Practically any metal can be melted with induction heating, from common industrial metals like iron and aluminum to precious metals like gold and platinum. The technology is also capable of melting high-performance superalloys and refractory metals that require extremely high temperatures. The key determining factor is not the type of metal, but its ability to conduct electricity.
Induction melting is not limited to a specific list of metals but is instead based on a fundamental physical property: electrical conductivity. If a material can conduct electricity, it can be heated and melted via induction, making the process exceptionally versatile for ferrous, non-ferrous, precious, and highly reactive alloy systems.

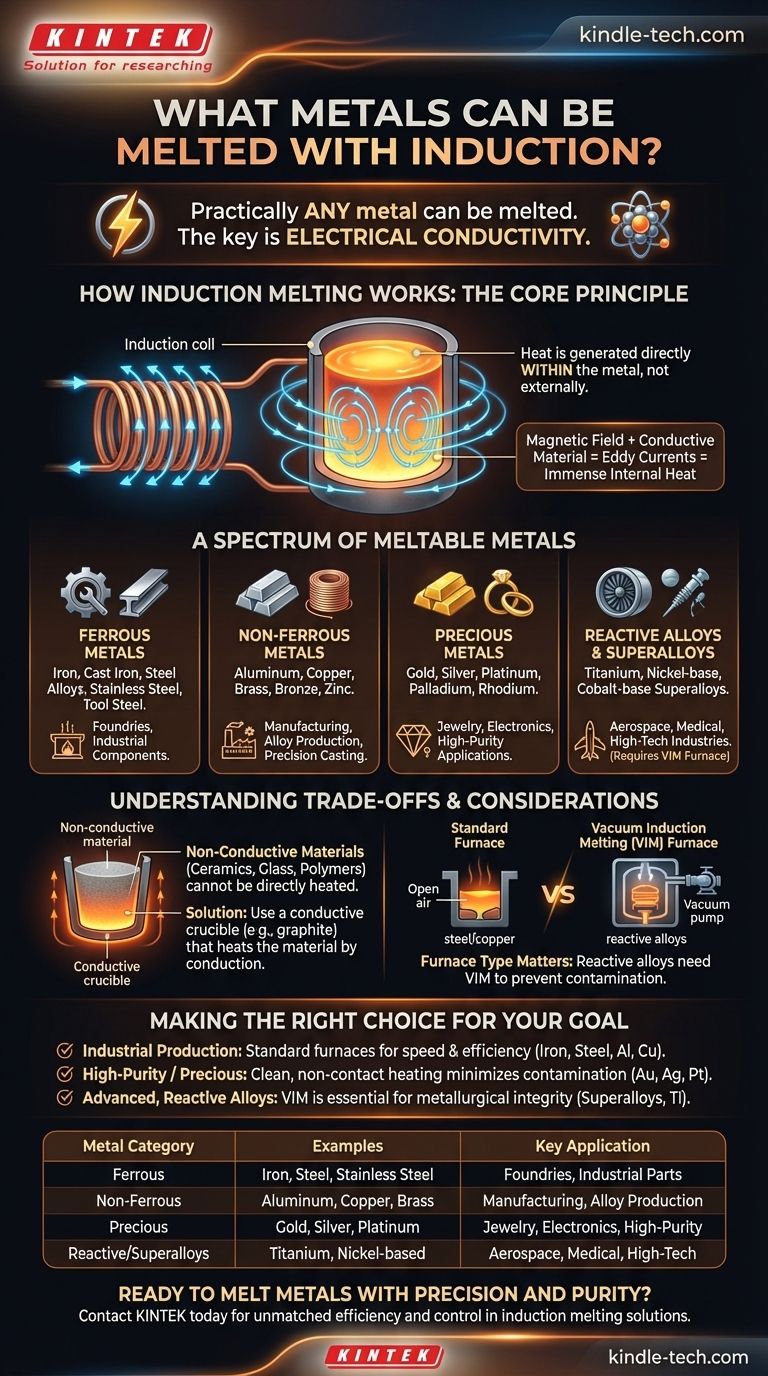
How Induction Melting Works: The Core Principle
To understand which metals can be melted, we must first understand how the process works. Induction heating is a non-contact method that uses fundamental physics to generate heat directly within the material itself.
