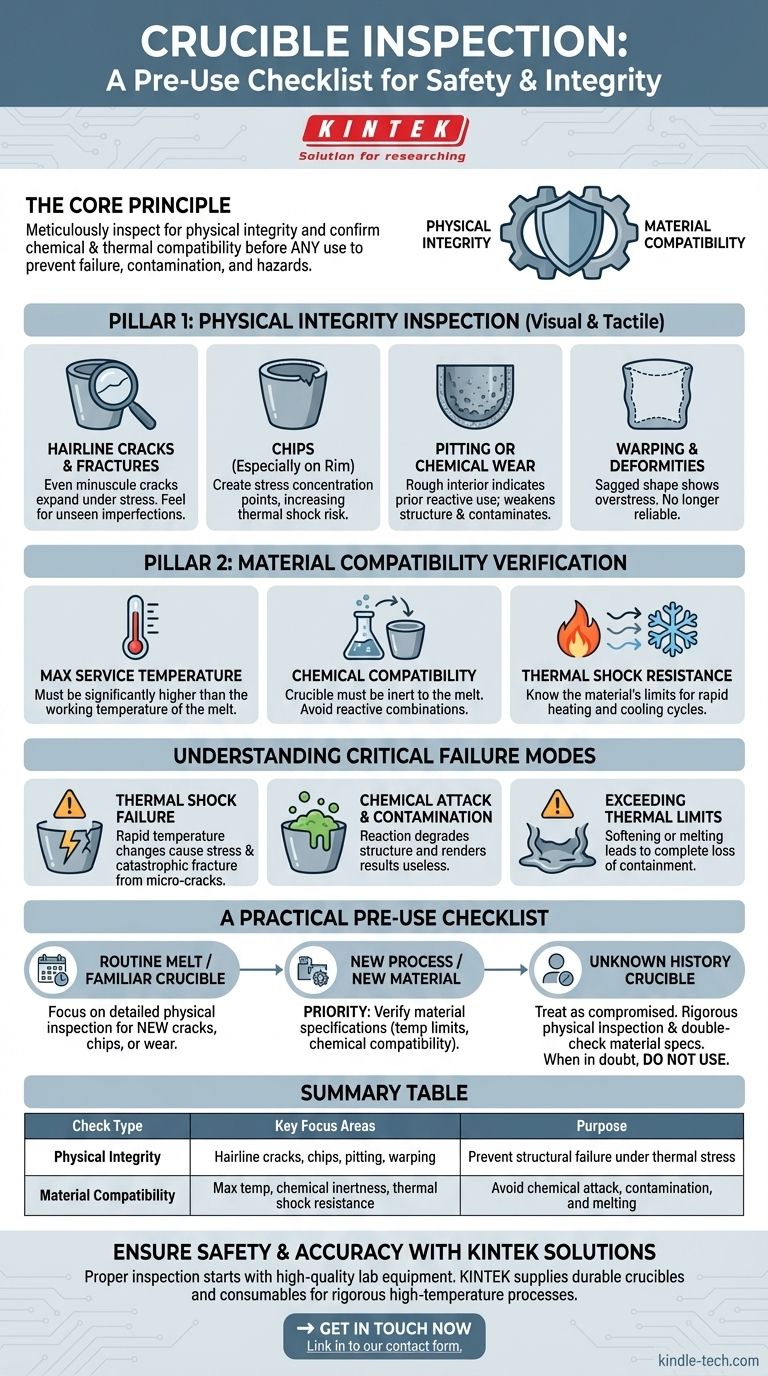
Before any use, a crucible must be meticulously inspected for physical integrity and confirmed for chemical and thermal compatibility with the materials to be heated. This two-part check ensures the crucible will not crack, break, or react during the process, which could lead to catastrophic failure, sample contamination, and significant safety hazards.
The core principle of a pre-use check is not just to spot existing damage, but to proactively confirm that the crucible's material properties are fundamentally suited for the specific temperature and chemical environment of your work. Failure on either front compromises both safety and results.

