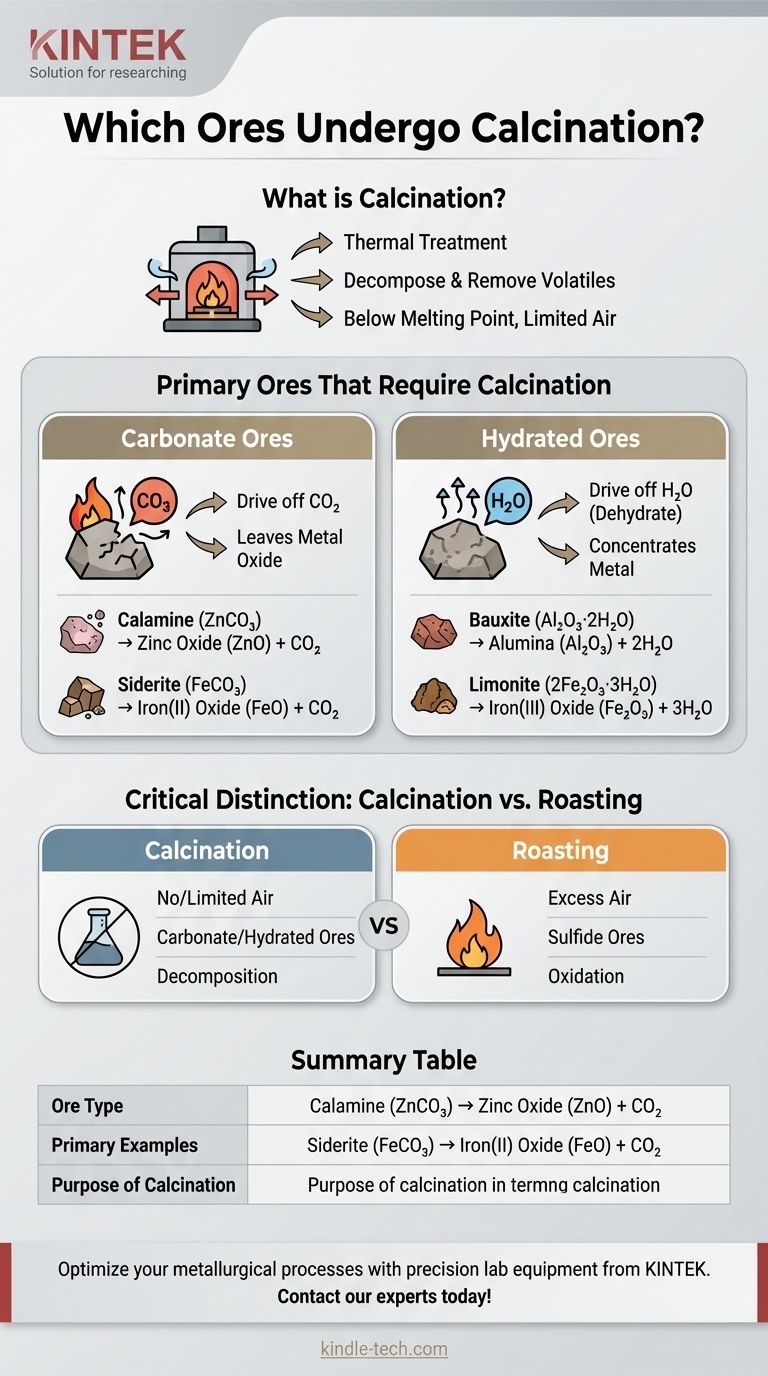
In metallurgy, calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to specific types of ores to purify them before the final metal extraction. It is used primarily for carbonate ores and hydrated ores, where the goal is to decompose the ore by heating it and drive off volatile impurities like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
The key to understanding calcination is to focus on the ore's chemical composition, not the metal it contains. The process is specifically designed to break down non-metallic compounds like carbonates and hydrates, leaving behind a more concentrated and reactive metal oxide.

