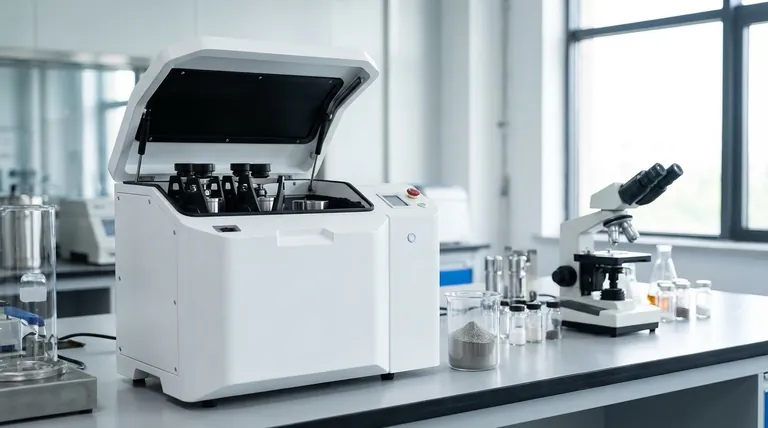
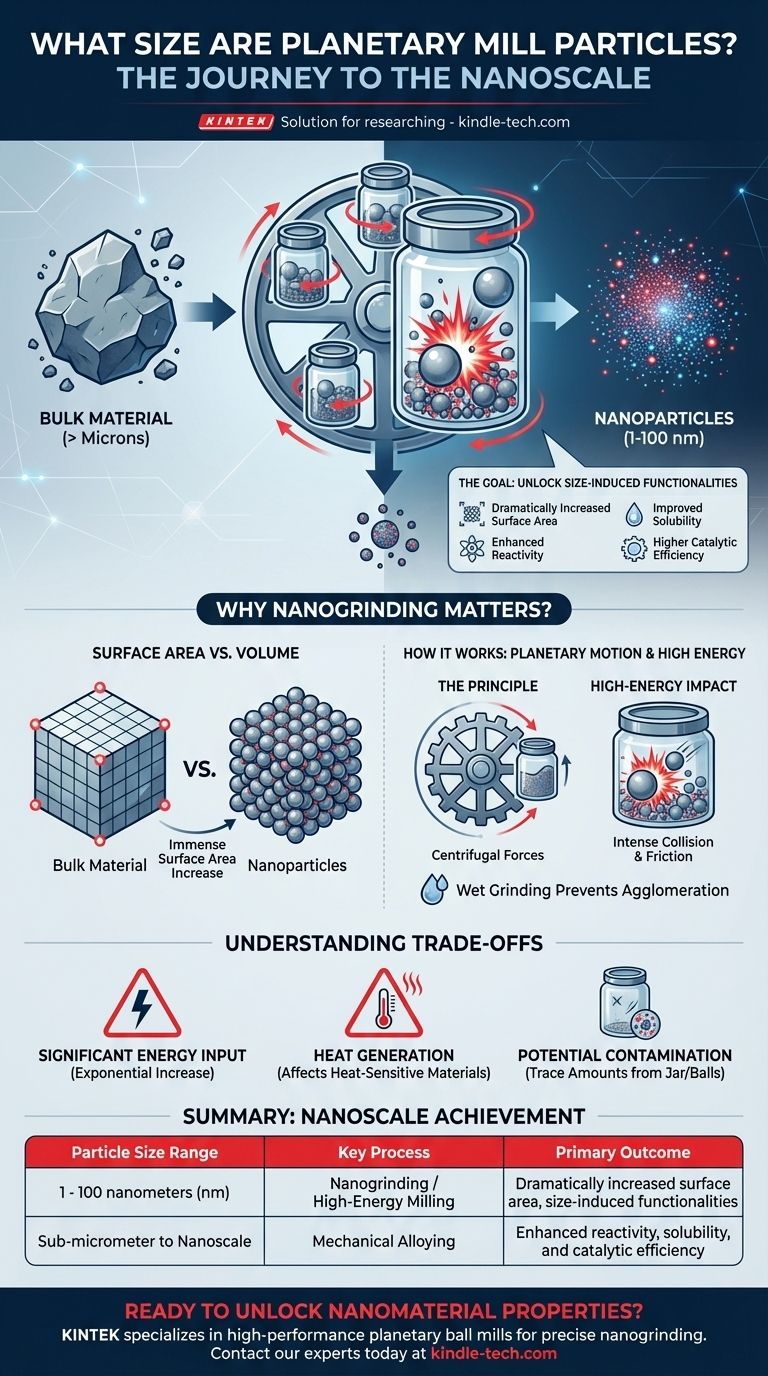
Planetary ball mills are specialized instruments designed to produce extremely fine particles. They are capable of reducing solid materials down to the nanoscale, a size range typically defined as being between 1 and 100 nanometers (nm). This process, known as nanogrinding, goes far beyond simple crushing to fundamentally alter a material's physical and chemical properties.
