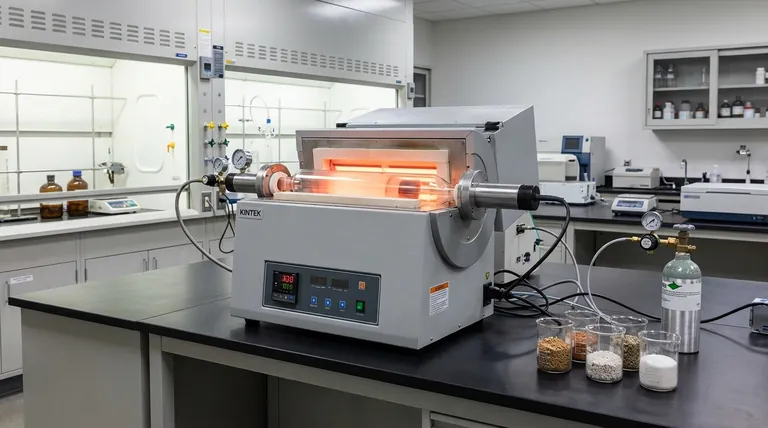
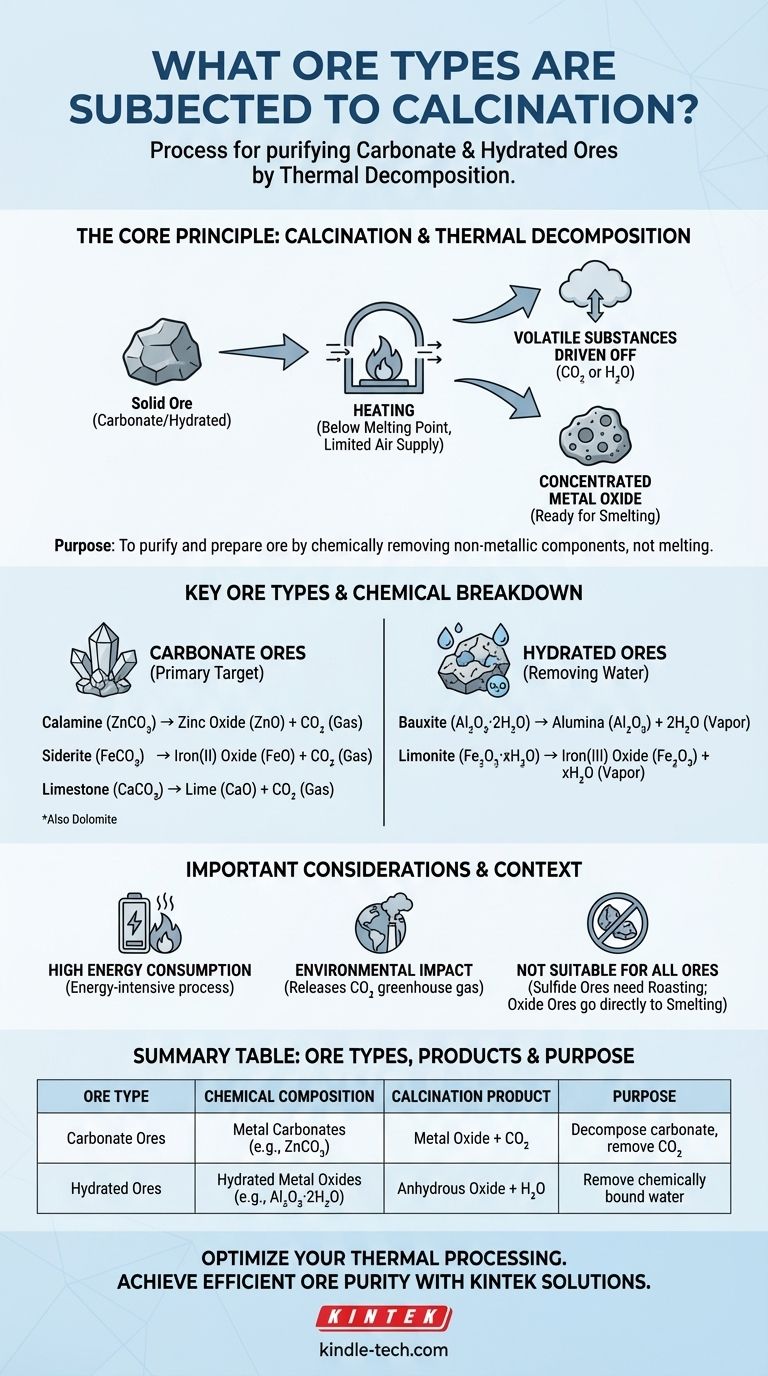
In short, calcination is a process primarily applied to carbonate and hydrated ores. This metallurgical heating process is specifically designed to thermally decompose the ore, driving off volatile substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) from carbonates or water (H2O) from hydrated minerals to produce a concentrated metal oxide.
