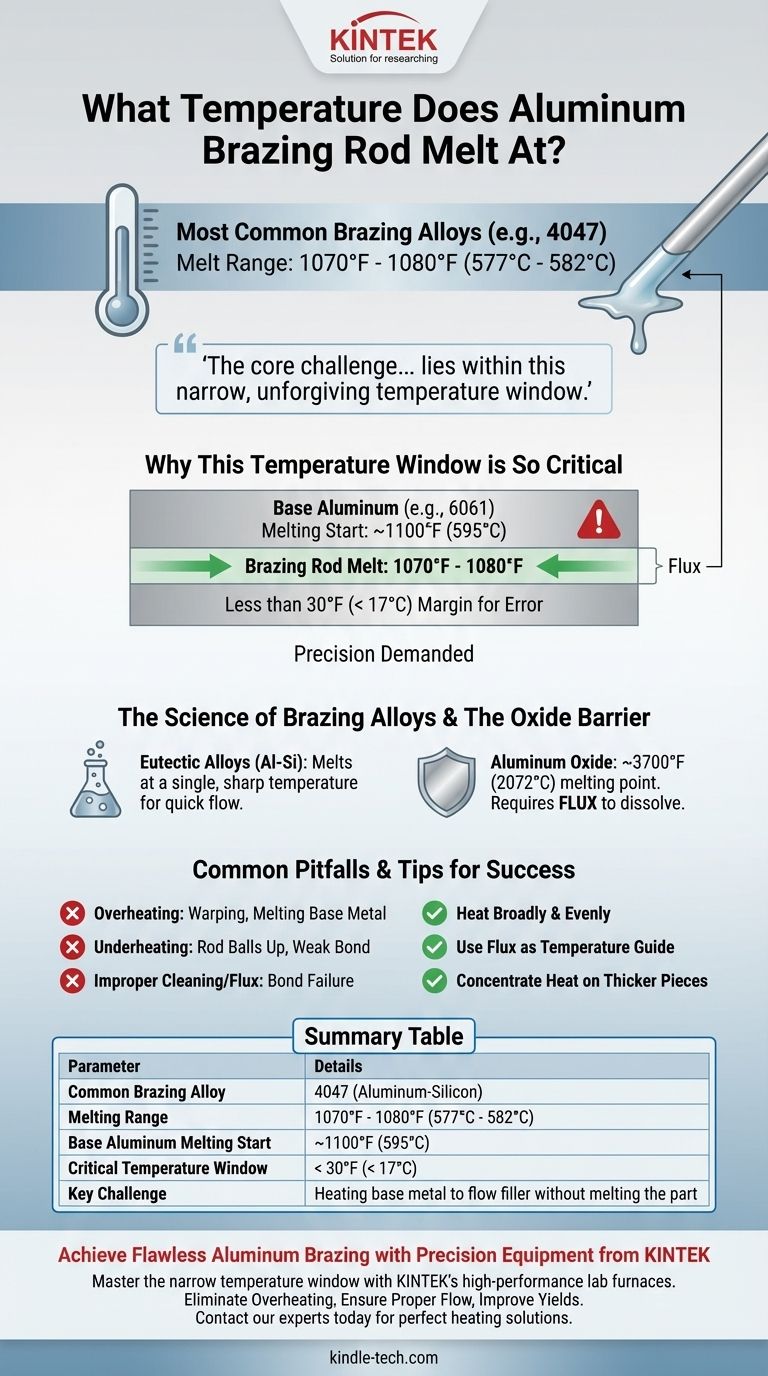
The melting point of an aluminum brazing rod is a precise and critical figure. Most common aluminum-silicon brazing alloys, such as 4047, melt in a very specific range of 1070°F to 1080°F (577°C to 582°C). This temperature is intentionally engineered to be just slightly below the melting point of the base aluminum parts you are joining, which is the secret to the entire process.
The core challenge of aluminum brazing is not simply melting the rod, but heating the base metal to a temperature that allows the molten rod to flow into the joint without melting the part itself. Success lies within this narrow, unforgiving temperature window.
