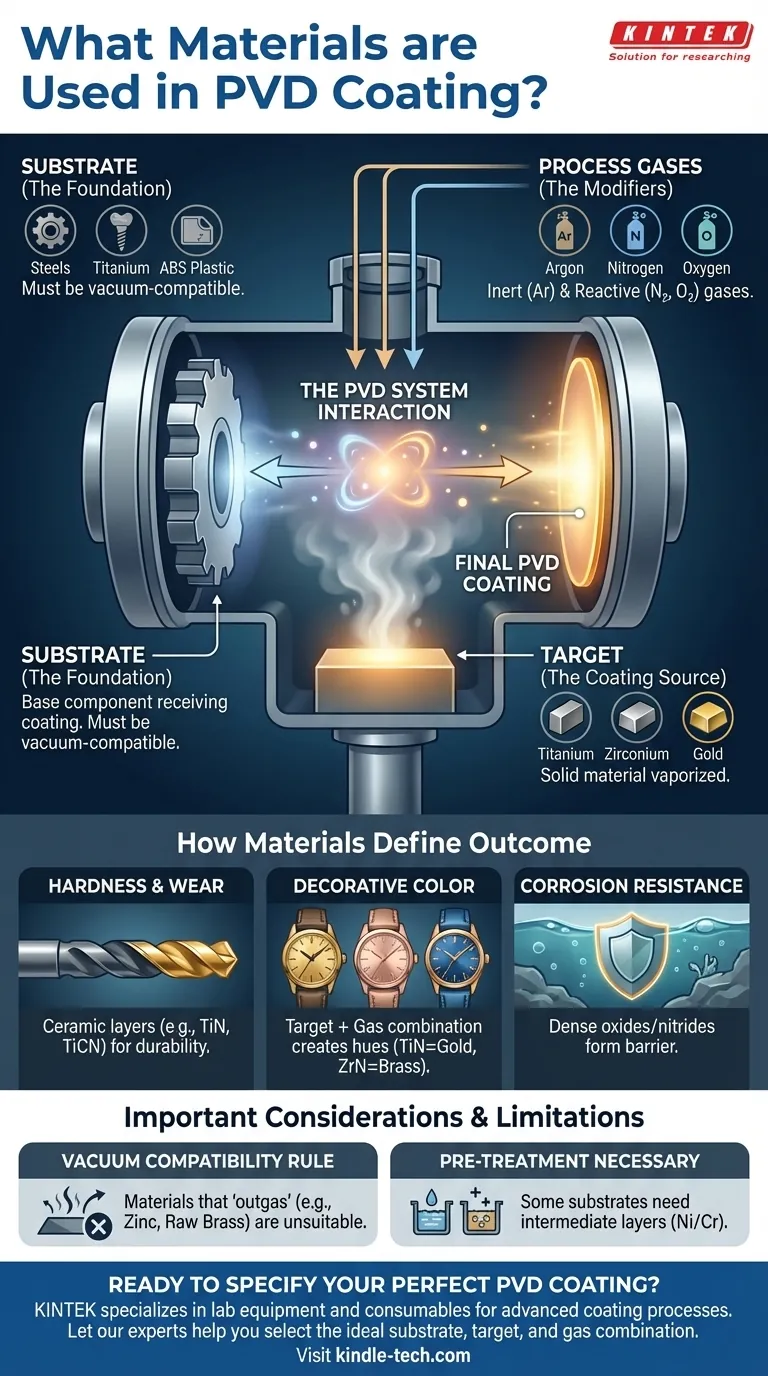
In short, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) utilizes a combination of three material types: the object being coated (the substrate), the solid material being deposited (the target), and the gases used within the vacuum chamber. Common substrates include steels, titanium, and ABS plastic, while common targets are metals like titanium, zirconium, and gold. Gases like nitrogen and oxygen are used to react with the target material to form the final, durable coating.
The core principle to grasp is that PVD is not about a single material, but a system. The final properties of a coated part—its hardness, color, and corrosion resistance—are a direct result of the interaction between the chosen substrate, the vaporized target material, and the reactive gases in the chamber.

The Three Core Material Types in PVD
To understand PVD, you must think in terms of three distinct roles. Each material is selected to contribute to the final goal.
Substrate Materials (The Foundation)
The substrate is the workpiece or component that receives the coating. The primary requirement is that it must be vacuum-compatible, meaning it won't release gases that would contaminate the process.
Common substrates include:
- Steels: Especially high-alloy families like tool steels, high-speed steels, and stainless steels.
- Non-Ferrous Metals: Titanium, aluminum, copper, and their alloys are frequently used.
- Hard Metals: Materials like tungsten carbide benefit immensely from PVD's wear resistance.
- Plated or Treated Materials: Substrates like brass or zinc are often pre-plated with nickel and chromium to make them suitable for PVD.
