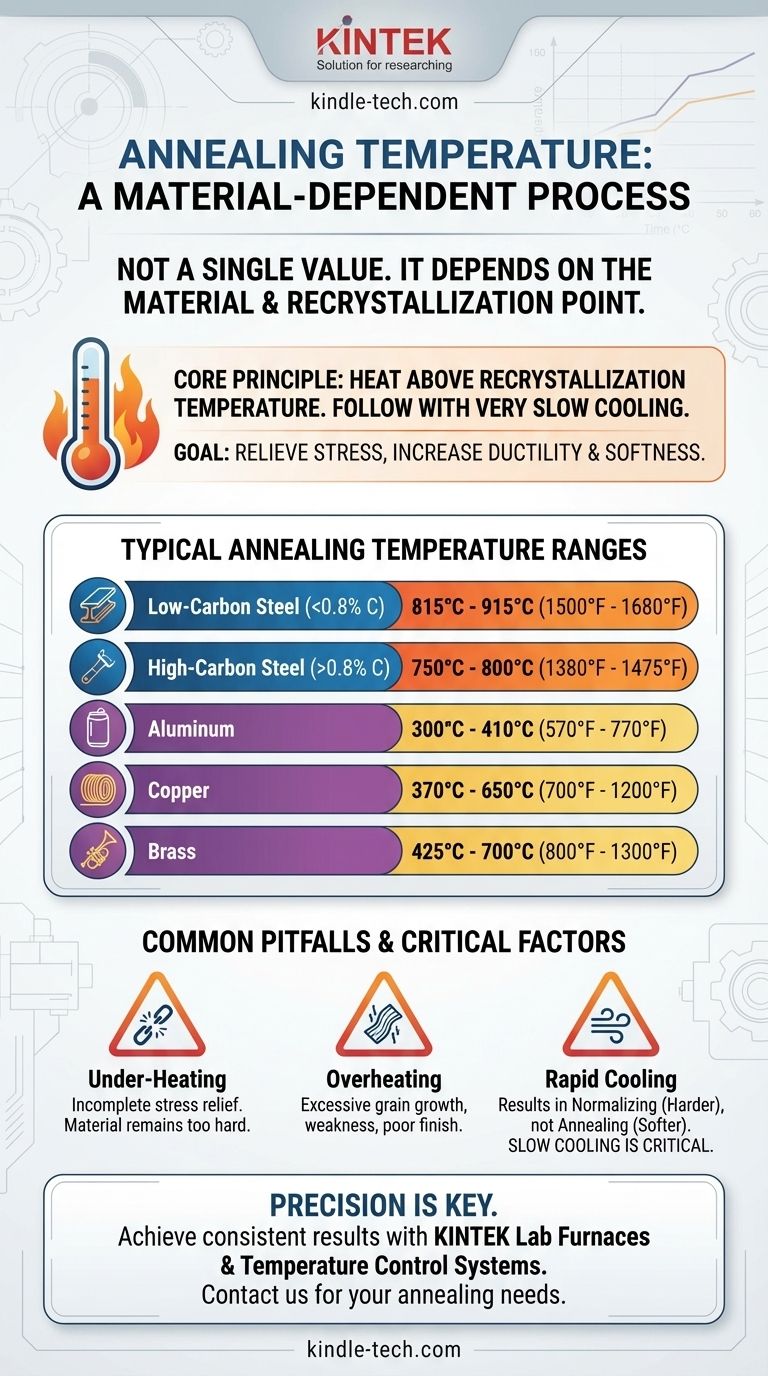
The temperature for annealing is not a single value; it is entirely dependent on the specific material you are working with. For common steels, this temperature typically ranges from 727°C to 915°C (1340°F to 1680°F), while for a metal like aluminum, it is much lower, around 300°C to 410°C (570°F to 770°F). The correct temperature is determined by the material's composition and its unique recrystallization point.
The core principle of annealing is to heat a material above its recrystallization temperature to relieve internal stresses and refine its grain structure. However, the target temperature is only half the equation; a very slow cooling rate is equally critical to achieving the desired softness and ductility.
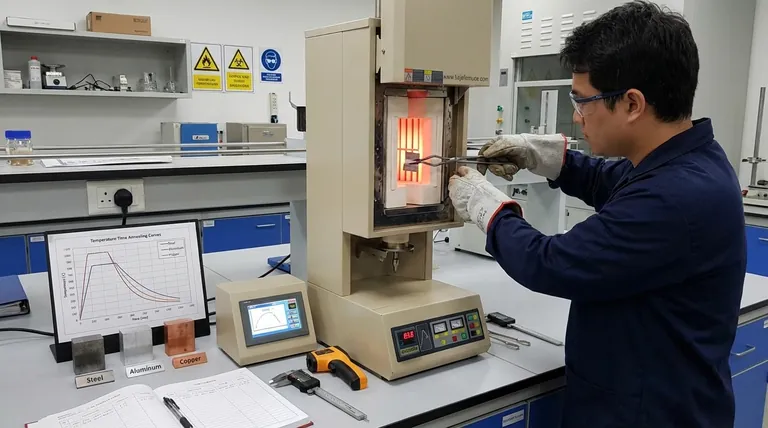

What is Annealing and Why is Temperature Critical?
