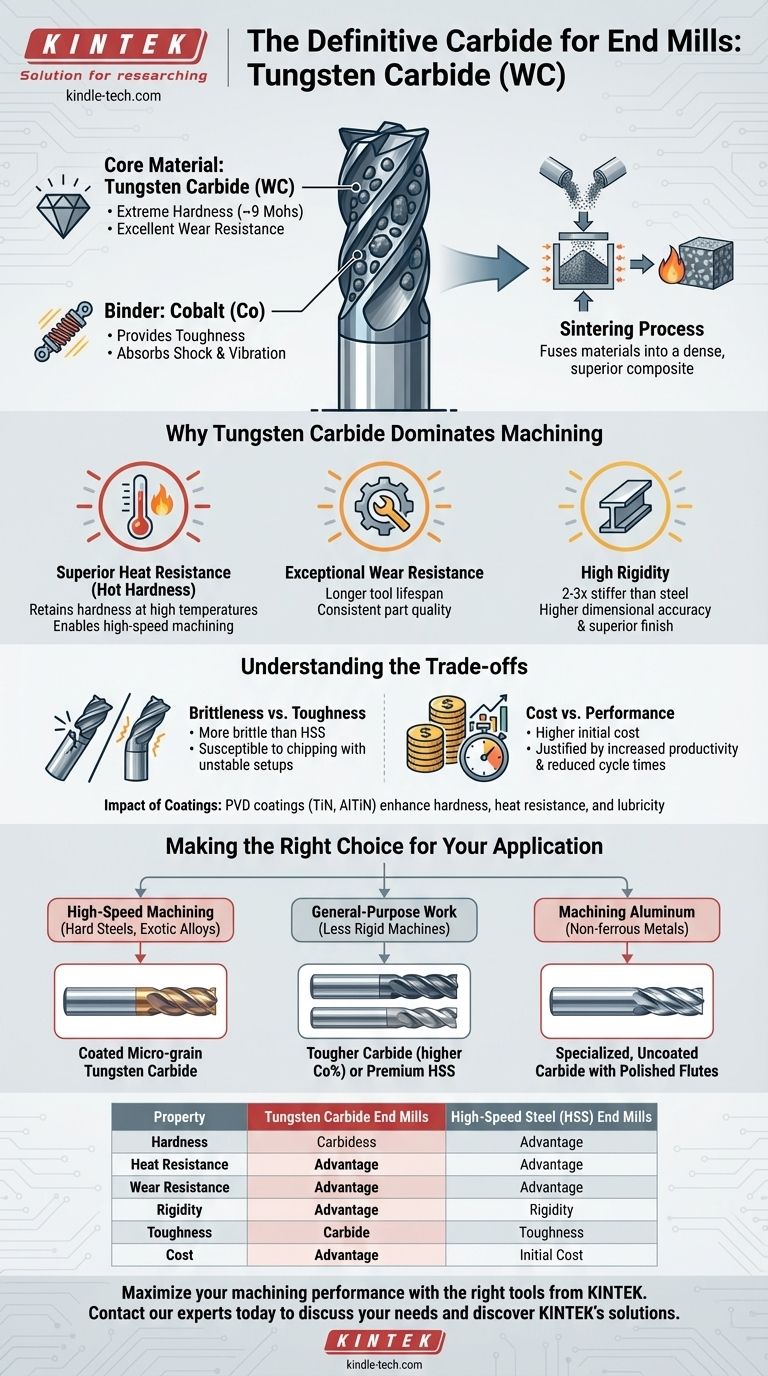
The definitive material used for modern, high-performance end mills is a composite material known as cemented carbide, most commonly tungsten carbide. This material isn't a simple metal but a matrix of extremely hard tungsten carbide (WC) particles held together, or "cemented," by a metallic binder, which is typically cobalt (Co) or sometimes nickel.
The choice of tungsten carbide is not merely about its hardness. It is a strategic decision to leverage a unique combination of heat resistance, wear resistance, and rigidity that unlocks higher speeds, superior precision, and longer tool life in demanding machining operations.

The Composition of a Carbide End Mill
To understand why this material is so effective, you must first understand its two primary components and how they work together.
The Core Material: Tungsten Carbide (WC)
Tungsten carbide particles provide the extreme hardness and wear resistance the tool is known for. On the Mohs scale of hardness, it ranks around 9, just below diamond.
This inherent hardness means the cutting edge stays sharp far longer than steel, even when cutting abrasive or hardened metals.
