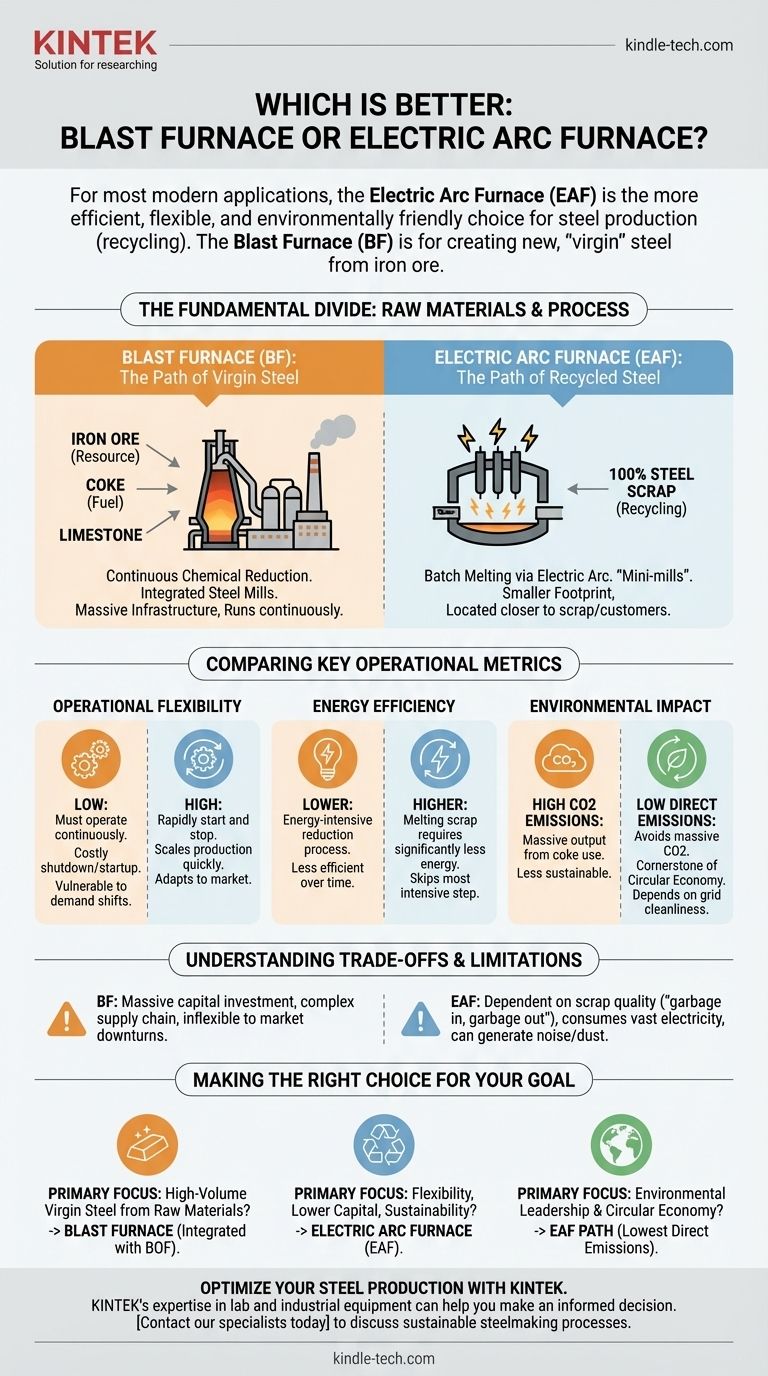
For most modern applications, the Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the more efficient, flexible, and environmentally friendly choice for steel production. This is because it is designed to recycle existing steel scrap, a process that requires significantly less energy and produces fewer emissions than creating steel from raw materials. The traditional Blast Furnace (BF) is not inherently inferior, but serves a different purpose: creating new, "virgin" steel from iron ore.
The choice between a Blast Furnace and an Electric Arc Furnace is not a simple matter of better versus worse. It is a strategic decision dictated by the primary input material: a Blast Furnace is for creating virgin steel from iron ore, while an Electric Arc Furnace is for recycling scrap steel into new products.
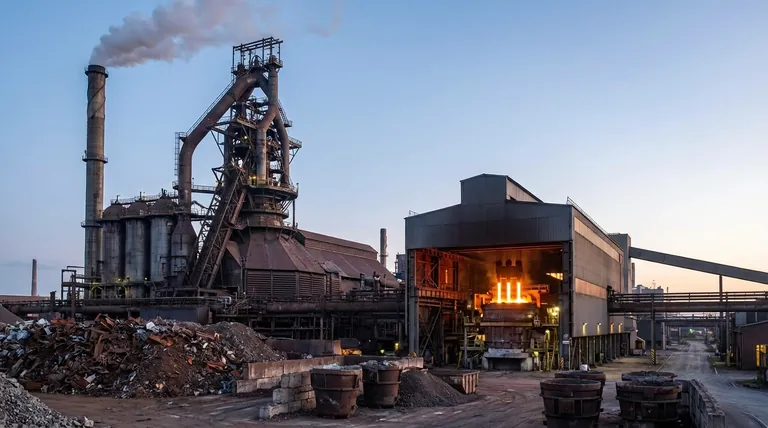

The Fundamental Divide: Raw Materials and Process
The core difference between these two furnace types lies in what they consume and how they operate. They represent two distinct philosophies in steelmaking.
