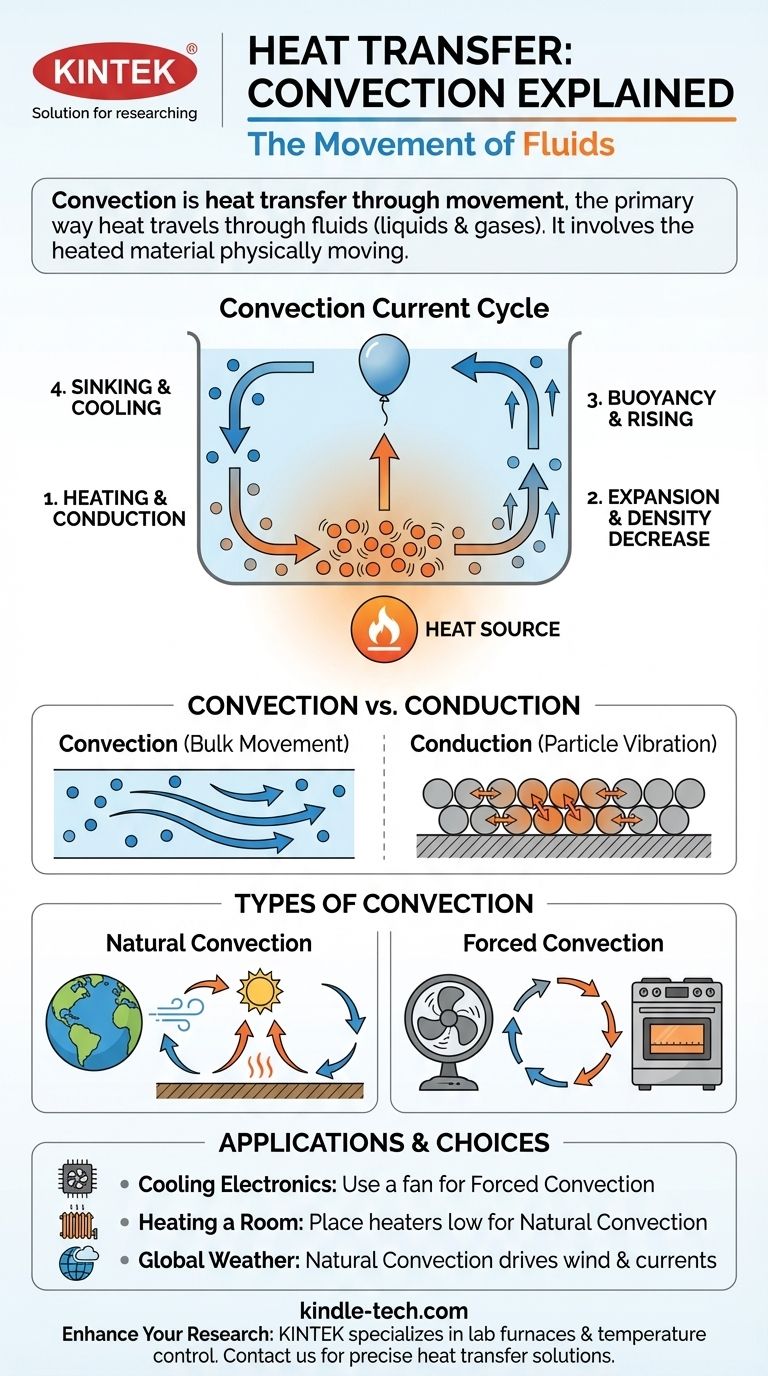
In simple terms, convection is heat transfer through movement. It is the primary way heat travels through fluids—liquids and gases. Unlike other forms of heat transfer, convection involves the heated material itself physically moving from a warmer area to a cooler one, carrying its thermal energy with it.
The crucial difference between convection and other heat transfer methods is the bulk movement of the medium itself. Heat is transported not just by molecular vibrations, but by the large-scale flow of the liquid or gas, driven by changes in density.

