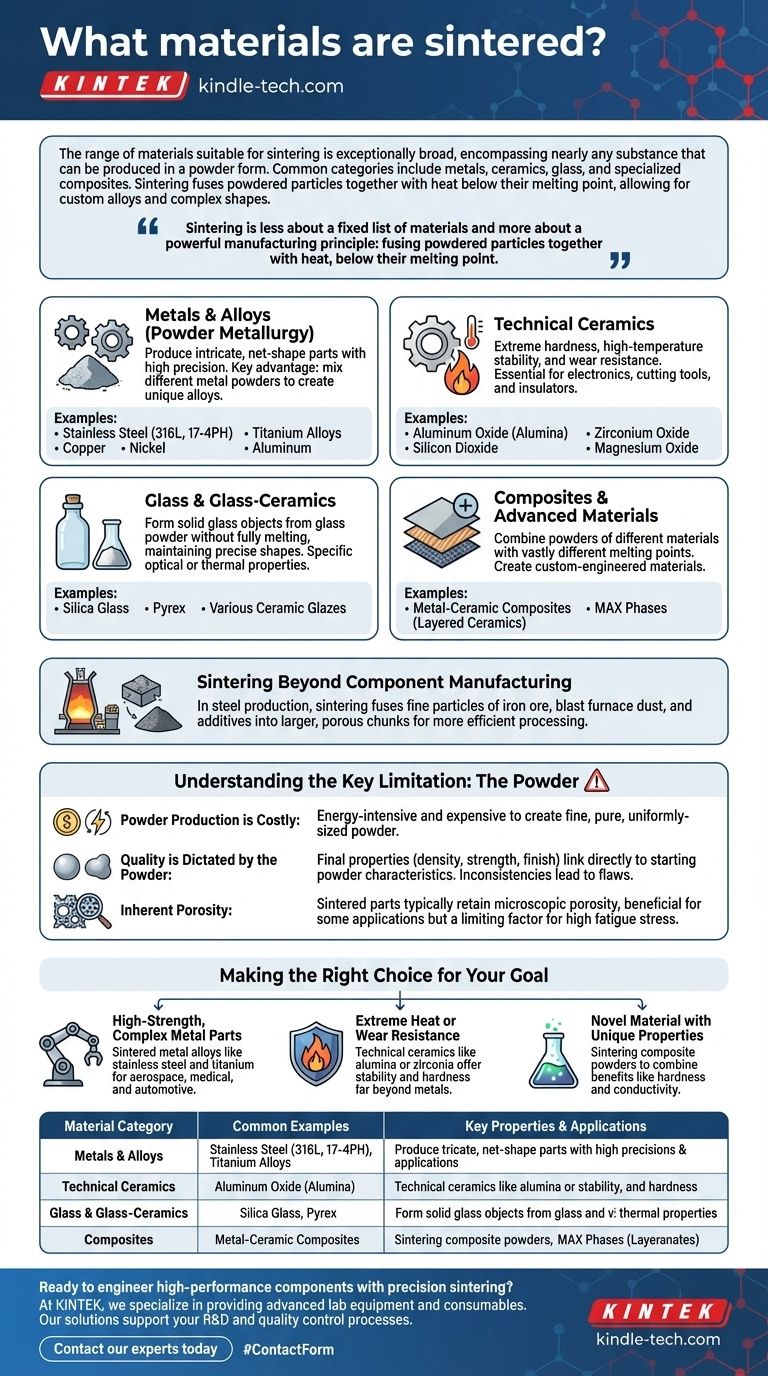
The range of materials suitable for sintering is exceptionally broad, encompassing nearly any substance that can be produced in a powder form. The most common categories include metals, ceramics, glass, and specialized composites. This versatility allows the process to be used for everything from creating high-strength stainless steel components and heat-resistant ceramic parts to processing raw iron ore for steel production.
Sintering is less about a fixed list of materials and more about a powerful manufacturing principle: fusing powdered particles together with heat, below their melting point. This core concept unlocks the ability to create custom alloys, work with high-melting-point materials, and produce complex shapes that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional casting or machining.