Blast Furnace: The Path of Virgin Steel
A Blast Furnace is the starting point for integrated steel mills, which create steel from natural resources. It operates through a continuous chemical reduction process.
The system is fed a mixture of iron ore, coke (a high-carbon fuel derived from coal), and limestone. This mixture is heated to extreme temperatures, causing chemical reactions that separate pure iron from its ore. This molten iron is then further processed into steel, typically in a Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF).
Because of this complex process, Blast Furnaces require massive infrastructure and are designed to run continuously, often for years at a time without stopping.
Electric Arc Furnace: The Path of Recycled Steel
An Electric Arc Furnace is the centerpiece of "mini-mills," which are smaller, more specialized operations. Its primary function is recycling.
The furnace is charged with up to 100% steel scrap. Large graphite electrodes are lowered into the furnace, and an immense electrical current creates an arc between them, generating intense heat that melts the scrap.
This process gives EAFs a much smaller physical footprint and allows them to be built closer to sources of scrap and the customers they serve.
Comparing Key Operational Metrics
When you evaluate the two technologies side-by-side, the advantages of the EAF model for a modern, dynamic market become clear.
Operational Flexibility
The ability to adapt to market demand is a critical difference. An EAF can be rapidly started and stopped, allowing a mill to scale production up or down in a matter of hours.
A Blast Furnace, by contrast, is highly inflexible. Once running, it must operate continuously. Shutting it down is a monumental and costly task, making plants with BFs vulnerable to sudden shifts in demand.
Energy Efficiency
An EAF is significantly more energy-efficient because melting scrap requires far less energy than chemically reducing iron ore. It skips the most energy-intensive step of primary steelmaking.
While Blast Furnaces have become more efficient over time, they cannot compete on this metric due to the fundamental physics and chemistry of their process.
Environmental Impact
The EAF route is the clear winner for environmental performance, particularly regarding carbon emissions. By using recycled scrap and electricity, an EAF avoids the massive CO2 output generated by using coke to reduce iron ore in a Blast Furnace.
This makes the EAF a cornerstone of the circular economy and a key technology for decarbonizing the steel industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Neither technology is perfect. Choosing one over the other involves accepting a specific set of operational constraints and challenges.
The Scrap Quality Dependency of EAFs
The mantra for an EAF is "garbage in, garbage out." The quality of the finished steel is directly dependent on the quality of the scrap metal used as input.
Contaminants in scrap, such as copper or tin, can be difficult and expensive to remove. This can limit the ability of some EAFs to produce the highest-purity steel grades required for certain demanding applications.
The Scale and Inflexibility of Blast Furnaces
A Blast Furnace is an enormous, long-term commitment. It requires massive capital investment, a complex supply chain for raw materials, and a stable, high-volume market for its output.
Its inability to shut down quickly means it must continue producing even during market downturns, leading to potential oversupply and financial losses.
EAFs Are Not Without an Environmental Footprint
While an EAF's direct emissions are low, it consumes a vast amount of electricity. The overall carbon footprint of an EAF is therefore tied to the cleanliness of the electrical grid it draws from.
Furthermore, the process can generate significant noise and dust, which must be managed through sophisticated environmental controls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "better" furnace is the one that aligns with your strategic objectives, resource availability, and market position.
- If your primary focus is producing high-volume steel from raw materials: The Blast Furnace, integrated with a Basic Oxygen Furnace (BF-BOF), remains the necessary technology for this traditional, large-scale approach.
- If your primary focus is flexibility, lower capital cost, and sustainability: The Electric Arc Furnace is the superior choice, capitalizing on recycled steel scrap to serve regional markets efficiently.
- If your primary focus is environmental leadership: The EAF path is the clear winner due to its drastically lower direct carbon emissions and its central role in the circular economy.
Ultimately, understanding your input material—virgin ore or recycled scrap—is the key to choosing the correct steelmaking technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Blast Furnace (BF) | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Input | Iron ore, coke, limestone | Scrap steel (up to 100%) |
| Process Type | Continuous chemical reduction | Batch melting via electric arc |
| Flexibility | Low (must run continuously) | High (can start/stop quickly) |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (energy-intensive reduction) | Higher (melting requires less energy) |
| Environmental Impact | High CO2 emissions from coke | Low direct emissions (depends on grid) |
| Ideal For | Large-scale virgin steel production | Recycling, regional markets, flexibility |
Optimize your steel production with the right furnace technology. Whether you're focused on large-scale virgin steel or flexible, eco-friendly recycling, KINTEK's expertise in lab and industrial equipment can help you make an informed decision. Contact our specialists today to discuss how our solutions support efficient, sustainable steelmaking processes tailored to your operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results



















