In short, vapor deposition is a family of processes used to apply very thin, high-performance coatings to a surface. It works by converting a source material into a gas (a vapor), transporting that vapor, and then allowing it to condense onto a target object (the substrate) as a solid film.
The fundamental difference between vapor deposition methods lies in how the material is turned into a vapor and how it forms a film. Some methods physically vaporize a solid source, while others use chemical reactions between gases to create a new material directly on the surface.
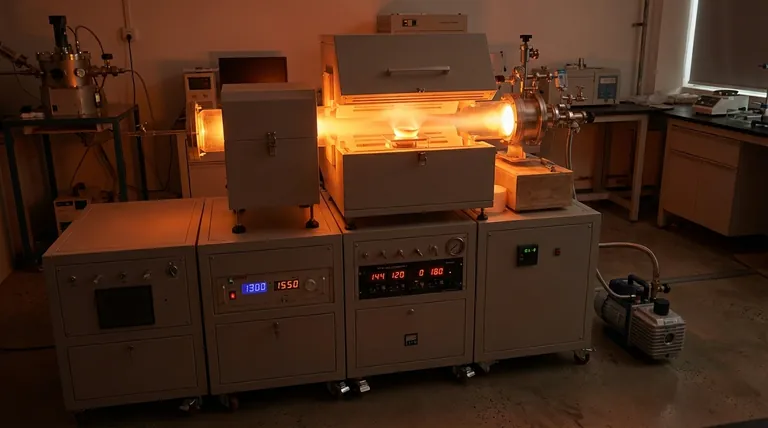

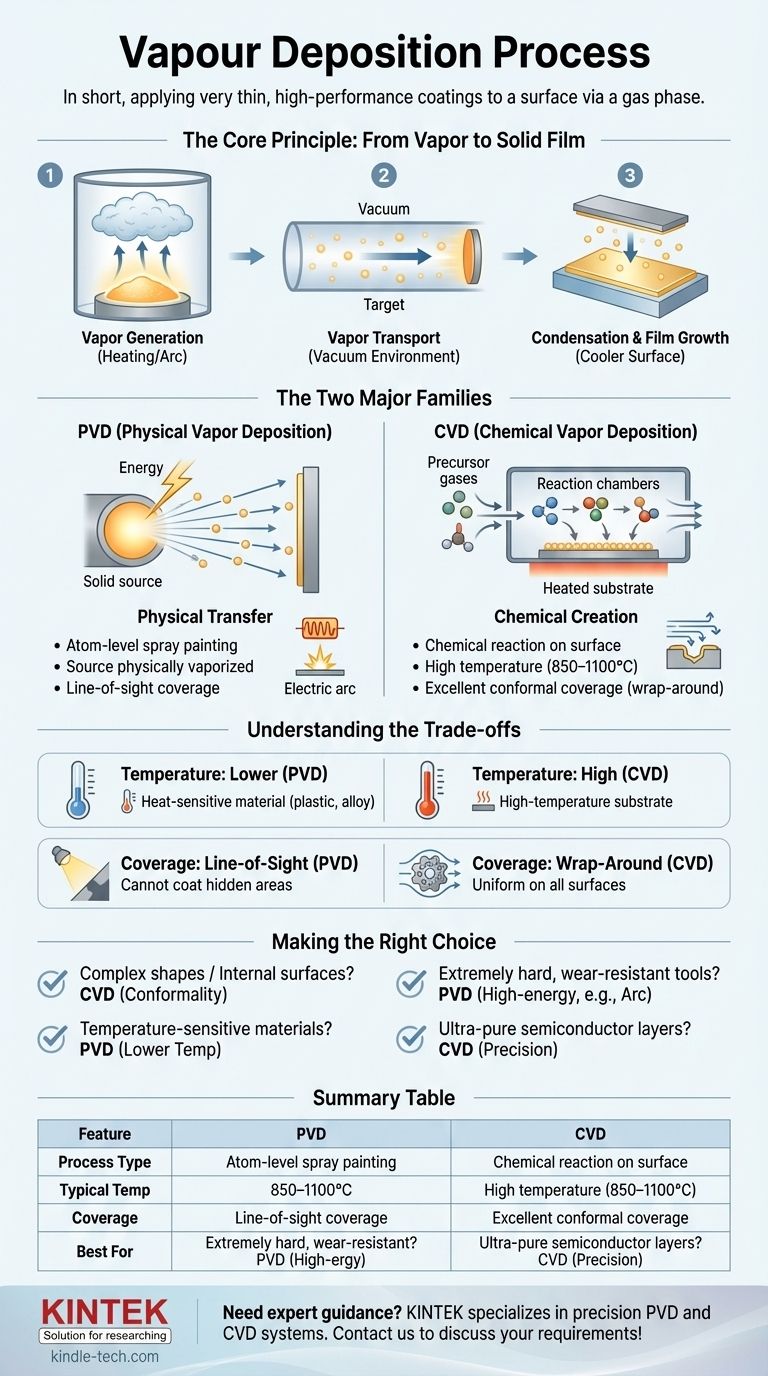
The Core Principle: From Vapor to Solid Film
All vapor deposition techniques, despite their differences, are built on a three-step foundation. Understanding this sequence is key to understanding the entire field.
