are designed to burn away cleanly during the heating stage.
Stage 2: Compaction into a 'Green Part'
The prepared powder mix is loaded into a mold and compressed. The goal is to create a green part with enough mechanical strength to be handled and moved to the furnace. The density of this green part is a critical factor for the final outcome.
Stage 3: Sintering (Heating and Fusing)
The green part is placed in a furnace with a controlled atmosphere (e.g., vacuum or inert gas to prevent oxidation). The temperature is raised to the sintering point, where the particles begin to fuse.
In some cases, Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS) is used. This involves adding a material with a lower melting point, which becomes liquid and accelerates the diffusion and bonding between the primary powder particles.
Stage 4: Cooling and Solidification
After being held at the sintering temperature for a specific duration, the part is carefully cooled. As it cools, it solidifies into its final, unified, and densified state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is a powerful technique, but it comes with specific considerations that must be managed for a successful outcome.
Porosity
Because the material is not fully melted, microscopic voids, or porosity, can remain in the final part. In some applications, like filters or self-lubricating bearings, this is a desired feature. In others, it can be a structural weakness that must be minimized through precise control of pressure, temperature, and material composition.
Shrinkage
As the particles fuse and the voids between them close, the overall part will shrink. This dimensional change is predictable but must be accurately calculated and compensated for in the initial mold design to ensure the final part meets its required specifications.
Process Control
The quality of a sintered part depends on extremely tight process control. Factors like the atmosphere inside the furnace, the thickness of the material layer, heating and cooling rates, and machine speed must be monitored and regulated to ensure consistent results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the goal of your component is key to leveraging the sintering process effectively.
- If your primary focus is complex metal parts: Sintering allows for the creation of intricate, net-shape components from custom alloys that would be costly or impossible to machine.
- If your primary focus is high-performance ceramics: This process is ideal for manufacturing hard, wear-resistant, and thermally stable parts from materials like zirconia or alumina for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is components with controlled porosity: Sintering is one of the few manufacturing methods that allows you to engineer a specific level of porosity into a material, creating products like filters and bearings.
Ultimately, sintering provides a remarkable level of control over a material's final form and microstructure, directly from its powdered state.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Sintering Process | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Powder | Raw material that forms the final part's composition | Metals (steel, aluminum, titanium), Ceramics (alumina, zirconia) |
| Pressure | Compacts powder into a 'green part' for handling | Applied via mechanical compaction in a die/mold |
| Heat | Fuses particles together below melting point | Controlled furnace environment (vacuum, inert gas) |
Need precision-sintered parts or reliable lab sintering equipment? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for sintering metals, ceramics, and custom alloys. Our expertise ensures you get durable, complex components with controlled material properties. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability



