The Fundamental Mechanism: How Convection Works
To understand convection, it is best to visualize it as a cyclical process. This cycle, known as a convection current, is responsible for everything from boiling water to global weather patterns.
The Initial Spark: Conduction's Role
The process begins when a fluid is heated by a source. The very first layer of fluid particles touching the heat source warms up through conduction—the direct transfer of vibrational energy from one particle to another.
Expansion and Density Change
As these fluid particles gain energy, they vibrate more vigorously and move farther apart. This expansion causes the heated portion of the fluid to become less dense than the cooler, surrounding fluid.
The Convection Current: Buoyancy in Action
Because it is now less dense, the warmer fluid becomes more buoyant and begins to rise. Think of a hot air balloon: the heated air inside is less dense than the cool air outside, causing the balloon to float upward.
As the warm fluid rises, cooler, denser fluid from above sinks to take its place near the heat source. This cooler fluid then gets heated, becomes less dense, and rises, continuing the cycle. This continuous circulation is the convection current.
Convection vs. Conduction: A Key Distinction
While both are methods of heat transfer, their mechanisms are fundamentally different. Confusing them is a common point of error.
Particle Vibration vs. Bulk Movement
Conduction is like a domino effect. Heat energy is passed from one particle to its immediate neighbor, but the particles themselves do not travel across the material. They remain in a fixed position, only vibrating.
Convection, however, is like a crowd moving across a room. The particles themselves travel from one location to another, carrying their heat with them. This involves the mass movement of the fluid.
The Medium Is the Message
This distinction explains why the medium is so important. Convection requires that particles are free to move around, which is why it only occurs in fluids (liquids and gases).
Heat transfer through solids happens primarily through conduction because their atoms are locked into a rigid structure and cannot flow.
Common Applications and Scenarios
Understanding convection is not just an academic exercise; it explains countless phenomena we observe and engineer every day.
Natural Convection: The Engine of Nature
When the fluid's movement is caused only by density differences due to temperature changes, it is called natural convection. This is the driving force behind many large-scale systems.
For example, wind is a result of natural convection. The sun heats the Earth's surface, which warms the air above it. This warm air rises, and cooler air rushes in to replace it, creating air currents.
Forced Convection: Engineering Heat Transfer
When an external force—like a fan or a pump—is used to move the fluid, it is called forced convection. This method is significantly more efficient at transferring heat.
A convection oven uses a fan to circulate hot air, cooking food faster and more evenly. The cooling fan in your computer is another example, using forced convection to pull heat away from the processor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Recognizing the type of convection at play is key to solving practical engineering and design problems.
- If your primary focus is cooling electronics: Relying on natural convection is a passive solution, but using a fan to create forced convection will dramatically improve cooling performance.
- If your primary focus is heating a room: Place heaters low to the ground to leverage natural convection, as the heated air will rise and circulate throughout the space efficiently.
- If your primary focus is understanding weather: Remember that natural convection is the fundamental engine driving wind, clouds, and ocean currents on a global scale.
By grasping the principle of heat transfer through fluid motion, you gain a foundational tool for analyzing and engineering the world around you.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Convection | Conduction |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Bulk movement of fluid | Molecular vibration |
| Medium | Fluids (liquids & gases) | Solids, fluids, or direct contact |
| Process | Fluid circulates via convection currents | Energy transfer without particle movement |
| Examples | Boiling water, wind, convection ovens | Touching a hot pan, heat through a metal rod |
Need precise temperature control for your lab processes? Convection is key to uniform heating and efficient cooling in laboratory equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, ovens, and temperature control systems that leverage convection principles for accurate, repeatable results. Whether you're conducting material tests, chemical reactions, or sample preparation, our solutions ensure optimal heat transfer for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment can enhance your research and workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Copper Foam
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of graphite? Unlock Superior Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential













