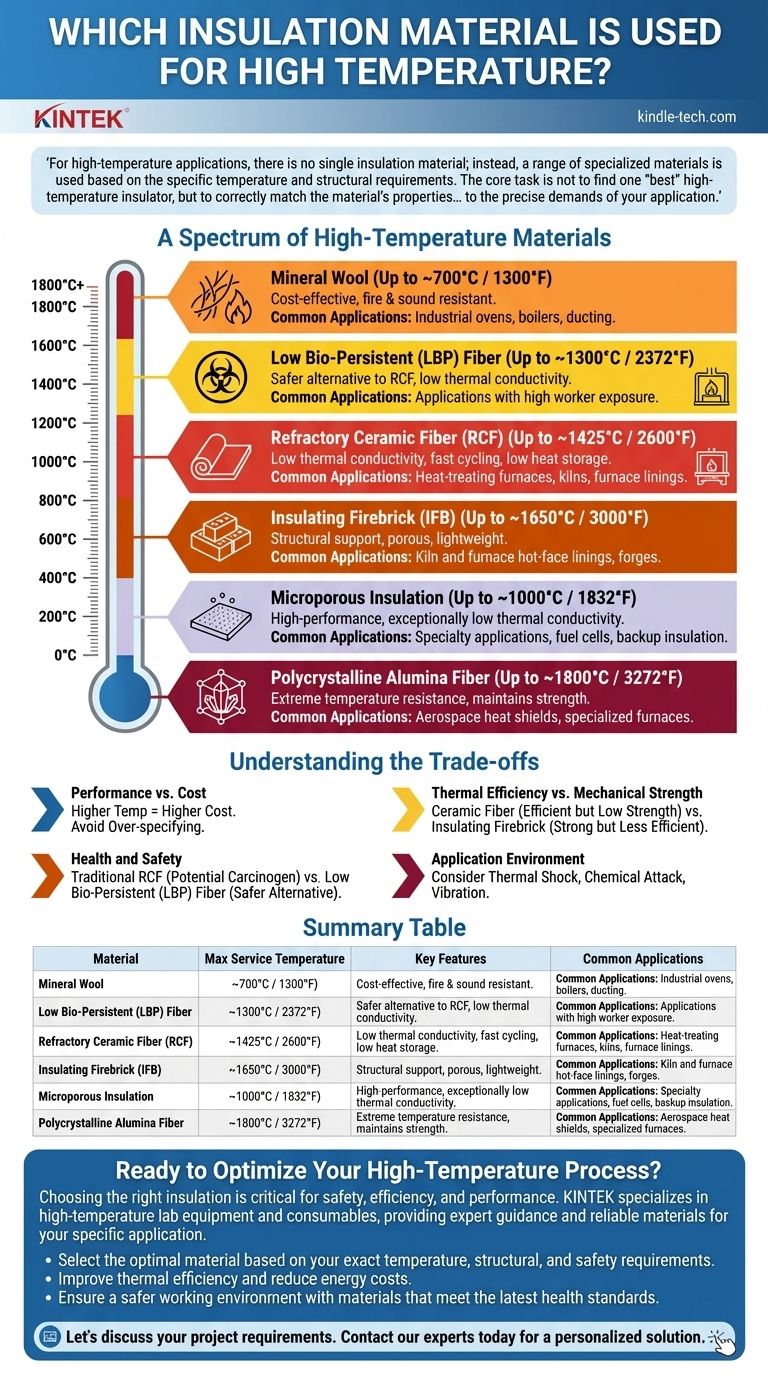
For high-temperature applications, there is no single insulation material; instead, a range of specialized materials is used based on the specific temperature and structural requirements. The most common choices include mineral wool for moderate heat, refractory ceramic fiber (RCF) for furnaces and kilns, and specialized insulating firebricks or polycrystalline fibers for the most extreme environments.
The core task is not to find one "best" high-temperature insulator, but to correctly match the material's properties—its maximum service temperature, physical form, and safety profile—to the precise demands of your application.
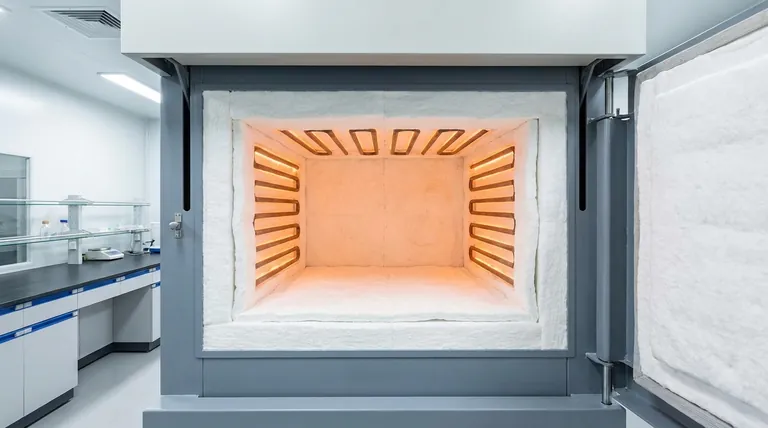

A Spectrum of High-Temperature Materials
"High temperature" is a relative term in engineering. A material suitable for a boiler is insufficient for a metallurgical furnace. The materials are best understood as a spectrum of increasing temperature resistance and cost.
Mineral Wool (Up to ~700°C / 1300°F)
Mineral wool, also known as rock or slag wool, is created by spinning molten rock and minerals into fine fibers. It serves as the entry point for high-temperature industrial applications.
It offers excellent fire resistance and sound-dampening qualities, making it a versatile choice for applications like industrial ovens, boiler systems, and exhaust ducting where temperatures exceed the limits of standard fiberglass.
Refractory Ceramic Fiber (RCF) (Up to ~1425°C / 2600°F)
Refractory Ceramic Fiber is the workhorse of high-temperature insulation. It is an aluminum-silicate material manufactured by melting and fiberizing minerals, available in forms like blankets, boards, paper, and modules.
RCF has very low thermal conductivity and low heat storage, meaning it heats up and cools down quickly. This makes it ideal for cyclical applications like heat-treating furnaces, kilns, and furnace linings.
Low Bio-Persistent (LBP) Fiber (Up to ~1300°C / 2372°F)
LBP fibers, also known as Alkaline Earth Silicate (AES) wool, were developed as a safer alternative to RCF. They have a chemical composition that allows them to be more readily dissolved and cleared by the body if inhaled.
These materials offer thermal performance very similar to RCF but with a significantly improved health and safety profile. They are increasingly used in Europe and for applications where worker exposure is a primary concern.
Insulating Firebrick (IFB) (Up to ~1650°C / 3000°F)
Unlike fiber blankets, Insulating Firebricks are rigid, lightweight bricks with a porous structure. Their key advantage is providing structural support in addition to insulation.
IFBs are graded by their maximum service temperature. They are used to build the hot-face lining of kilns, forges, and certain types of furnaces where mechanical stability is required.
Microporous Insulation (Up to ~1000°C / 1832°F)
Microporous insulation is a high-performance material typically composed of pressed fumed silica, opacifiers, and reinforcing fibers. Its unique structure gives it exceptionally low thermal conductivity, often outperforming fiber blankets of the same thickness.
Due to its high cost, it is used in specialty applications where space is extremely limited but maximum thermal performance is non-negotiable, such as in fuel cells or as backup insulation in industrial ladles.
Polycrystalline Alumina Fiber (Up to ~1800°C / 3272°F)
For the most extreme temperature environments, polycrystalline alumina (PCW) or zirconia fibers are used. These materials are manufactured through a chemical sol-gel process rather than melting.
They maintain their strength and insulating properties at temperatures far beyond the limits of standard ceramic fibers. Common applications include aerospace heat shields and specialized laboratory or semiconductor furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material requires a clear understanding of its inherent compromises. No material is perfect for every scenario.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct and steep correlation between a material's maximum service temperature and its cost. A roll of mineral wool is exponentially cheaper than a similar-sized blanket of polycrystalline alumina fiber. Over-specifying the material leads to unnecessary expense.
Thermal Efficiency vs. Mechanical Strength
Materials like ceramic fiber blankets are extremely efficient insulators but have almost no mechanical strength. Conversely, insulating firebricks provide structural support but are generally less effective insulators than fiber products of the same thickness.
Health and Safety
This is a critical consideration. Traditional Refractory Ceramic Fibers (RCF) are classified as a potential carcinogen, requiring strict handling procedures and personal protective equipment (PPE). The development of Low Bio-Persistent fibers directly addresses this risk, often making them the superior choice despite a slightly lower temperature rating.
Application Environment
The choice is not just about temperature. You must consider factors like thermal shock (rapid temperature changes), chemical attack from process gases, and vibration. A rigid board may be better than a blanket in a high-vibration environment, even if their temperature ratings are identical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct material, start by defining the absolute requirements of your project. The answer will emerge from these constraints.
- If your primary focus is general industrial use (furnaces, kilns below 1300°C): Your choice is likely between Refractory Ceramic Fiber (RCF) and its safer Low Bio-Persistent (LBP) alternative.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and load-bearing: Your only viable option is an appropriately graded Insulating Firebrick (IFB).
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal performance in a tight space: Microporous insulation is the superior technical choice, provided the budget allows for it.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures above 1400°C: You must use advanced materials like Polycrystalline Alumina (PCW) or Zirconia fibers.
By moving beyond a single material and focusing on these operational requirements, you can select an insulation solution that is safe, efficient, and perfectly suited to your goal.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Service Temperature | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral Wool | Up to 700°C (1300°F) | Cost-effective, fire & sound resistant | Industrial ovens, boilers, ducting |
| Refractory Ceramic Fiber (RCF) | Up to 1425°C (2600°F) | Low thermal conductivity, fast cycling | Heat-treating furnaces, kilns |
| Low Bio-Persistent (LBP) Fiber | Up to 1300°C (2372°F) | Safer alternative to RCF | Applications with high worker exposure |
| Insulating Firebrick (IFB) | Up to 1650°C (3000°F) | Structural support, porous | Kiln and furnace hot-face linings |
| Polycrystalline Alumina Fiber | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) | Extreme temperature resistance | Aerospace, semiconductor furnaces |
Ready to Optimize Your High-Temperature Process?
Choosing the right insulation is critical for safety, efficiency, and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and reliable materials for your specific application—whether you're operating a furnace, kiln, or a specialized research environment.
We help you:
- Select the optimal material based on your exact temperature, structural, and safety requirements.
- Improve thermal efficiency and reduce energy costs.
- Ensure a safer working environment with materials that meet the latest health standards.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today for a personalized solution that maximizes your lab's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a furnace and an oven in a laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Heat Needs
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Research
- What is the use of high temperature muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the annealing temperature of quartz? Achieve Optimal Thermal Stability for Your Components



















