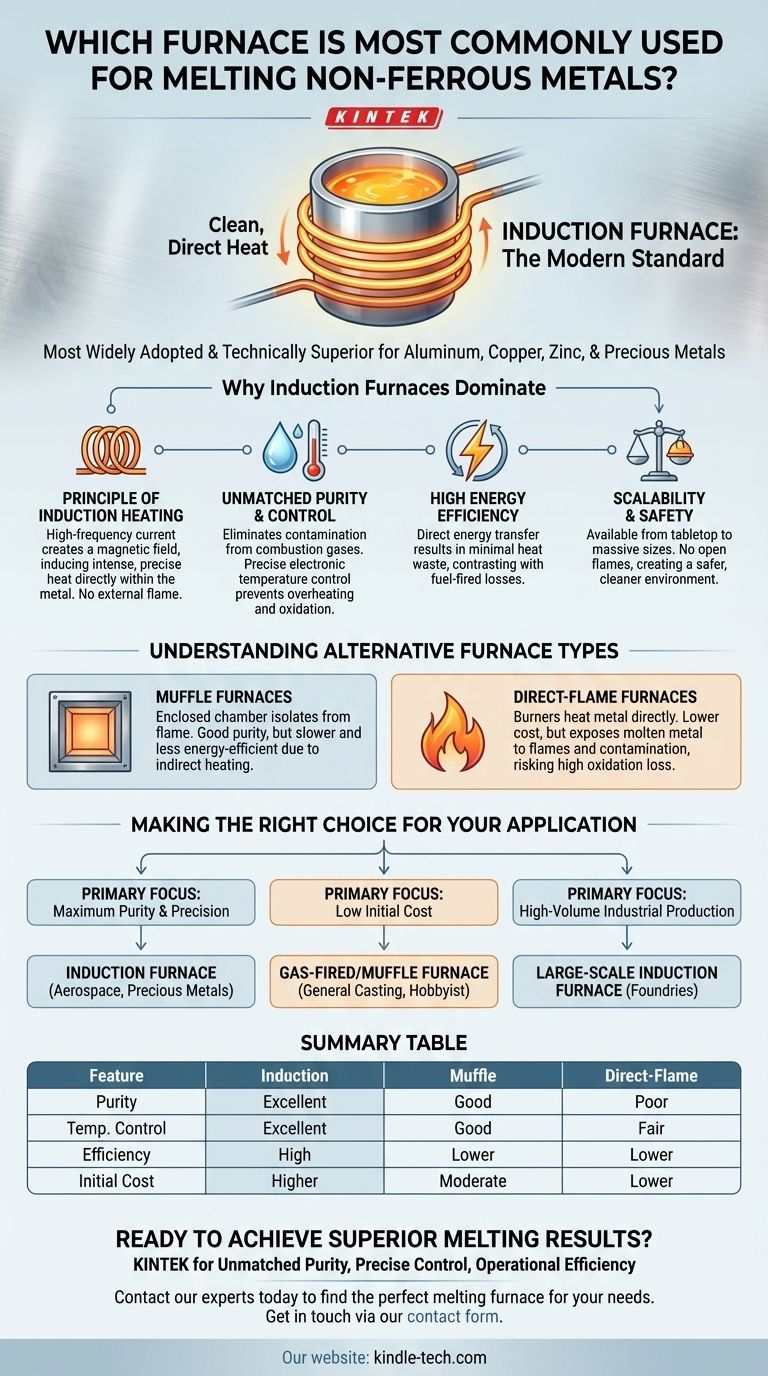
For melting non-ferrous metals, the induction furnace is the most widely adopted and technically superior choice in modern settings. Its design provides a clean, highly controllable, and energy-efficient process perfectly suited for materials like aluminum, copper, zinc, and precious metals, where purity and precise temperature management are critical.
While other furnace types exist, the induction furnace has become the standard for quality-sensitive non-ferrous metal processing due to its unique ability to heat the metal directly without contamination from fuel or flames.
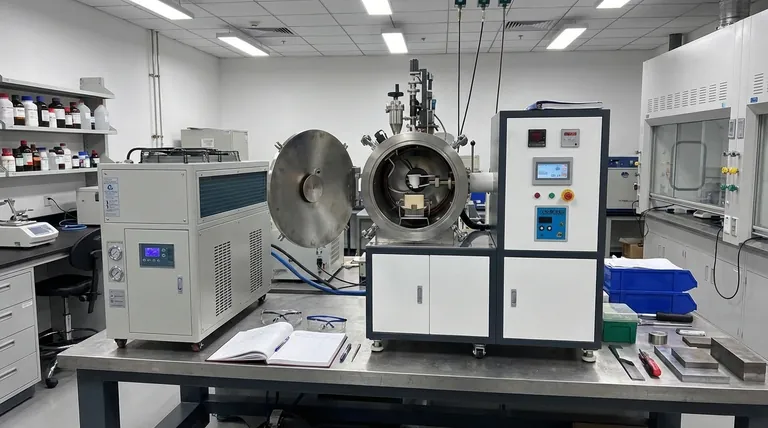

Why Induction Furnaces Dominate for Non-Ferrous Metals
The preference for induction technology isn't arbitrary; it stems from its fundamental operating principle, which offers significant advantages over older, combustion-based methods.