- Other Materials: Certain polymers like ABS plastic and even glass can be coated after proper surface preparation.
Target Materials (The Coating Source)
The target is a block of high-purity solid material that is vaporized by an energy source (like an arc or a sputter gun) inside the vacuum chamber. This vapor is what travels and deposits onto the substrate.
Popular target materials include:
- Titanium (Ti): Extremely versatile and widely used for creating gold-colored (TiN) or gray (TiCN) hard coatings.
- Zirconium (Zr): Often used to produce coatings with a pale yellow or brass-like appearance (ZrN).
- Chromium (Cr): A standard for hard, corrosion-resistant, and decorative silver-colored coatings.
- Gold (Au): For applications requiring a true gold finish, targets of 9k to 24k gold can be used.
Process Gases (The Modifiers)
Gases are introduced into the chamber to either facilitate the process or chemically react with the vaporized target material.
- Inert Gases: Argon (Ar) is almost always used. It is bombarded at the target to dislodge atoms (sputtering) and helps sustain the plasma in the chamber without reacting chemically.
- Reactive Gases: These gases combine with the metal vapor to form new ceramic compounds on the substrate's surface. This is the key to creating specific properties.
- Nitrogen (N₂): Reacts with metal vapor to form hard nitrides (e.g., Titanium Nitride, TiN).
- Oxygen (O₂): Creates highly stable and corrosion-resistant oxides.
- Hydrocarbon Gases (e.g., Acetylene, C₂H₂): Introduce carbon to form extremely hard carbonitrides (e.g., TiCN) or diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings.
How Materials Define the Outcome
The combination of substrate, target, and gas is a precise recipe engineered to achieve a specific result.
For Hardness and Wear Resistance
The goal here is to form a hard ceramic layer. For example, a titanium target combined with nitrogen gas deposits a Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating. When applied to a Ti-6Al-4V alloy substrate, this coating can significantly increase the part's fatigue limit and endurance.
For Decorative Color and Finish
Color is a direct function of the compound formed. By changing the reactive gas or target material, a wide palette becomes available.
- Titanium Nitride (TiN) produces a classic gold color.
- Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) creates a light brass or champagne gold color.
- Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) can range from a bluish-gray to a modern rose gold, depending on the gas mixture.
For Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Coatings like oxides and nitrides form a dense, non-reactive barrier between the substrate and the environment. This is why PVD-coated stainless steel or titanium parts are exceptionally resistant to rust, tarnish, and chemical attack.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. The material constraints are critical to understand.
The Vacuum-Compatibility Rule
This is the most important limitation. Materials that "outgas" under vacuum are unsuitable because they poison the chamber and ruin the coating.
- Galvanized materials (zinc-plated) are generally not used because the zinc will vaporize at low temperatures.
- Raw brass can also outgas, which is why it is almost always plated with a barrier layer of nickel-chromium before PVD is applied.
Pre-Treatment is Often Necessary
Some materials, like the aforementioned brass or plastics, cannot be coated directly. They require an intermediate layer, typically electroplated nickel and/or chromium, to provide a stable, vacuum-compatible surface for the PVD coating to adhere to.
The Coating is a Surface, Not a Bulk Change
PVD creates an exceptionally hard thin film, but it relies entirely on the strength of the underlying substrate. A hard coating on a soft substrate can crack or fail if the part itself deforms under load. The substrate must be strong enough for the intended application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right materials is about matching them to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: Opt for nitride or carbonitride coatings (from Ti, Cr, or Zr targets) on a high-strength substrate like tool steel or a titanium alloy.
- If your primary focus is a specific decorative color: Choose your target and reactive gas based on the desired hue and apply it to a substrate with good surface finish, like polished stainless steel or nickel-chrome plated parts.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and corrosion resistance: Use titanium or zirconium-based coatings on medical-grade stainless steel or titanium substrates to create a safe, inert surface.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between substrate, target, and gas is the key to unlocking the full potential of PVD technology for your project.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Steels, Titanium, ABS Plastic | The base component receiving the coating |
| Target | Titanium, Zirconium, Gold | The source material vaporized to form the coating |
| Gases | Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon | Reacts with target vapor to create the final coating properties |
Ready to specify the perfect PVD coating for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced coating processes. Our experts can help you select the ideal substrate, target, and gas combination to achieve the precise hardness, color, and corrosion resistance your project demands.
Contact our team today for a consultation and discover how our solutions can enhance your product's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- Are CVD diamonds worth it? Unlock Brilliant Value & Ethical Clarity
- What is the CVD method for synthetic diamonds? Grow Lab Diamonds from Gas with Precision
- How does PVD differ from CVD? Choosing the Right Thin-Film Coating Process
- How long does it take to process a CVD diamond? A Guide to the 2-4 Week Growth Cycle
- Why is CVD better than PVD? Achieve Superior, Uniform Coatings on Complex Geometries



