Step 1: Vapor Generation
The process begins by creating a vapor from the coating material. This can be achieved by heating a solid until it evaporates, using an electric arc to vaporize it, or introducing precursor gases that will later react.
Step 2: Vapor Transport
Once in a gaseous state, the material must travel from its source to the substrate. This typically occurs in a vacuum or a controlled low-pressure environment to prevent contamination and ensure the vapor particles can move freely.
Step 3: Condensation and Film Growth
When the vapor particles reach the cooler surface of the substrate, they condense back into a solid state. They arrange themselves atom by atom, growing into a thin, uniform, and often highly pure film.
The Two Major Families of Vapor Deposition
The "how" of vapor deposition splits the field into two primary categories: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Physical Transfer
In PVD, the coating material is physically transferred from a solid source to the substrate without a fundamental chemical change. Think of it as an atomic-level spray painting process.
The source material is bombarded with energy, causing atoms or molecules to be ejected. These travel through a vacuum and stick to the substrate.
Common PVD methods include:
- Thermal Deposition: A simple method where the source material is heated by an electric heater until it evaporates and condenses on the substrate.
- Arc Vapor Deposition: Uses a powerful, low-voltage electric arc that moves across the source material (cathode). This generates a highly ionized vapor, meaning the atoms have an electric charge, which can be used to accelerate them toward the substrate for an exceptionally dense coating.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A Chemical Creation
In CVD, the film is created by a chemical reaction directly on the substrate's surface. One or more precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber containing the heated substrate.
The gases decompose and react on the hot surface, leaving behind the desired solid material as a film. The byproduct gases are then pumped out.
CVD offers unique advantages, including the ability to grow high-purity crystalline layers and to coat complex shapes evenly due to the nature of gas flow.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between PVD and CVD requires understanding their inherent limitations and strengths. The decision almost always involves a trade-off between temperature, coverage, and the desired film properties.
The Challenge of Temperature
CVD typically requires very high temperatures (often 850–1100°C) for the chemical reactions to occur. This heat can damage or warp many substrate materials, such as plastics or certain metal alloys.
PVD, in contrast, is a lower-temperature process, making it suitable for a much wider range of heat-sensitive substrates.
The Challenge of Coverage (Line-of-Sight)
PVD is generally a line-of-sight process. Like a can of spray paint, it can only coat surfaces it can "see." This makes it difficult to evenly coat complex geometries with holes or internal surfaces.
CVD excels in this area. Because it uses gases that can flow around an object, it provides excellent "wrap-around" coverage (conformality), ensuring even coating thickness on all surfaces.
The Control of Film Properties
Both methods offer excellent control over the final film. CVD parameters can be adjusted to control the chemical composition, crystal structure, and grain size with extreme precision.
Advanced PVD methods like Arc Deposition produce a highly ionized vapor. This allows the film-forming ions to be accelerated with a bias voltage, creating coatings that are exceptionally hard and dense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine whether PVD or CVD is the appropriate technology.
- If your primary focus is coating complex shapes or internal surfaces: CVD is often the superior choice due to its excellent conformality and "wrap-around" capability.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive materials: PVD is the clear choice because it operates at significantly lower temperatures than traditional CVD.
- If your primary focus is creating an extremely hard, dense wear-resistant coating on a tool: High-energy PVD methods like Arc Vapor Deposition are ideal for their ability to create tightly bonded films.
- If your primary focus is growing ultra-pure, perfectly structured semiconductor layers: CVD is the foundational technology of the electronics industry for this exact purpose.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to select the precise deposition tool needed to achieve your engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical transfer (evaporation/sputtering) | Chemical reaction on substrate surface |
| Typical Temperature | Lower temperature | High temperature (850–1100°C) |
| Coverage | Line-of-sight | Excellent conformal coverage |
| Best For | Heat-sensitive materials, hard coatings | Complex shapes, semiconductors |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right vapor deposition solution for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision PVD and CVD systems. Whether you're working with temperature-sensitive substrates or require complex geometric coating, our expertise ensures optimal thin-film performance.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is a major limitation of standard CVD? Solve the Thermal Barrier with Advanced Coating Solutions
- What are the atmosphere control requirements for CVD of silica/SiC nanowires? Master 1100°C Precursor Management
- What is the process of CVD semiconductor? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) method for growing diamonds? Discover Precision Carbon Synthesis
- What is the use of chemical vapor deposition? Create High-Performance Thin Films & Coatings
- What is the difference between chemical vapor transport and chemical vapor deposition? Master Vapor-Phase Material Processing
- What is a thin film coating? Engineer New Surface Properties for Your Substrate



