The central purpose of calcination is not to melt the ore, but to purify and prepare it for smelting. By heating the ore below its melting point, you chemically remove non-metallic components, which makes the subsequent extraction of the final metal more efficient and economical.

The Core Principle of Calcination: Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a highly specific thermal treatment step in extractive metallurgy. Understanding its core chemical goal is key to knowing which ores are suitable for the process.
What is Calcination?
Calcination is the process of heating a solid material, like an ore, to a high temperature in the absence or limited supply of air. This controlled atmosphere is critical.
The temperature is kept high enough to cause a chemical breakdown (thermal decomposition) but remains below the ore's melting point.
The Chemical Goal: Removing Volatiles
The primary goal is to drive off volatile substances that are chemically bound within the ore's structure. This purifies the ore by increasing the concentration of the desired metal oxide.
This process makes the ore more porous, which enhances its reactivity for the next stage of metal extraction, which is typically reduction (smelting).
Why a Limited Air Supply is Crucial
The limited air supply distinguishes calcination from a similar process called roasting. Roasting is done with an excess of air to intentionally cause oxidation, which is necessary for sulfide ores.
Calcination specifically avoids oxidation and focuses solely on decomposition.
Key Ore Types Requiring Calcination
The ores subjected to calcination are defined by their chemical composition—specifically, the presence of components that can be driven off by heat.
Carbonate Ores (The Primary Target)
These are the most common candidates for calcination. The process breaks down the metal carbonate into a metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas.
- Calamine (Zinc Carbonate, ZnCO₃) → Zinc Oxide (ZnO) + CO₂
- Siderite (Iron(II) Carbonate, FeCO₃) → Iron(II) Oxide (FeO) + CO₂
- Limestone (Calcium Carbonate, CaCO₃) → Lime (CaO) + CO₂
- Dolomite (Calcium Magnesium Carbonate, CaMg(CO₃)₂)
Hydrated Ores (Removing Water)
For these ores, calcination's purpose is to remove water molecules that are chemically integrated into the mineral's crystal structure.
- Bauxite (Hydrated Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃·2H₂O) → Alumina (Al₂O₃) + 2H₂O
- Limonite (Hydrated Iron(III) Oxide, Fe₂O₃·xH₂O) → Iron(III) Oxide (Fe₂O₃) + xH₂O
Understanding the Limitations and Context
While essential for certain ores, calcination is not a universal solution. Its application is highly specific, and it comes with important considerations.
Energy Consumption
Heating massive quantities of ore to high temperatures is an energy-intensive process. This represents a significant operational cost in any metallurgical plant.
Not Suitable for All Ores
Calcination is ineffective or inappropriate for other major ore classes.
- Sulfide Ores (e.g., Galena, PbS) must be roasted (heated in excess air) to be converted into oxides.
- Oxide Ores (e.g., Hematite, Fe₂O₃) are already in their oxidized state and do not require decomposition, so they can proceed directly to smelting.
Environmental Impact
The decomposition of carbonate ores releases large volumes of carbon dioxide (CO₂) a potent greenhouse gas. This is a major environmental consideration for industries relying on this process.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing between calcination and other thermal treatments depends entirely on the starting chemistry of your ore.
- If your primary focus is a carbonate ore (like ZnCO₃): Calcination is the essential first step to decompose it into its metal oxide (ZnO) before reduction.
- If your primary focus is a hydrated ore (like Al₂O₃·2H₂O): Calcination is necessary to drive off chemically bound water and produce the anhydrous oxide (Al₂O₃).
- If your primary focus is a sulfide ore (like PbS): Roasting, not calcination, is the correct process to convert the sulfide into an oxide through oxidation.
Ultimately, calcination is a targeted purification step designed to simplify the ore's chemistry before the final extraction begins.
Summary Table:
| Ore Type | Chemical Composition | Calcination Product | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonate Ores | Metal Carbonates (e.g., ZnCO₃, FeCO₃) | Metal Oxide + CO₂ | Decompose carbonate, remove CO₂ |
| Hydrated Ores | Hydrated Metal Oxides (e.g., Al₂O₃·2H₂O) | Anhydrous Oxide + H₂O | Remove chemically bound water |
Need to optimize your thermal processing of carbonate or hydrated ores? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces and equipment designed for precise calcination processes. Our solutions help you achieve efficient thermal decomposition, improve ore purity, and enhance your overall metallurgical workflow. Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can meet your specific ore processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic



















