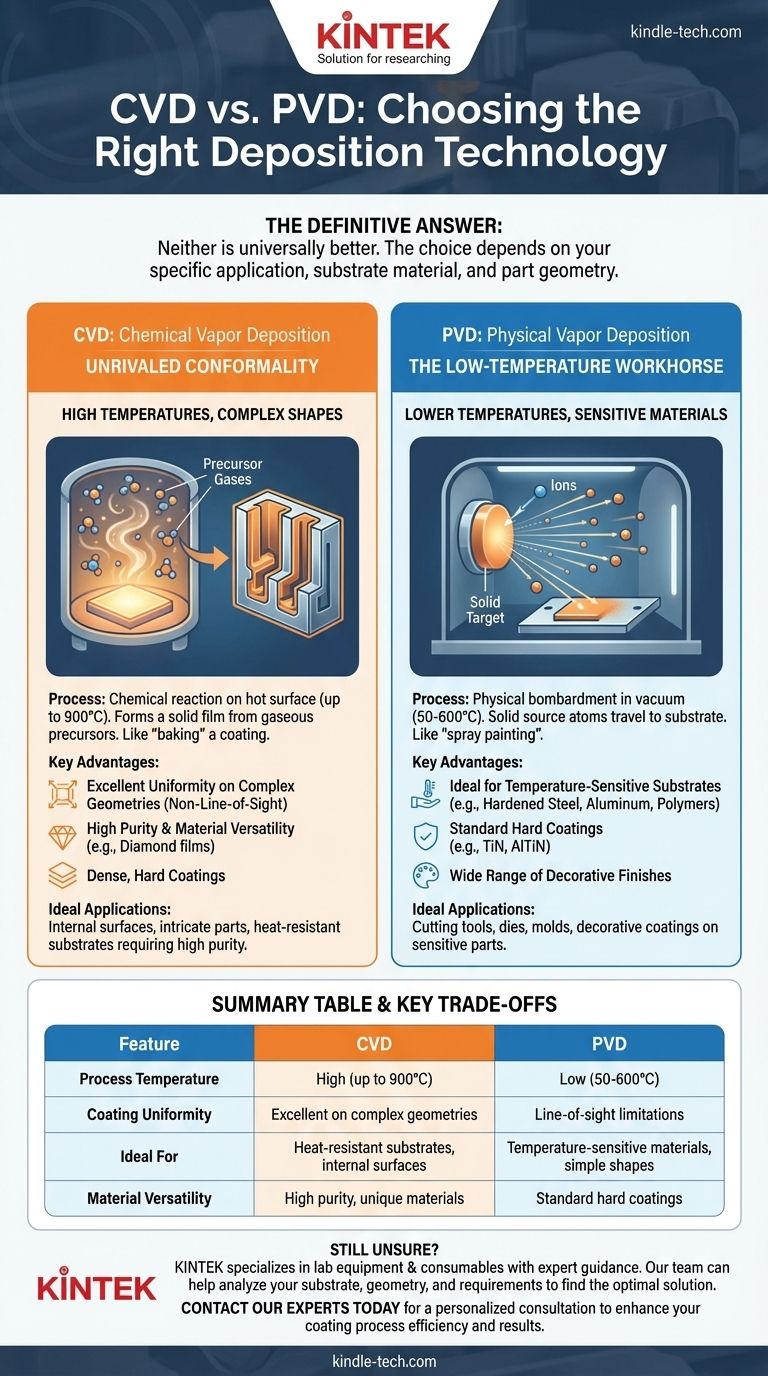
The definitive answer is that neither is universally better. Choosing between Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a critical engineering decision that depends entirely on your specific application, the material of your substrate, and the geometry of the part being coated. CVD excels at creating uniform, conformal coatings on complex shapes but requires very high temperatures. PVD operates at much lower temperatures, making it ideal for heat-sensitive materials, but it is a line-of-sight process with limitations in coating uniformity on intricate parts.
The core trade-off is simple: CVD offers superior coating uniformity and purity at the cost of high processing temperatures, while PVD provides a lower-temperature solution that is ideal for sensitive substrates but is limited by its line-of-sight application.

The Fundamental Difference: Chemical vs. Physical
To make an informed choice, you must first understand how each process works. Their names describe their core mechanisms, which dictate their respective strengths and weaknesses.