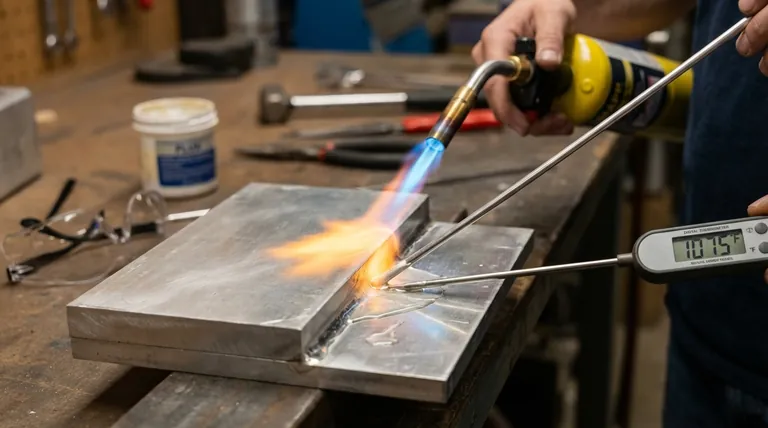

Why This Temperature Window is So Critical
Understanding the relationship between the filler rod and the base metal is fundamental. The small temperature difference is what makes aluminum brazing a skillful process that demands precision.
The Parent Metal's Melting Point
Common aluminum alloys like 6061 begin to melt around 1100°F (595°C) and become fully liquid by 1205°F (652°C).
As you can see, there is very little room for error—less than 30°F—between the filler rod melting and the workpiece beginning to fail. This is why direct, intense heat on a single spot is a recipe for disaster.
The Science of Brazing Alloys
Aluminum brazing rods are typically eutectic alloys, most often a combination of aluminum and silicon.
A eutectic alloy has a distinct advantage: it melts at a single, sharp temperature rather than going through a soft, "mushy" phase. This allows it to become fully liquid and flow quickly and cleanly via capillary action once the correct temperature is reached.
The Unseen Barrier: Aluminum Oxide
The surface of aluminum is always covered by a layer of aluminum oxide, which is tough, resilient, and has a staggeringly high melting point of about 3700°F (2072°C).
You cannot braze aluminum without first dealing with this oxide layer. This is the job of flux, which activates at brazing temperatures to chemically dissolve the oxide, allowing the molten filler metal to bond with the pure aluminum underneath.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Precise temperature control is everything. Even experienced technicians face challenges due to the unique properties of aluminum.
The Primary Risk: Overheating
Unlike steel, which glows red hot as a warning, aluminum gives very little visual indication before it collapses. Overheating the workpiece will cause it to warp, sag, or melt completely.
The Consequence of Underheating
If the base metal is not hot enough, the brazing rod will melt but will simply ball up on the surface. It will not "wet" the aluminum or be drawn into the joint, resulting in a weak bond with no structural integrity.
Improper Cleaning or Flux Application
If the part is not mechanically cleaned and properly fluxed, the bond will fail. The flux must be active and liquid—often a sign that you're in the right temperature range—for the filler metal to flow where it's needed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving the correct temperature is about technique, not just firepower. Your approach should be dictated by the workpiece itself.
- If your primary focus is a successful bond: Heat the workpiece broadly and evenly, not the rod. Apply the rod to the joint, and if the workpiece is at the correct temperature, it will melt the rod instantly.
- If you are a beginner: Use the flux as your temperature guide. Most aluminum brazing fluxes will appear as a white powder when applied, but they will turn clear and watery right as the metal reaches the ideal brazing temperature.
- If you are joining thick and thin pieces: Concentrate the majority of your heat on the thicker component. Heat transfer will bring the thinner piece up to temperature more safely than heating it directly.
Mastering aluminum brazing comes from understanding and controlling the precise thermal balance between your filler rod and your base metal.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Brazing Alloy | 4047 (Aluminum-Silicon) |
| Melting Range | 1070°F - 1080°F (577°C - 582°C) |
| Base Aluminum Melting Start | ~1100°F (595°C) |
| Critical Temperature Window | < 30°F (< 17°C) |
| Key Challenge | Heating base metal to flow filler without melting the part |
Achieve Flawless Aluminum Brazing with Precision Equipment from KINTEK
Mastering the narrow temperature window of aluminum brazing requires reliable and accurate heat control. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and heating equipment that deliver the precise, uniform temperatures essential for successful brazing operations.
Whether you are in R&D, manufacturing, or repair, our solutions help you:
- Eliminate Overheating: Prevent warping and melting of base metals.
- Ensure Proper Flow: Achieve consistent results with even heat distribution.
- Improve Yields: Increase efficiency and reduce costly errors.
Ready to enhance your brazing process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your specific aluminum joining needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
People Also Ask
- What is the suitability of tungsten as an electrical conducting material for heating applications? Master Extreme High-Temperature Heating
- Why tungsten is not used as heating element? Discover the critical role of oxidation resistance.
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten filament? Key Limitations in Lighting Technology
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications















