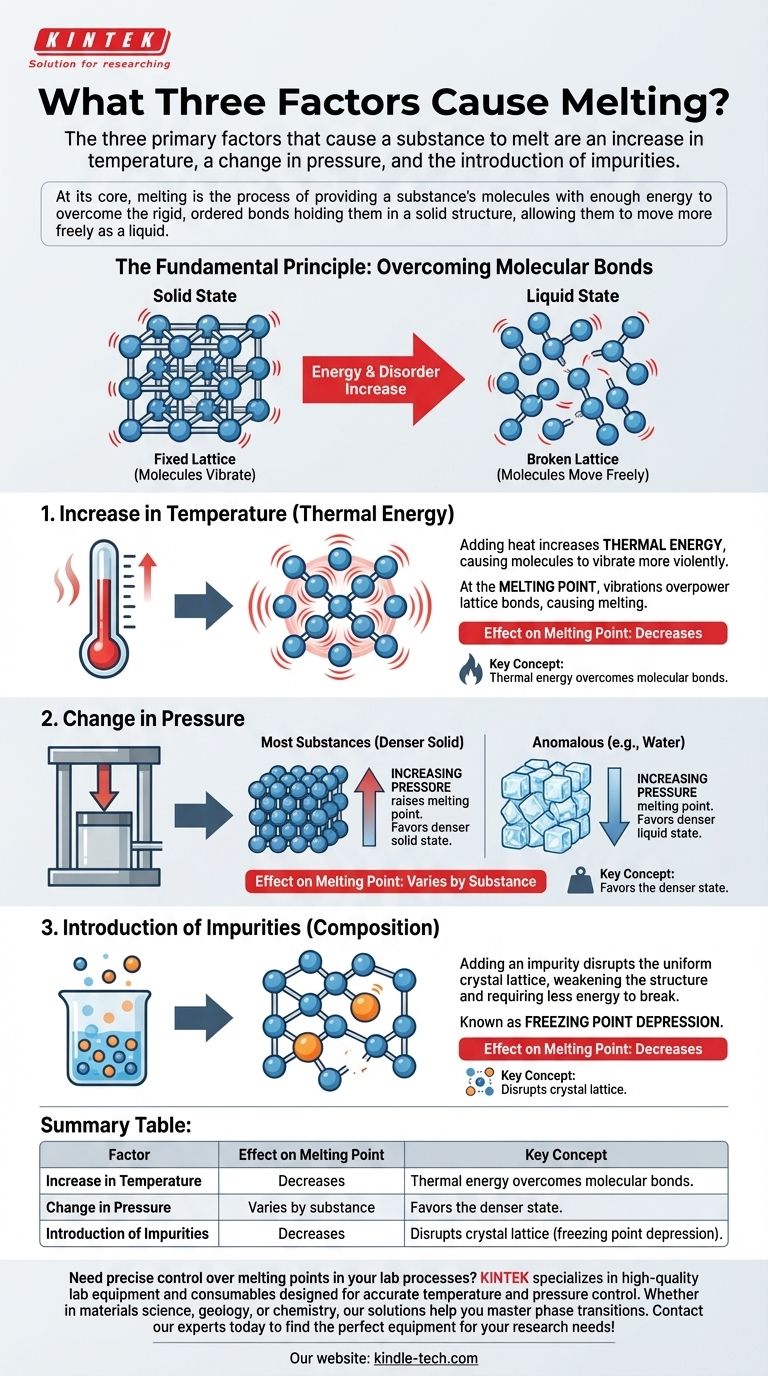
The three primary factors that cause a substance to melt are an increase in temperature, a change in pressure, and the introduction of impurities. While temperature is the most intuitive factor, pressure and composition play equally critical roles in determining the precise conditions under which a solid will transition into a liquid.
At its core, melting is the process of providing a substance's molecules with enough energy to overcome the rigid, ordered bonds holding them in a solid structure, allowing them to move more freely as a liquid.

The Fundamental Principle: Overcoming Molecular Bonds
Before examining the factors, it's crucial to understand what melting is at a microscopic level. It represents a fundamental shift in a substance's physical state, known as a phase transition.
The Solid State
In a solid, atoms and molecules are locked into a fixed, often crystalline structure called a lattice. They vibrate in place but lack the energy to break free from their neighbors. This is what gives a solid its definite shape and volume.
The Liquid State
In a liquid, molecules have absorbed enough energy to break out of that rigid lattice. They can now slide past one another, which is why a liquid flows and takes the shape of its container, even though it maintains a relatively constant volume.
The Three Core Factors of Melting
Each of the three factors provides a different mechanism for disrupting the solid lattice and enabling the transition to a liquid.
1. Increase in Temperature (Thermal Energy)
This is the most common cause of melting. Adding heat to a substance increases its thermal energy.
This added energy translates directly into increased kinetic energy for the molecules, causing them to vibrate more and more violently. At a specific temperature, the melting point, these vibrations become so intense that they overpower the bonds holding the lattice together, and the substance melts.
2. Change in Pressure
Pressure's effect on melting is less intuitive because it depends on the substance. It works by favoring the denser state of matter.
For most substances, the solid form is denser than the liquid form. Increasing pressure forces the molecules closer together, reinforcing the solid lattice and making it harder to melt. This means an increase in pressure raises the melting point.
However, for anomalous substances like water, the solid form (ice) is less dense than the liquid form. Here, an increase in pressure favors the denser liquid state, effectively lowering the melting point. This is why an ice skater's blade can melt the ice directly beneath it.
3. Introduction of Impurities (Composition)
Adding a different substance, or an impurity, to a pure solid can significantly lower its melting point. This phenomenon is known as freezing point depression.
The foreign molecules of the impurity disrupt the formation of the uniform crystal lattice. This weakened structure requires less energy to break apart. A common example is salting icy roads; the salt mixes with the ice, lowering its melting point and causing it to melt even when the ambient temperature is below water's normal freezing point of 0°C (32°F).
Understanding the Interplay of Factors
These three factors do not operate in isolation. The state of a substance—solid, liquid, or gas—is determined by the precise combination of temperature, pressure, and composition.
Phase Diagrams
Scientists use charts called phase diagrams to map out a substance's state under different conditions of temperature and pressure. These diagrams clearly show how changing one variable can alter the melting point.
A Combined Effect
In many real-world scenarios, multiple factors are at work. For instance, the melting of rock to form magma deep within the Earth is a complex result of immense heat, extreme pressures, and the presence of various minerals and water (impurities).
Applying These Principles
Understanding these factors allows you to predict and explain physical phenomena in different contexts.
- If your primary focus is everyday phenomena: Temperature and the addition of impurities are the most relevant factors for things like melting ice or making ice cream.
- If your primary focus is geology or planetary science: The interplay between immense pressure and high temperature is critical to understanding processes like the formation of magma or the composition of planetary cores.
- If your primary focus is materials science: Composition is key, as creating alloys with specific melting points is fundamental to engineering and metallurgy.
Ultimately, the transition from a solid to a liquid is a universal process governed by the constant battle between molecular bonds and energy.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Melting Point | Key Concept |
|---|---|---|
| Increase in Temperature | Decreases | Thermal energy overcomes molecular bonds. |
| Change in Pressure | Varies by substance | Favors the denser state (raises or lowers melting point). |
| Introduction of Impurities | Decreases | Disrupts crystal lattice (freezing point depression). |
Need precise control over melting points in your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed for accurate temperature and pressure control. Whether you're in materials science, geology, or chemistry, our solutions help you master phase transitions. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your research needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More