The Role of Electrical Conductivity
An induction coil generates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When an electrically conductive material, like a metal, is placed inside this field, the field induces electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Creating Heat from Within
The resistance of the metal to the flow of these eddy currents generates immense heat. This is the same principle behind the heating element in an electric stove, but it happens inside the metal itself without any external flame or heating element. This internal heating is fast, clean, and highly efficient.
A Spectrum of Meltable Metals
Because the only real requirement is electrical conductivity, induction is suitable for a vast range of metals and alloys, often categorized by their application and properties.
Ferrous Metals (Iron and Steel)
This is one of the most common applications for induction furnaces. The technology is used extensively for melting iron, cast iron, and various steel alloys, including stainless steel, tool steel, and ultra-high strength steel. It is a cornerstone of modern foundries for producing high-quality steel components.
Non-Ferrous Metals
Induction is highly effective for melting common non-ferrous metals. These include pure metals and their alloys like copper, aluminum, brass (copper-zinc), and bronze (copper-tin). The process allows for precise temperature control, which is critical for maintaining alloy integrity.
Precious Metals
The clean, non-contact nature of induction heating makes it ideal for high-value materials where purity is paramount. It is widely used for melting gold, silver, platinum, palladium, and rhodium. Because the heat is generated within the metal itself, there is a lower risk of contamination from the crucible or atmosphere.
High-Performance and Reactive Alloys
For advanced applications in aerospace or medical industries, special alloys are required. A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is used for these materials. The vacuum prevents highly reactive metals from being contaminated by oxygen and nitrogen. This includes nickel-base, cobalt-base, and iron-base superalloys as well as other materials with a high affinity for atmospheric gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While incredibly versatile, the effectiveness of induction melting is not universal across all materials and depends on the right equipment.
The Conductivity Requirement
The primary limitation of induction is that it cannot directly heat non-conductive materials. Materials like ceramics, glass, or polymers do not respond to the magnetic field. However, they can be melted inside a conductive crucible (like graphite), where the crucible is heated by induction and then transfers its heat to the non-conductive material.
The Importance of Furnace Type
The specific metal dictates the type of induction furnace required. A standard furnace is perfect for steel or copper, but melting reactive alloys like titanium or superalloys demands a VIM furnace to protect them from atmospheric contamination. The furnace's power, frequency, and design must be matched to the metal's properties and the volume being melted.
Furnace Size and Material Shape
The efficiency of induction heating is influenced by the size, shape, and mass of the material being heated. The magnetic field must be able to couple effectively with the charge. This is why induction works well for everything from tiny amounts of gold powder to massive scrap steel recycling operations, but the equipment for each is vastly different.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best approach depends entirely on the material you are working with and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is industrial production of common metals: Standard induction furnaces offer unmatched speed and efficiency for melting iron, steel, copper, and aluminum.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or precious metals: The clean, non-contact, and precise nature of induction heating is ideal for gold, silver, and platinum, as it minimizes contamination and material loss.
- If your primary focus is advanced, reactive alloys: A vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure the metallurgical integrity of superalloys and other sensitive materials.
Ultimately, the versatility of induction melting stems from its reliance on a fundamental property of metals, making it a cornerstone of modern metallurgy.
Summary Table:
| Metal Category | Examples | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Iron, Steel, Stainless Steel | Foundries, Industrial Parts |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Aluminum, Copper, Brass, Bronze | Manufacturing, Alloy Production |
| Precious Metals | Gold, Silver, Platinum, Palladium | Jewelry, Electronics, High-Purity Applications |
| Reactive Alloys & Superalloys | Titanium, Nickel-based Alloys | Aerospace, Medical, High-Tech Industries |
Ready to melt metals with precision and purity? Whether you're working with common alloys, precious metals, or advanced superalloys, KINTEK's induction melting solutions deliver unmatched efficiency, cleanliness, and control. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right furnace for your specific metal and application. Contact us today to discuss your melting needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory or production process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















