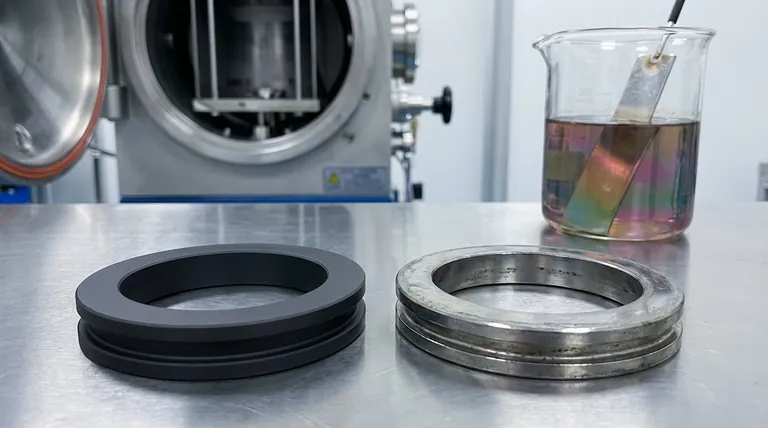
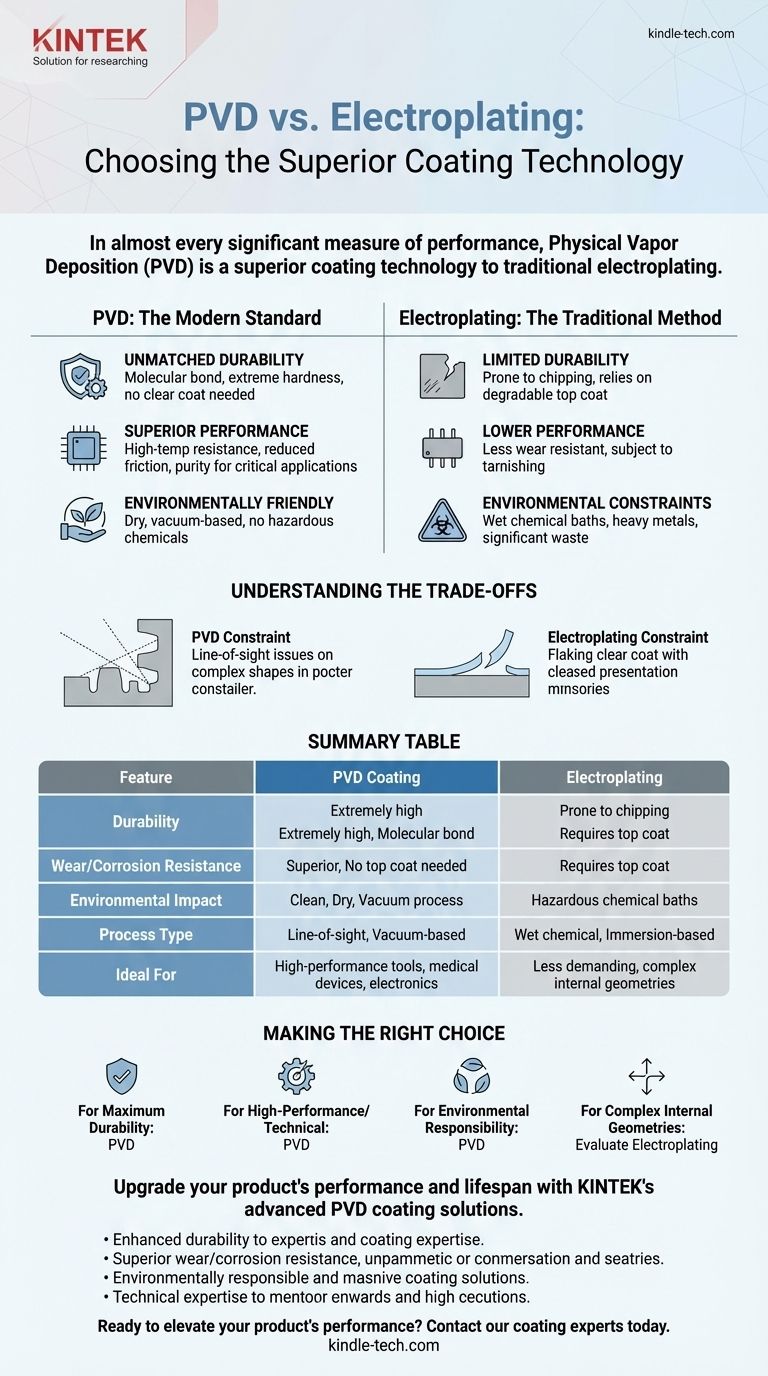
In almost every significant measure of performance, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a superior coating technology to traditional electroplating. PVD provides a finish that is significantly more durable, corrosion-resistant, and wear-resistant. Furthermore, it is a much more environmentally friendly process, avoiding the hazardous chemical baths inherent to electroplating.