The Two Pillars of a Crucible Check
A thorough inspection is a non-negotiable step that can be divided into two distinct but equally important areas: assessing the physical condition and verifying the material's suitability for the task.
Pillar 1: Physical Integrity Inspection
This is a hands-on visual and tactile examination to find any defects that could lead to structural failure under the extreme stress of heating and cooling.
Look for hairline cracks or fractures. Even minuscule cracks can rapidly expand under thermal stress, causing the crucible to break apart mid-process. Run a gloved finger along the surfaces to feel for imperfections you cannot see.
Check for chips, especially around the rim. Chips and other surface damage create stress concentration points, making the crucible more susceptible to cracking from thermal shock.
Examine the interior for signs of pitting or chemical wear. A surface that is no longer smooth may indicate that the crucible was previously used with a reactive material. This degradation weakens the crucible and can contaminate your current melt.
Confirm the crucible has no structural warping or deformities. If a crucible has sagged or changed shape from a previous use, it has been stressed beyond its limits and is no longer reliable.
Pillar 2: Material Compatibility Verification
This step involves confirming that the crucible's material is appropriate for your specific process. Using the wrong type of crucible is a primary source of failure and contamination.
Ensure the crucible's maximum service temperature is well above your planned working temperature. The material must have a melting point significantly higher than the substance it will hold.
Verify its chemical compatibility with your melt. For example, a graphite crucible is excellent for many metals but will react with materials that form carbides. A ceramic crucible might be inert to one chemical but react violently with another.
Consider its resistance to thermal shock. Some materials, like fused silica, handle rapid temperature changes very well, while others require a slow, controlled heating and cooling cycle to prevent cracking. Know the properties of your specific crucible.
Understanding Critical Failure Modes
Failing to properly inspect a crucible can lead to several predictable and dangerous outcomes. Understanding these risks highlights the importance of the pre-use check.
Thermal Shock Failure
This is the most common cause of crucible failure. When a crucible is heated or cooled too quickly, different parts expand or contract at different rates, creating immense internal stress. A pre-existing micro-crack acts as a weak point, allowing a catastrophic fracture to occur.
Chemical Attack and Contamination
If the crucible material is not inert to the melt, a chemical reaction will occur. This reaction simultaneously degrades the crucible's structure and contaminates your material, rendering your results useless.
Exceeding Thermal Limits
Operating a crucible above its specified maximum temperature will cause it to soften, deform, or even melt. This leads to a complete loss of containment and a significant safety risk from spilled molten material.
A Practical Pre-Use Checklist
Apply these checks to ensure the integrity of your process. Your focus may shift slightly depending on the context of the work.
- If you are performing a routine melt with a familiar crucible: Your primary focus should be on a detailed physical inspection for any new cracks, chips, or wear that has developed since the last use.
- If you are starting a new process or using a new material: Your priority is to verify the crucible's material specifications. Confirm its temperature limits and chemical compatibility with your new substance before anything else.
- If you are using a crucible with an unknown history: Treat it as potentially compromised. Perform the most rigorous physical inspection possible and double-check its material type against your process requirements. If in doubt, do not use it.
A few moments spent on a diligent inspection are the foundation of a safe, successful, and accurate high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Check Type | Key Focus Areas | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Integrity | Hairline cracks, chips, pitting, warping | Prevent structural failure under thermal stress |
| Material Compatibility | Max service temperature, chemical inertness, thermal shock resistance | Avoid chemical attack, contamination, and melting |
Ensure your lab's safety and accuracy with the right equipment from KINTEK.
Proper crucible inspection is critical, but it starts with using high-quality, reliable lab equipment. KINTEK specializes in supplying durable crucibles and a full range of lab equipment and consumables designed to meet the rigorous demands of your high-temperature processes.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect crucible for your specific application, material, and temperature requirements. Let us help you build a foundation for safe and successful results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis



