How CVD Works
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a substrate is placed in a chamber and heated to a high temperature, often up to 900°C. Precursor gases are introduced, which then react or decompose on the hot surface of the substrate.
This chemical reaction forms a new, solid material as a thin film directly on the part. Think of it as "baking" a coating onto a surface; the reaction happens everywhere the surface is hot, ensuring a uniform layer.
How PVD Works
In Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), a solid source material (the "target") is bombarded with high-energy ions inside a vacuum chamber. This bombardment physically knocks atoms or molecules off the target, which then travel in a straight line and deposit onto the cooler substrate.
This process is analogous to spray painting. The coating material travels directly from the source to the part, which is why it is called a line-of-sight process.
When to Choose CVD: Unrivaled Conformality
CVD is the superior choice when the geometry of your part or the purity of the film is the most critical factor.
The Power of Conformal Coating
Because CVD is driven by a surface chemical reaction, it is not limited by line-of-sight effects. The precursor gases flow around the part, reaching every exposed surface.
This allows CVD to deposit a film of highly uniform thickness over complex shapes, inside deep holes, and within intricate channels—areas PVD simply cannot reach effectively.
High Purity and Material Versatility
The CVD process results in extremely high-purity, fine-grained, and dense coatings that are often harder than materials produced by other methods.
Furthermore, it can be used to deposit materials that are difficult to evaporate for PVD. If an element is available as a volatile chemical compound, it can likely be used in a CVD process.
When to Choose PVD: The Low-Temperature Workhorse
PVD's primary advantage is its ability to coat materials that cannot survive the extreme heat of the CVD process.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
PVD processes operate at significantly lower temperatures, typically between 50°C and 600°C. This makes PVD the only viable choice for coating temperature-sensitive substrates.
This includes hardened tool steels, aluminum alloys, polymers, and other materials whose properties would be negatively altered or destroyed by the high heat of CVD.
Common Applications
PVD is widely used to deposit hard, wear-resistant coatings on cutting tools, dies, and molds. It is also a popular choice for decorative coatings in industries from automotive to jewelry, providing durable color and finish on temperature-sensitive parts.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Your decision will ultimately come down to balancing four key factors.
Substrate Temperature vs. Material
This is the most important constraint. If your part cannot withstand temperatures of 800-900°C without warping, softening, or losing its temper, CVD is not an option. PVD is the clear solution for heat-sensitive materials.
Coating Uniformity vs. Part Geometry
If you need to coat the inside of a tube or a component with complex, non-line-of-sight features, CVD is the superior technology. PVD will result in an uneven coating, with thick deposits on exposed faces and little to no coating in shaded areas.
Material Choice and Film Properties
CVD is capable of producing certain unique materials, like large-area graphene sheets or highly pure diamond films, that are difficult or impossible with PVD. However, PVD offers an extremely broad portfolio of standard hard coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) that are industry standards for wear resistance.
Cost and Process Complexity
While CVD is sometimes cited as being more cost-effective, the total cost depends heavily on the specific materials, equipment, and production volume. The high energy and vacuum requirements for PVD can be costly, but the high temperatures and precursor gas handling for CVD also represent significant expenses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
There is no single "best" method. Base your decision on your primary technical goal.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex internal geometry or achieving exceptional purity: CVD is the superior choice, provided your substrate material can withstand the extreme processing heat.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material like hardened steel, aluminum, or a polymer: PVD is the default—and often only—viable technology.
- If your primary focus is applying a standard wear-resistant coating to a simple, line-of-sight surface: PVD offers a mature, versatile, and highly effective range of solutions.
By analyzing your substrate, geometry, and performance requirements, you can confidently select the deposition technology that best achieves your engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | High (up to 900°C) | Low (50-600°C) |
| Coating Uniformity | Excellent on complex geometries | Line-of-sight limitations |
| Ideal For | Heat-resistant substrates, internal surfaces | Temperature-sensitive materials, simple shapes |
| Material Versatility | High purity, unique materials (e.g., diamond films) | Standard hard coatings (e.g., TiN, AlTiN) |
Still unsure which coating technology is right for your project?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert guidance on deposition technologies. Our team can help you analyze your substrate material, part geometry, and performance requirements to determine whether CVD or PVD is the optimal solution for your specific application.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how we can enhance your coating process efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