The core difference is one of technology and performance. PVD is a modern, vacuum-based process that creates a strong, molecularly bonded coating, while electroplating is a traditional, wet chemical process that is fundamentally less durable and poses greater environmental risks.

Why PVD Has Eclipsed Electroplating
Physical Vapor Deposition is not just an alternative to electroplating; it is a technological leap forward. The process involves vaporizing a solid material in a vacuum and depositing it onto the target object, creating an extremely pure, hard, and thin film.
Unmatched Durability and Wear Resistance
The bond created by PVD is at the molecular level, making it incredibly strong. This results in a finish that is far harder and more resistant to scratches and corrosion than electroplated coatings.
A key weakness of electroplating is its reliance on a clear top coat to protect against tarnishing. This top coat degrades over time, exposing the plated layer to wear and discoloration. PVD coatings do not require a clear coat, ensuring their brilliant finish lasts significantly longer.
Superior Performance in Demanding Applications
PVD coatings offer a combination of hardness, reduced friction, and high-temperature resistance. These properties are essential for high-performance applications.
This makes PVD the standard choice for components that must function flawlessly under stress, such as medical devices, microchips, solar panels, and high-performance tooling. The purity and cleanliness of the PVD process are critical for these sensitive applications.
A Modern, Environmentally Friendly Process
The environmental impact is a stark point of contrast. Electroplating involves submerging parts in chemical baths containing heavy metals and hazardous substances, creating significant waste disposal challenges.
PVD is a dry, vacuum-based process. It does not release harmful chemicals or produce hazardous waste, making it a much cleaner and more sustainable technology.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD is superior in performance, no technology is without its specific considerations. The decision between PVD and electroplating hinges on understanding their fundamental operational differences.
The Limitations of Electroplating
The primary drawback of electroplating is its lack of durability. The finish is prone to chipping, flaking, and tarnishing, especially when the protective clear coat fails. This leads to a shorter product lifespan and higher maintenance.
Process and Geometry Constraints
PVD is a line-of-sight process, meaning the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This can make it challenging to evenly coat highly complex shapes with deep recesses or internal channels.
Electroplating, being a wet process, can sometimes offer more uniform coverage on these intricate geometries. However, for most common product shapes, PVD technology provides excellent coverage.
Cost vs. Lifecycle Value
While traditional electroplating may sometimes have a lower initial cost, PVD often provides superior long-term value. The extended lifespan, low maintenance, and enhanced performance of PVD-coated products prevent the need for costly recoating or replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be driven by the performance requirements and long-term goals for your product.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and longevity: PVD is the definitive choice for a finish that resists wear, corrosion, and tarnishing for years.
- If your primary focus is a high-performance or technical application: PVD is the only viable option for parts requiring purity, heat resistance, and reliability, such as in medical or electronic devices.
- If your primary focus is environmental responsibility: PVD is the far superior process, avoiding the hazardous waste streams associated with electroplating.
- If your primary focus is coating a highly complex internal geometry: You must evaluate if PVD's line-of-sight process can provide adequate coverage, as this is one of the few scenarios where electroplating might be considered.
Choosing the right coating is an investment in your product's quality, reputation, and lifespan.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Extremely high, molecular bond | Prone to chipping and flaking |
| Wear/Corrosion Resistance | Superior, no top coat needed | Requires protective top coat |
| Environmental Impact | Clean, dry, vacuum process | Uses hazardous chemical baths |
| Process Type | Line-of-sight, vacuum-based | Wet chemical, immersion-based |
| Ideal For | High-performance tools, medical devices, electronics | Less demanding applications, complex internal geometries |
Upgrade your product's performance and lifespan with KINTEK's advanced PVD coating solutions.
As a specialist in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK understands the critical need for durable, reliable coatings that withstand demanding environments. Our PVD coating services provide:
- Enhanced durability for longer product lifecycles
- Superior wear and corrosion resistance reducing maintenance needs
- Environmentally responsible processes aligning with modern sustainability goals
- Technical expertise for medical, electronic, and industrial applications
Ready to elevate your product's performance? Contact our coating experts today to discuss how our PVD solutions can meet your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers



















