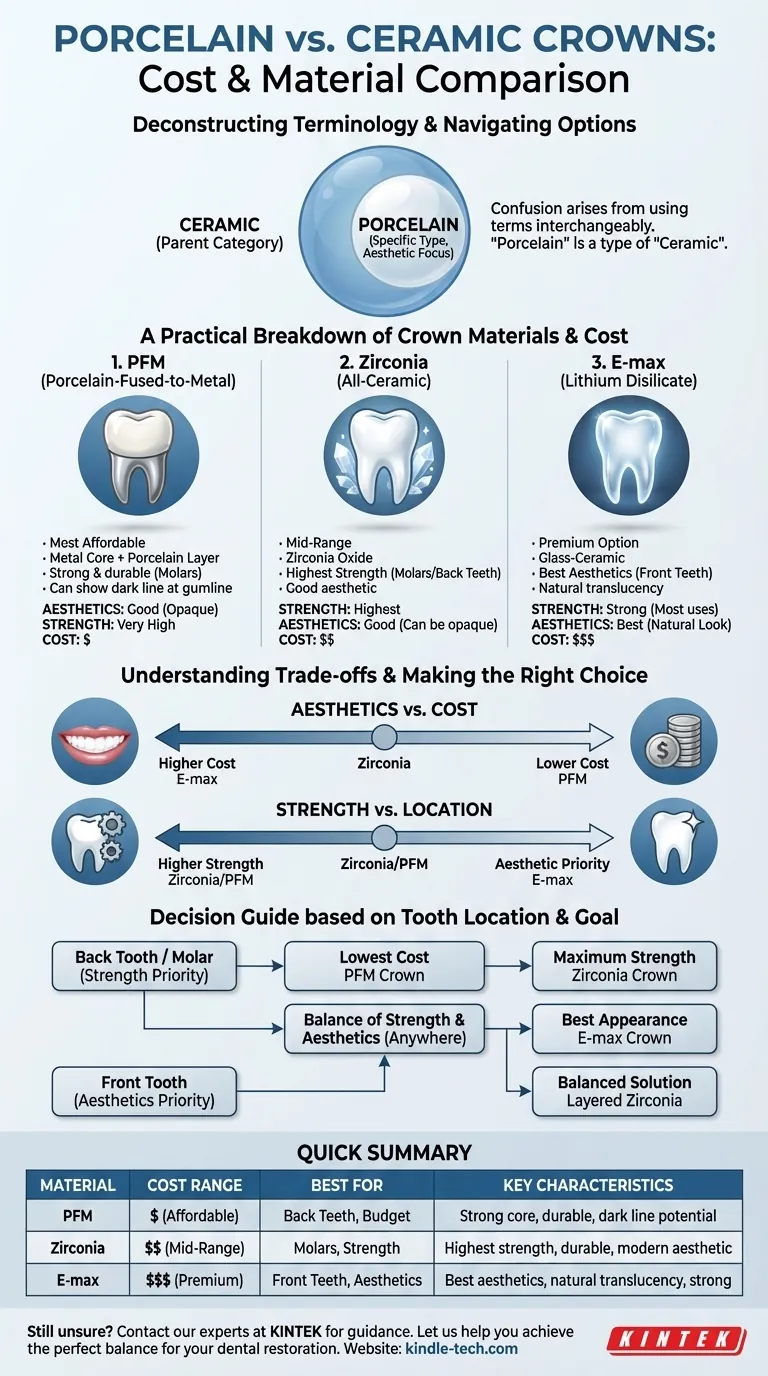
In most clinical situations, a standard ceramic crown is cheaper than a premium all-porcelain crown. However, the terms "ceramic" and "porcelain" are often used interchangeably, which creates confusion. The true cost difference depends on the specific type of ceramic material used, such as Zirconia, E-max, or Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM), as the price reflects a trade-off between strength, aesthetics, and manufacturing complexity.
The question isn't simply "porcelain vs. ceramic," because porcelain is a type of ceramic. The real decision is between different ceramic materials, each offering a unique balance of cost, durability, and appearance suited for different teeth in your mouth.
Deconstructing the Terminology: Porcelain vs. Ceramic
To understand the cost, you must first understand the materials. The confusion between these terms is the primary source of ambiguity in pricing.
What is "Ceramic"?
In dentistry, ceramic is a broad category of materials that are non-metallic and inorganic. Think of it as the parent category that includes everything from glass-like materials to incredibly tough, opaque ones.
Modern dental ceramics are prized for their biocompatibility and ability to mimic the appearance of natural teeth.