The Binder: Cobalt (Co)
Pure tungsten carbide is too brittle to be used as a tool on its own. Cobalt is added as a metallic binder that holds the hard carbide grains together.
The cobalt provides toughness, which is the ability to absorb energy and resist chipping or fracturing from the shock and vibration of cutting forces. The percentage of cobalt (typically 3-15%) directly influences the tool's properties.
The Manufacturing Process: Sintering
The powders of tungsten carbide and cobalt are mixed, pressed into the shape of an end mill blank, and heated under pressure in a process called sintering.
This process fuses the materials into a solid, dense composite with properties far superior to either of its constituent parts alone.
Why Tungsten Carbide Dominates Machining
The physical properties of tungsten carbide directly translate to tangible benefits on the shop floor. These advantages are why it has become the industry standard for performance.
Superior Heat Resistance (Hot Hardness)
This is arguably carbide's most important trait. Tungsten carbide retains its hardness at the high temperatures generated during aggressive cutting operations.
Materials like High-Speed Steel (HSS) soften dramatically when hot, forcing you to reduce cutting speeds. Carbide's "hot hardness" enables the high-speed machining that defines modern manufacturing.
Exceptional Wear Resistance
Because the cutting edge does not dull quickly, a single carbide end mill can produce many more parts than an HSS equivalent before needing replacement.
This leads to a longer tool lifespan and more consistent part quality over a production run, as noted by the reduction in equipment wear and increase in work efficiency.
High Rigidity
Carbide is approximately two to three times stiffer than steel. This high modulus of elasticity means the tool deflects very little under load.
Less tool deflection results in higher dimensional accuracy, straighter walls in pockets and slots, and a superior surface finish on the workpiece.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the limitations of carbide is critical for using it effectively and avoiding tool failure.
Brittleness vs. Toughness
The primary trade-off for carbide's extreme hardness is its relative brittleness. Compared to HSS, it is more susceptible to chipping or catastrophic breakage.
This makes it less forgiving of unstable setups, excessive vibration (chatter), or interruptions in the cut, especially in older, less rigid machines.
Cost
Solid carbide end mills are significantly more expensive to purchase than their HSS counterparts. However, this higher initial cost is often justified by increased productivity, longer tool life, and reduced cycle times.
The Impact of Coatings
Many carbide end mills are enhanced with advanced physical vapor deposition (PVD) coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN). These microscopic layers add even more hardness, heat resistance, and lubricity to the tool's surface, further extending its performance envelope.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct end mill requires matching the tool's properties to the material you are cutting and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-speed machining of hard steels, stainless, or exotic alloys: A coated, micro-grain tungsten carbide end mill is the only viable choice for its unmatched heat and wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose work on less rigid machines: A tougher grade of carbide (with a higher cobalt percentage) or a premium HSS tool might be more forgiving and prevent premature tool breakage from chatter.
- If your primary focus is machining aluminum or other soft, non-ferrous metals: A specialized, uncoated carbide end mill with sharp, polished flutes is ideal for preventing material buildup on the cutting edge.
By understanding that a carbide end mill is a precisely engineered composite, you can make more informed decisions to maximize your machining performance.
Summary Table:
| Property | Tungsten Carbide End Mills | High-Speed Steel (HSS) End Mills |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Mohs) | ~9 (Very High) | ~7-8 (High) |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent (Hot Hardness) | Good (Softens at High Temperatures) |
| Wear Resistance | Exceptional (Long Tool Life) | Moderate |
| Rigidity | 2-3x Stiffer than Steel | Less Rigid |
| Toughness | Brittle (Prone to Chipping) | More Forgiving |
| Cost | Higher Initial Cost | Lower Initial Cost |
Maximize your machining performance with the right tools from KINTEK.
As a specialist in high-performance lab and machining equipment, KINTEK provides premium tungsten carbide end mills designed for superior heat resistance, wear resistance, and rigidity. Whether you're machining hard steels, stainless, or exotic alloys, our tools deliver longer life, higher speeds, and consistent precision.
Let us help you select the perfect end mill for your application. Contact our experts today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK’s solutions can enhance your productivity and reduce downtime.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to maintain an argon atmosphere for Cu-Zr-Ti ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Amorphous Alloys
- Why is secondary ball milling necessary for sulfur cathodes? Master Solid-State Electrolyte Composite Preparation
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- How does a laboratory ball mill contribute to the processing of solid polysilanes into coating powders?
- How do you increase production in a ball mill? Optimize Speed, Media, and Feed for Maximum Throughput



