Annealing is a precise heat treatment process designed to make a material, usually a metal, softer and more workable. Understanding its purpose reveals why temperature control is paramount.
The Goal: Relieving Stress and Increasing Ductility
When a metal is bent, stretched, or compressed (a process known as cold working), its internal crystal structure becomes distorted and stressed. This makes the material harder but also more brittle.
Annealing reverses this effect. By heating the material, we give the atoms enough energy to move and rearrange themselves into a more orderly, stress-free structure. This process increases the material's ductility (ability to be drawn or stretched) and reduces its hardness.
The Key: Recrystallization
The most important phase of annealing is recrystallization. This is the temperature at which new, strain-free crystals (or grains) begin to form, replacing the old, deformed ones.
Heating below this temperature will not achieve true annealing. Heating significantly above it can cause the new grains to grow too large, which can make the material weak or brittle.
Determining the Correct Annealing Temperature
The right temperature depends on the material's alloy composition. Even small variations, like the percentage of carbon in steel, can significantly change the required temperature.
Common Temperatures for Steels
Steel is an iron-carbon alloy, and its annealing temperature is closely tied to its critical temperatures (A1, A3), which are points where its crystal structure changes.
- Low-Carbon Steels (<0.8% carbon): These are heated to about 30-50°C (50-90°F) above the upper critical temperature (A3). This is typically in the range of 815°C to 915°C (1500°F to 1680°F).
- High-Carbon Steels (>0.8% carbon): These are heated to just above the lower critical temperature (A1). This is typically around 750°C to 800°C (1380°F to 1475°F).
Common Temperatures for Non-Ferrous Metals
Metals that do not contain iron have their own distinct annealing ranges.
- Copper: The annealing temperature for copper is generally between 370°C to 650°C (700°F to 1200°F). A lower temperature in this range will result in a finer grain structure.
- Aluminum: Aluminum and its alloys are annealed at much lower temperatures, typically between 300°C to 410°C (570°F to 770°F).
- Brass: This copper-zinc alloy anneals in the range of 425°C to 700°C (800°F to 1300°F), depending on the specific alloy composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Achieving a successful anneal requires avoiding common errors related to temperature and cooling. The process is unforgiving, and small mistakes can lead to undesirable results.
The Risk of Under-Heating
If the material does not reach its full recrystallization temperature, the internal stresses will not be fully relieved. The metal will be softer than its cold-worked state but will not have the full ductility and uniformity that a proper anneal provides.
The Dangers of Overheating
Heating a material too far above its target temperature can cause excessive grain growth. Large grains can reduce the material's strength and toughness. It can also lead to a rough surface finish (known as "orange peel") if the part is formed later. In extreme cases, overheating causes oxidation and scaling on the surface.
Why Cooling Rate is Just as Important
Full annealing is defined by its slow cooling rate. Typically, this is achieved by turning off the furnace and allowing the part to cool down with it over many hours.
If the material is cooled too quickly (for example, in open air), it is no longer an annealing process. It becomes a different heat treatment, such as normalizing, which results in a harder and stronger material—the opposite of the goal of annealing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Selecting the correct temperature and process is a matter of matching the technique to the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is low-carbon steel: Heat the material well above its A3 critical temperature (into the 815-915°C range) and ensure it is cooled very slowly in the furnace.
- If your primary focus is high-carbon steel: Heat the material just above its A1 critical temperature (~750°C) to avoid forming a brittle microstructure upon cooling.
- If your primary focus is a non-ferrous metal like copper or aluminum: Use the lower temperature ranges specific to that alloy, as they are far more sensitive to overheating than steel.
- If you are ever unsure: Always consult a material data sheet or a heat treatment handbook for the specific alloy you are working with.
Precision in heat treatment is what separates a successful, workable material from a failed part.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Annealing Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Low-Carbon Steel | 815°C to 915°C (1500°F to 1680°F) |
| High-Carbon Steel | 750°C to 800°C (1380°F to 1475°F) |
| Aluminum | 300°C to 410°C (570°F to 770°F) |
| Copper | 370°C to 650°C (700°F to 1200°F) |
| Brass | 425°C to 700°C (800°F to 1300°F) |
Achieve precise and consistent results with the right lab equipment.
Unsure about the exact annealing profile for your specific alloy? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and temperature control systems designed for reliable heat treatment processes. Our equipment helps you accurately reach and maintain critical temperatures, ensuring your materials achieve the desired softness, ductility, and grain structure every time.
Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your annealing needs and elevate your laboratory's capabilities. Get in touch via our contact form.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