What is "Porcelain"?
Porcelain is a specific type of ceramic, traditionally made from feldspar, kaolin, and quartz. It is known for its excellent translucency and lifelike appearance, making it a benchmark for dental aesthetics.
However, traditional porcelain can be more brittle than newer ceramic formulations.
Why the Confusion?
The confusion arises from common dental shorthand. When a dentist says "porcelain crown," they might be referring to a Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) crown or a traditional feldspathic porcelain crown.
When they say "all-ceramic crown," they are typically referring to modern, high-strength options like Zirconia or E-max (lithium disilicate), which contain no metal.
A Practical Breakdown of Crown Materials & Cost
The cost of a crown is directly tied to the material used and the labor involved. Here is a breakdown from the most common and cost-effective to the most premium options.
1. Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Crowns
PFM crowns have a metal alloy core covered by a layer of porcelain. For decades, they were the standard for restorative dentistry.
- Cost: Generally the most affordable option.
- Strength: Very strong and durable due to the metal substructure. Suitable for any tooth, including molars.
- Aesthetics: Good, but not perfect. The metal base blocks light, making them look more opaque than natural teeth. A dark line can also become visible at the gumline over time if gums recede.
2. All-Ceramic: Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia is a type of ceramic oxide that is exceptionally strong and fracture-resistant. It is the modern workhorse for crowns, especially on back teeth.
- Cost: A mid-range option, often slightly more expensive than PFM but cheaper than premium aesthetic ceramics.
- Strength: The strongest all-ceramic option, making it the ideal choice for molars that endure heavy chewing forces.
- Aesthetics: Good, but can be opaque. Newer formulations and layering techniques have greatly improved their appearance, making them suitable for some front teeth as well.
3. All-Ceramic: E-max (Lithium Disilicate) Crowns
E-max is a specific brand of lithium disilicate, a type of glass-ceramic known for its outstanding aesthetics.
- Cost: A premium option, generally more expensive than both PFM and Zirconia.
- Strength: Strong enough for most applications, including molars, but not as fracture-proof as solid zirconia.
- Aesthetics: Considered the gold standard for appearance. Its high translucency and light-handling properties allow it to blend seamlessly with natural teeth, making it the top choice for front teeth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a crown is never about a single factor. You are always balancing three key considerations.
Cost vs. Aesthetics
The most lifelike and translucent materials, like E-max, command a higher price. The most cost-effective option, PFM, makes a compromise on aesthetics due to its metal base. Zirconia sits in the middle, offering good strength and acceptable aesthetics at a moderate price point.
Strength vs. Location in the Mouth
The location of the tooth is critical. A back molar needs maximum strength to withstand chewing forces, making a Zirconia or PFM crown an excellent choice. A front tooth is highly visible, making aesthetics the priority, which points toward an E-max crown.
Biocompatibility and Gum Health
All-ceramic crowns like Zirconia and E-max are highly biocompatible and do not have a metal margin. This eliminates the risk of the "dark line" at the gumline that can appear with PFM crowns, leading to a more natural-looking and stable result over the long term.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Consult with your dentist about the specific needs of your tooth, but use this guide to inform your conversation.
- If your primary focus is the lowest cost for a back tooth: A PFM crown is a time-tested and durable solution.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability for a molar: A solid Zirconia crown is the modern standard and offers excellent value.
- If your primary focus is the best possible appearance for a visible front tooth: An E-max (lithium disilicate) crown is the superior choice for a seamless, natural look.
- If you want a balance of good aesthetics and strength anywhere in the mouth: A layered Zirconia crown offers a strong core with a more beautiful porcelain exterior.
Understanding these materials empowers you to have an informed discussion with your dentist about the best long-term solution for your health and budget.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Cost Range | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| PFM (Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal) | Most Affordable | Back teeth, budget-conscious patients | Strong metal core, good durability, may show dark gumline |
| Zirconia | Mid-Range | Molars, strength-focused restorations | Highest strength, good durability, modern aesthetic option |
| E-max (Lithium Disilicate) | Premium | Front teeth, aesthetic-focused restorations | Best aesthetics, natural translucency, strong for most applications |
Still unsure which crown material is right for your specific dental needs?
Our dental experts at KINTEK are here to help you navigate the complexities of restorative materials. We provide high-quality dental ceramics and equipment to dental professionals worldwide, ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Let us help you achieve the perfect balance of aesthetics, strength, and value for your dental restoration.
Contact our dental specialists today for personalized guidance on crown material selection and implementation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability



