The core purpose of a planetary mill is not merely to make particles smaller, but to achieve a nanoscale size that dramatically increases the material's surface-area-to-volume ratio. This unlocks unique "size-induced functionalities" that are not present in the bulk material.

The Goal: From Bulk Material to Nanoparticles
Achieving nanoscale dimensions is a highly specialized task. Planetary mills are a key technology for this process, often referred to as high-energy milling or mechanical alloying.
What is Nanogrinding?
Nanogrinding is the mechanical process of reducing particle sizes to the sub-micrometer level, specifically into the nanometer range. This is distinct from conventional milling, which typically produces particles in the micron range.
Why Particle Size Matters
The defining characteristic of nanoparticles is their immense surface area relative to their volume. As a particle is broken down, more of its internal atoms become exposed on its surface.
This enlarged surface dramatically increases a material's reactivity, solubility, and catalytic efficiency. Essentially, the material behaves in a completely new way once it reaches the nanoscale.
Unlocking "Size-Induced Functionalities"
The unique properties that emerge at the nanoscale are called "size-induced functionalities." A material that is inert in its bulk form might become a highly effective catalyst as a nanoparticle. A drug that dissolves poorly can become much more bioavailable when ground to this size.
How Planetary Mills Achieve This Reduction
The effectiveness of a planetary mill comes from the extraordinarily high energy it imparts to the sample material.
The Planetary Motion Principle
The grinding jars, which contain the sample and grinding balls, are mounted on a rotating "sun wheel." Simultaneously, the jars themselves rotate in the opposite direction on their own axes.
This combination of movements creates extremely high centrifugal forces. It causes the grinding balls to detach from the inner wall of the jar and fly across its internal diameter, striking the opposite wall with tremendous force.
The Role of Grinding Media
The sample material is pulverized by the intense impact and friction from these high-energy collisions with the grinding balls. The efficiency of the process depends on the size, density, and material of the grinding balls and jar.
The Advantage of Wet Grinding
While grinding can be done dry, wet grinding is often used for achieving the finest particles. Adding a liquid helps to dissipate the intense heat generated during the process and prevents the newly formed nanoparticles from clumping back together (agglomerating).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, high-energy milling is not without its challenges. Understanding these limitations is critical for successful application.
Significant Energy Input
Reducing materials to the nanoscale is an energy-intensive process. The energy required increases exponentially as you target smaller and smaller particle sizes.
Heat Generation
The immense friction and impact generate considerable heat. This can be detrimental to heat-sensitive materials, potentially causing phase changes or degradation. This is a primary reason why wet grinding is often preferred.
Potential for Contamination
The constant, high-energy impact can cause microscopic wear on the grinding jar and balls. This wear introduces trace amounts of the jar/ball material into the sample, which can be a critical issue for high-purity applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
A planetary mill is a specialized tool for specific, demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is creating novel materials: A planetary mill is essential for exploring the unique physical and chemical properties that only emerge at the nanoscale.
- If your primary focus is enhancing reaction rates or solubility: This method is ideal for dramatically increasing surface area, which is the key driver for accelerating chemical reactions or improving dissolution.
- If your primary focus is general size reduction (not nanoscale): A less energy-intensive milling technique may be a more efficient and cost-effective solution for your needs.
Ultimately, a planetary mill is a precision instrument for fundamentally manipulating a material's properties by controlling its size at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Particle Size Range | Key Process | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 - 100 nanometers (nm) | Nanogrinding / High-Energy Milling | Dramatically increased surface area, size-induced functionalities |
| Sub-micrometer to Nanoscale | Mechanical Alloying | Enhanced reactivity, solubility, and catalytic efficiency |
Ready to unlock the unique properties of nanomaterials?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance planetary ball mills designed for precise nanogrinding. Whether you're developing novel materials, enhancing reaction rates, or improving solubility, our lab equipment ensures you achieve consistent, nanoscale results efficiently.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect milling solution for your laboratory's advanced research needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of ball milling? A Deep Dive into Mechanical Alloying and Material Transformation
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a planetary ball mill? Unlock the Right Grinding Technology for Your Lab
- What are the parameters of a planetary ball mill? Master Speed, Time, and Media for Perfect Grinding
- What is the principle of planetary ball mill? Achieve Rapid, High-Energy Grinding for Your Materials
- What is the working principle of planetary ball mill? Unlock High-Energy Grinding for Nanoscale Results



