The Primary Categories of Sintered Materials
Sintering's flexibility stems from its ability to work with distinct families of materials, each offering unique properties for specific engineering challenges.
Metals and Alloys
This is the most common application of sintering, often referred to as powder metallurgy. By starting with fine metal powders, manufacturers can produce intricate, net-shape parts with high precision.
Common sintered metals include stainless steel (e.g., 316L, 17-4PH), titanium alloys, copper, nickel, and aluminum. A key advantage is the ability to mix different metal powders to create unique alloys not possible through melting.
Technical Ceramics
Ceramics are valued for their extreme hardness, high-temperature stability, and wear resistance. Sintering is the primary method for consolidating them into dense, functional components.
Materials like aluminum oxide (alumina), zirconium oxide, silicon dioxide, and magnesium oxide are frequently sintered. These are essential for applications in electronics, cutting tools, and high-temperature insulators.
Glass and Glass-Ceramics
Sintering can also be used to form solid glass objects from glass powder without fully melting the material, which helps maintain precise shapes.
This includes materials such as silica glass, Pyrex, and various ceramic glazes. The process is used to create components with specific optical or thermal properties.
Composites and Advanced Materials
The true power of sintering is realized when creating composite materials. Because it doesn't rely on melting, powders of different materials with vastly different melting points can be combined.
This allows for the creation of metal-ceramic composites or advanced materials like MAX phases (a class of layered ceramics). These custom-engineered materials deliver a unique combination of properties, such as high strength and good thermal conductivity.
Sintering Beyond Component Manufacturing
While often associated with creating finished parts, sintering is also a critical intermediate step in heavy industry.
Agglomeration of Ores
In steel production, sintering is used to fuse fine particles of iron ore, blast furnace dust, and other additives into larger, porous chunks.
These sintered chunks are then fed into a blast furnace. This process is not about creating a final product but about preparing raw materials for more efficient processing.
Understanding the Key Limitation: The Powder
The versatility of sintering is powerful, but it comes with a fundamental trade-off: the process is entirely dependent on the quality of the initial powdered material.
Powder Production is Costly
Creating fine, pure, and uniformly-sized powder—especially for metals and technical ceramics—is an energy-intensive and expensive process. This can make the raw material for sintering significantly more costly than the bulk ingots used in casting or machining.
Quality is Dictated by the Powder
The final properties of a sintered part, such as its density, strength, and finish, are directly linked to the characteristics of the starting powder. Inconsistent particle size or impurities in the powder will translate directly to flaws in the final component.
Inherent Porosity
Unless secondary processing steps like hot isostatic pressing are used, sintered parts typically retain a small amount of microscopic porosity. While this can be a benefit for applications like self-lubricating bearings, it can also be a limiting factor for components subjected to high fatigue stress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material is about matching its inherent properties with the demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is high-strength, complex metal parts: Sintered metal alloys like stainless steel and titanium are ideal for producing components for the aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat or wear resistance: Technical ceramics like alumina or zirconia offer stability and hardness far beyond what any metal can achieve.
- If your primary focus is creating a novel material with unique properties: Sintering composite powders allows you to combine the benefits of different material classes, such as the hardness of a ceramic with the conductivity of a metal.
By understanding that sintering is a process defined by powder, not a limited list of materials, you can leverage its power to engineer components for nearly any technical challenge.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Properties & Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metals & Alloys | Stainless Steel, Titanium, Copper | High strength, complex shapes, automotive & aerospace parts |
| Technical Ceramics | Alumina, Zirconia | Extreme hardness, heat resistance, wear-resistant components |
| Glass & Glass-Ceramics | Silica Glass, Pyrex | Specific optical/thermal properties, precise shapes |
| Composites | Metal-Ceramic, MAX Phases | Custom properties, combining strength & conductivity |
Ready to engineer high-performance components with precision sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and testing sintered materials. Whether you're working with metal powders for aerospace components, technical ceramics for cutting-edge electronics, or novel composites, our solutions support your R&D and quality control processes.
We understand the critical role of powder quality and sintering parameters in achieving your desired material properties. Let us help you optimize your sintering process for superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's sintering needs and help you bring your material innovations to life.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics



















