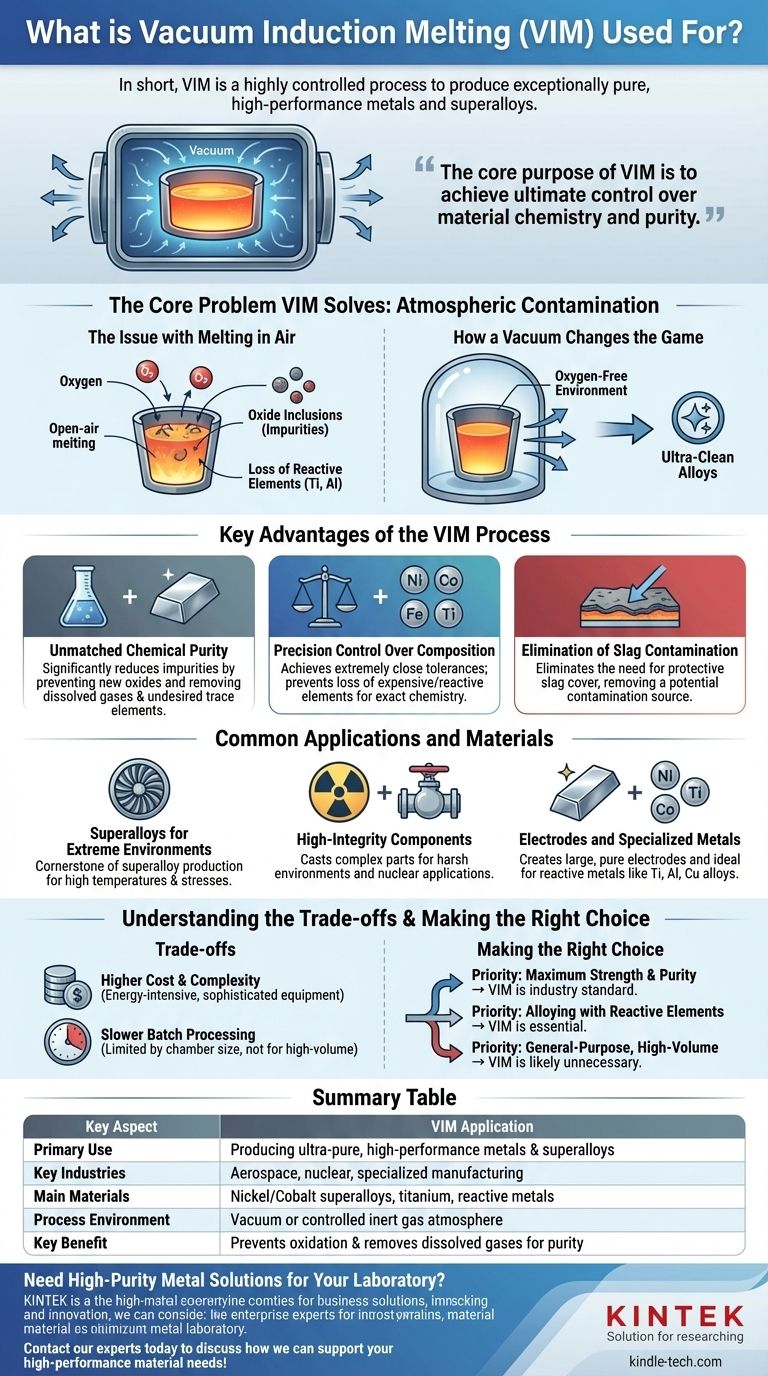
In short, Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) is a highly controlled process used to produce exceptionally pure, high-performance metals and superalloys. Its primary applications are in manufacturing mission-critical components for the world's most demanding industries, including aerospace, nuclear, and specialized manufacturing.
The core purpose of Vacuum Induction Melting is not simply to melt metal, but to achieve ultimate control over the material's chemistry and purity. By removing the reactive atmosphere, VIM creates the ultra-clean alloys required for components where failure is not an option.
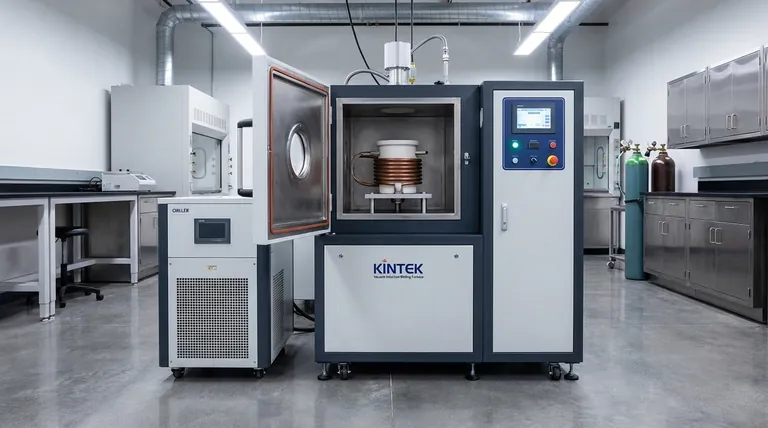

The Core Problem VIM Solves: Atmospheric Contamination
To understand the value of VIM, you must first understand the fundamental problem with melting metal in the open air.