The Principle of Induction Heating
An induction furnace does not use an external flame. Instead, it uses a powerful, high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil.
This creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around a crucible (often made of graphite). The magnetic field induces powerful electrical eddy currents within the crucible and the metal inside it.
These currents generate intense heat precisely where it's needed, causing the metal to melt from the inside out. This process is clean, contained, and exceptionally fast.
Unmatched Purity and Control
Because there is no burning fuel, there are no byproducts of combustion (like sulfur or excess carbon) to contaminate the molten metal. This is essential for maintaining the specific properties of non-ferrous alloys and precious metals.
Furthermore, the heat is controlled electronically. This allows for extremely precise temperature regulation, preventing overheating that can lead to metal loss through oxidation or damage to the alloy's structure.
High Energy Efficiency
Induction heating is remarkably efficient. The energy is transferred directly to the metal charge, with very little heat wasted to the surrounding environment.
This contrasts sharply with fuel-fired furnaces, where a significant portion of the energy is lost as heat up the flue stack and through the furnace walls.
Scalability and Safety
Induction furnaces are available in a vast range of sizes, from small tabletop units for jewelers to massive systems capable of melting many tons of metal in large foundries.
They also operate without open flames, reducing fire hazards and creating a safer, cleaner working environment compared to traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
Understanding Alternative Furnace Types
While induction is often the best choice, it's important to understand the alternatives to appreciate the context.
Muffle Furnaces
A muffle furnace isolates the material being heated from direct contact with flames or heating elements in a "muffle," or enclosed chamber.
This design prevents contamination from combustion gases, offering better purity than a direct-flame furnace. However, it is generally less energy-efficient and slower than an induction furnace because the heat must transfer indirectly through the chamber walls.
Direct-Flame Furnaces
These are simpler furnaces where burners (using gas or oil) heat the metal either in an open hearth or a crucible. They are common due to their lower initial cost.
However, they expose the molten metal directly to flames and combustion gases. This leads to a higher risk of contamination and oxidation, where metal is lost by chemically reacting with oxygen—a significant issue for valuable non-ferrous metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is perfect for every situation. The choice of a furnace involves balancing performance with practical constraints.
Initial Investment Cost
The primary drawback of induction furnaces is their higher upfront cost. The sophisticated power supplies and copper coils are more expensive to manufacture than the simple burners and refractory materials of a fuel-fired furnace.
Complexity and Maintenance
While highly reliable, the electronics that power an induction furnace are more complex than the plumbing of a gas burner. Diagnosing and repairing issues with the power supply or coil requires specialized knowledge.
The Crucible as a Consumable
The crucible, particularly the graphite ones used for their excellent heating properties, is a consumable item. It degrades over time and with thermal cycling, requiring periodic replacement, which is an ongoing operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires a clear understanding of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and precision (precious metals, aerospace alloys): The induction furnace is the definitive choice, as its clean and controllable melting process is non-negotiable for these applications.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost for general casting or hobbyist work: A gas-fired crucible or muffle furnace can be a viable entry point, but you must accept the trade-offs in efficiency and potential metal contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, efficient industrial production: A large-scale induction furnace provides the best combination of melt speed, energy efficiency, and metallurgical control for most industrial non-ferrous foundries.
Ultimately, choosing the right tool is about aligning the technology's capabilities with your specific operational and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Muffle Furnace | Direct-Flame Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity / Contamination | Excellent (No combustion gases) | Good (Isolated chamber) | Poor (Direct flame contact) |
| Temperature Control | Excellent (Precise electronic) | Good | Fair |
| Energy Efficiency | High (Direct heating) | Lower (Indirect heating) | Lower (Heat loss) |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Moderate | Lower |
| Best For | High-purity alloys, precious metals | General casting, hobbyist work | Low-cost entry point |
Ready to Achieve Superior Melting Results?
For laboratory professionals and foundries where metal purity, precise temperature control, and energy efficiency are paramount, the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction melting systems designed for non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, and precious metals.
Let us help you enhance your process with a solution that delivers:
- Unmatched Purity: Eliminate contamination from combustion gases.
- Precise Control: Achieve exact temperatures for consistent alloy quality.
- Operational Efficiency: Reduce melting times and energy costs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect melting furnace for your needs. Get in touch via our contact form to get started.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting



















