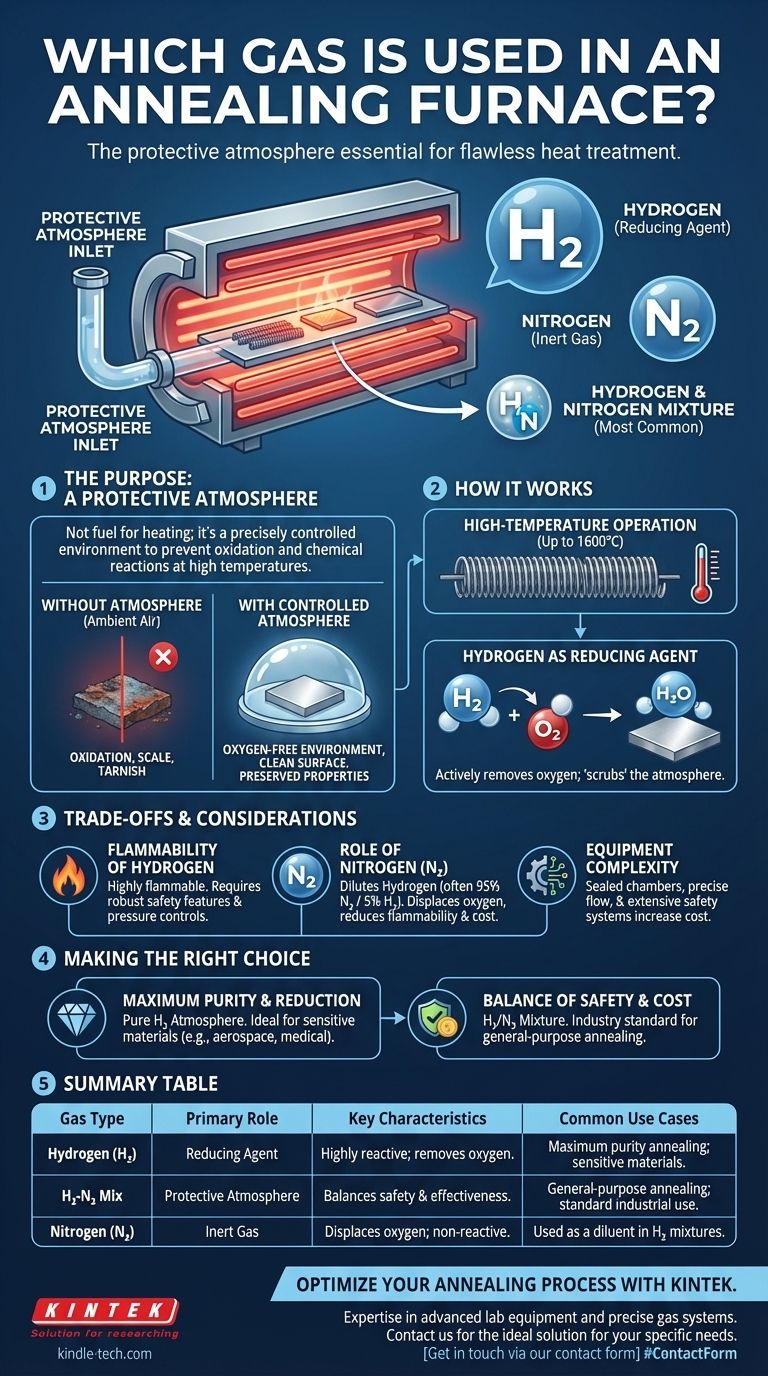
The primary gas used in this type of specialized heat treatment is hydrogen, or more commonly, a controlled mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen. This combination acts as a protective atmosphere, which is essential for the annealing process.
The gas in an annealing furnace is not a fuel for heating; it is a precisely controlled protective atmosphere. Its core purpose is to prevent oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions on the material's surface at high temperatures.