The Issue with Melting in Air
When metals are melted in the presence of oxygen, they react. This process, known as oxidation, creates non-metallic impurities (oxide inclusions) that weaken the final material.
Furthermore, reactive and expensive alloying elements like titanium and aluminum can be lost to oxidation, making it difficult to achieve a precise chemical composition.
How a Vacuum Changes the Game
Vacuum Induction Melting takes place inside a sealed chamber where the air has been removed. By operating in a vacuum or a controlled inert gas environment, the process fundamentally solves the problem of atmospheric contamination.
This oxygen-free environment prevents oxidation, protecting the integrity of the melt and ensuring the final product is as pure as possible.
Key Advantages of the VIM Process
The controlled environment of VIM provides several distinct and critical advantages over conventional melting techniques.
Unmatched Chemical Purity
The primary benefit is the significant reduction in impurities. The vacuum not only prevents the formation of new oxides but also helps remove dissolved gases (like oxygen and nitrogen) and undesired trace elements from the molten metal.
This results in a cleaner, stronger, and more reliable final alloy.
Precision Control Over Composition
Without the threat of oxidation, manufacturers can achieve extremely close compositional tolerances. Expensive and reactive elements are not lost, allowing for the creation of complex alloys with exact, repeatable chemistry.
This level of precision is essential for materials like superalloys, where even minor deviations can compromise performance at high temperatures.
Elimination of Slag Contamination
Many conventional melting processes require a protective layer of slag to shield the molten metal from the air. This slag can sometimes become trapped in the final casting, creating a significant impurity.
VIM eliminates the need for a protective slag cover, thereby removing another potential source of contamination.
Common Applications and Materials
The unique benefits of VIM make it the preferred method for producing a range of high-performance materials.
Superalloys for Extreme Environments
VIM is the cornerstone of superalloy production. These nickel, cobalt, or iron-based alloys are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and stresses, making them essential for parts like aircraft turbine blades and engine components.
High-Integrity Components
The process is used to cast complex, high-integrity parts for harsh environments. This includes specialized valves for the chemical industry and critical components for nuclear applications, where material reliability is paramount.
Electrodes and Specialized Metals
VIM is also used to create large, pure electrodes that are then re-melted in subsequent processes to produce even more refined materials. It is also ideal for melting special reactive metals like titanium and certain aluminum or copper-based alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While VIM offers unparalleled quality, it is a specialized process with specific considerations.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Creating and maintaining a vacuum is energy-intensive and requires sophisticated equipment. As a result, VIM is significantly more expensive and complex than standard air-melting processes. It is reserved for applications where the cost is justified by the required performance.
Slower Batch Processing
VIM is a batch process, limited by the size of the vacuum chamber. This makes it less suitable for the high-volume, continuous production of common metals, where cost-per-ton is the primary driver.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether VIM is necessary depends entirely on the performance requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum material strength and purity for mission-critical parts: VIM is the undisputed industry standard for achieving the necessary quality.
- If your primary focus is alloying with highly reactive elements like titanium or aluminum: VIM is essential to prevent these valuable elements from being lost to oxidation.
- If your primary focus is producing general-purpose metals at high volume and low cost: VIM is likely unnecessary, and more conventional melting processes are far more economical.
Ultimately, choosing Vacuum Induction Melting is a strategic decision to prioritize material perfection over production cost.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | VIM Application |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Producing ultra-pure, high-performance metals and superalloys |
| Key Industries | Aerospace, nuclear, specialized manufacturing |
| Main Materials | Nickel/Cobalt superalloys, titanium, reactive metals |
| Process Environment | Vacuum or controlled inert gas atmosphere |
| Key Benefit | Prevents oxidation and removes dissolved gases for maximum purity |
Need High-Purity Metal Solutions for Your Laboratory?
At KINTEK, we understand that material purity is critical for mission-critical applications. Our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed to support advanced processes like vacuum induction melting, ensuring you achieve the precise chemical composition and ultra-clean alloys your research demands.
Whether you're developing superalloys for aerospace components or working with reactive metals, KINTEK provides the reliable equipment and expertise to help you succeed.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your high-performance material needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals



