Understanding the "Why" Behind Calcination
Calcination is a precise pyrometallurgical process. It involves heating an ore to a high temperature, but one that is still below its melting point, in a controlled atmosphere with little to no air.
The Core Purpose: Decomposition
The fundamental goal of calcination is to cause thermal decomposition. This chemical reaction breaks down the ore into a more desirable form, typically a metal oxide, which is easier to reduce to a pure metal in a later step.
The Key Condition: Limited Air
Calcination is deliberately carried out in the absence or a limited supply of air. This is a critical distinction, as it prevents the ore from oxidizing. The goal is simply to remove existing volatile components, not to add oxygen.
The Primary Ores That Require Calcination
Based on the principles above, we can identify the specific categories of ores that are ideal candidates for calcination.
Carbonate Ores
This is the most common application of calcination. Heating a metal carbonate drives off carbon dioxide, leaving the metal oxide.
Examples include:
- Calamine (Zinc Carbonate, ZnCO₃) → Zinc Oxide (ZnO) + CO₂
- Siderite (Iron(II) Carbonate, FeCO₃) → Iron(II) Oxide (FeO) + CO₂
- Limestone (Calcium Carbonate, CaCO₃) → Lime (CaO) + CO₂
Hydrated Ores
These ores contain water molecules (water of crystallization) chemically bonded within their structure. Calcination is used to drive off this water.
This process dehydrates the ore, which increases the concentration of the metal and often makes the ore more porous, improving its reactivity in subsequent smelting operations.
Examples include:
- Bauxite (Hydrated Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃·2H₂O) → Alumina (Al₂O₃) + 2H₂O
- Limonite (Hydrated Iron(III) Oxide, 2Fe₂O₃·3H₂O) → Iron(III) Oxide (Fe₂O₃) + 3H₂O
Critical Distinction: Calcination vs. Roasting
A common point of confusion is the difference between calcination and roasting. While both involve heating ores, their goals and conditions are fundamentally different, and they are applied to different types of ore.
Calcination: Decomposition Without Oxidation
As discussed, calcination's purpose is to remove pre-existing volatile compounds like CO₂ and H₂O. It is performed in the absence of air on carbonate and hydrated ores.
Roasting: Oxidation with Excess Air
Roasting, in contrast, is an oxidation process. It is performed in an excess of air and is primarily used for sulfide ores. The goal is to convert the metal sulfide into a metal oxide by reacting it with oxygen.
For example, Zinc Blende (ZnS) is roasted, not calcined, to produce Zinc Oxide (ZnO).
Applying This to Your Analysis
To determine the correct process, you must first identify the chemical nature of the ore.
- If your primary ore is a carbonate (e.g., ZnCO₃): Calcination is the required process to drive off carbon dioxide and produce the metal oxide.
- If your primary ore is hydrated (e.g., Al₂O₃·2H₂O): Calcination is used to remove the water of crystallization, yielding a concentrated, anhydrous oxide.
- If your primary ore is a sulfide (e.g., PbS or ZnS): Roasting is the appropriate process to convert the sulfide into an oxide; calcination is incorrect.
Ultimately, understanding the ore's chemical formula is the key to selecting the correct and most efficient metallurgical process.
Summary Table:
| Ore Type | Primary Examples | Purpose of Calcination |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonate Ores | Calamine (ZnCO₃), Siderite (FeCO₃) | Decompose to oxide, drive off CO₂ |
| Hydrated Ores | Bauxite (Al₂O₃·2H₂O), Limonite (2Fe₂O₃·3H₂O) | Dehydrate, remove H₂O, concentrate metal |
Optimize your metallurgical processes with precision lab equipment from KINTEK.
Understanding the precise thermal treatment required for calcination is critical for purifying carbonate and hydrated ores. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment designed for controlled, high-temperature processes like calcination, ensuring you achieve the perfect decomposition of your ores every time.
Whether you are processing bauxite for aluminum or calamine for zinc, our robust and reliable solutions help you increase yield, improve purity, and enhance operational efficiency.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal processing solution for your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