The Purpose of a Controlled Atmosphere
Why an Atmosphere is Necessary
When metals and other materials are heated to the high temperatures required for annealing, they become highly reactive. If exposed to ambient air, the oxygen would rapidly cause oxidation, forming a layer of scale or tarnish on the surface.
This oxidation can compromise the material's dimensions, surface finish, and mechanical properties, defeating the purpose of the annealing process itself.
Hydrogen as a Reducing Agent
A hydrogen annealing furnace uses either pure hydrogen or a hydrogen-nitrogen mixture (often called forming gas) to create an oxygen-free environment.
Hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent. This means it actively seeks out and reacts with any oxygen present inside the furnace, effectively "scrubbing" the atmosphere clean and preventing the workpiece from oxidizing.
Mechanics of a Hydrogen Annealing Furnace
High-Temperature Operation
These furnaces are designed for extreme heat. They often use molybdenum wire as a heating element, which has a melting point of 2630℃, allowing the furnace to reach operating temperatures as high as 1600℃.
Precision Environmental Control
The entire system is engineered to maintain the integrity of the protective atmosphere. This includes a sealed metal shell for air tightness, precise temperature controls (often with a precision of ±1℃), and automated pressure control for both gas and water cooling systems.
Broad Industrial Applications
The ability to heat-treat materials without oxidation is critical in many advanced fields. These furnaces are used for ceramic sintering, brazing, metallization, and annealing high-value metal parts for the aerospace, medical, and electronics industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
The Flammability of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas. This inherent risk is the most significant consideration when operating these furnaces. Modern systems are equipped with extensive safety features, including robust pressure controls and automated systems, to manage this risk effectively.
The Role of Nitrogen
To mitigate the flammability and reduce operational costs, pure hydrogen is often diluted with nitrogen. A common mixture is 5% hydrogen and 95% nitrogen.
Nitrogen is an inert gas, meaning it does not react with the material being treated. It serves to displace the oxygen while the smaller amount of hydrogen provides the necessary reducing action to eliminate any residual oxygen.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Due to the need for sealed chambers, precise gas flow controls, and extensive safety systems, hydrogen annealing furnaces are significantly more complex and costly than standard furnaces that operate in open air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The specific gas composition you need depends directly on the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and oxide reduction: A pure hydrogen atmosphere provides the most aggressive reducing environment, ideal for the most sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose annealing with a balance of safety and cost: A hydrogen-nitrogen mixture is the industry standard, offering excellent protection from oxidation with reduced flammability risk.
Ultimately, selecting the correct protective atmosphere is a critical decision that directly influences the quality and integrity of the final product.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Role | Key Characteristics | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Reducing Agent | Highly reactive; removes oxygen; prevents oxidation. | Maximum purity annealing; sensitive materials. |
| Hydrogen-Nitrogen Mix | Protective Atmosphere | Balances safety and effectiveness; reduces flammability. | General-purpose annealing; standard industrial use. |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Inert Gas | Displaces oxygen; non-reactive. | Used as a diluent in hydrogen mixtures. |
Optimize your annealing process with the right protective atmosphere. The quality of your final product depends on precise environmental control. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including high-performance annealing furnaces and the necessary gas systems. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution for your materials—whether for aerospace components, medical devices, or electronics. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and ensure flawless results. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a 1937 K high-temperature atmosphere furnace required for iron-free magnesium spinels? Achieve Phase Purity
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding
- What are the typical air-to-gas ratios for endothermic generators? Optimize Natural Gas and Propane Settings
- Why argon is used in annealing? To Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Purity in Heat Treatment
- What is the hydrogen atmosphere for annealing furnace? Achieve a Bright, Oxide-Free Finish
- What is the pressure inside a furnace? Mastering Controlled Environments for Your Lab
- What critical environmental conditions does a vacuum atmosphere resistance furnace provide? Advanced Magnesium Research
- What are the primary functions of a high-temperature atmosphere muffle furnace in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis?



















