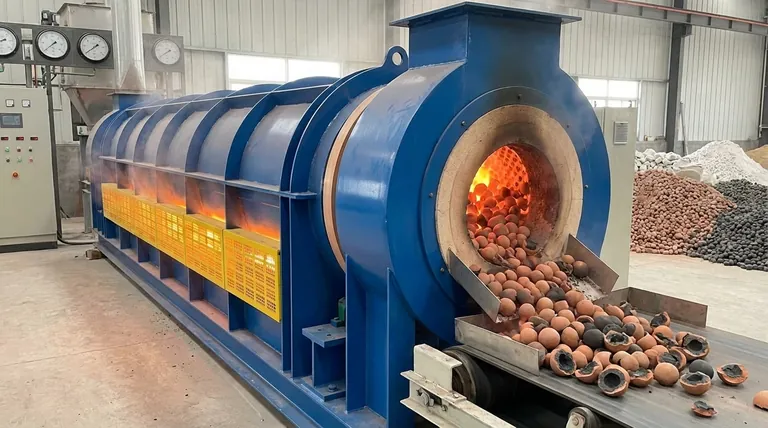
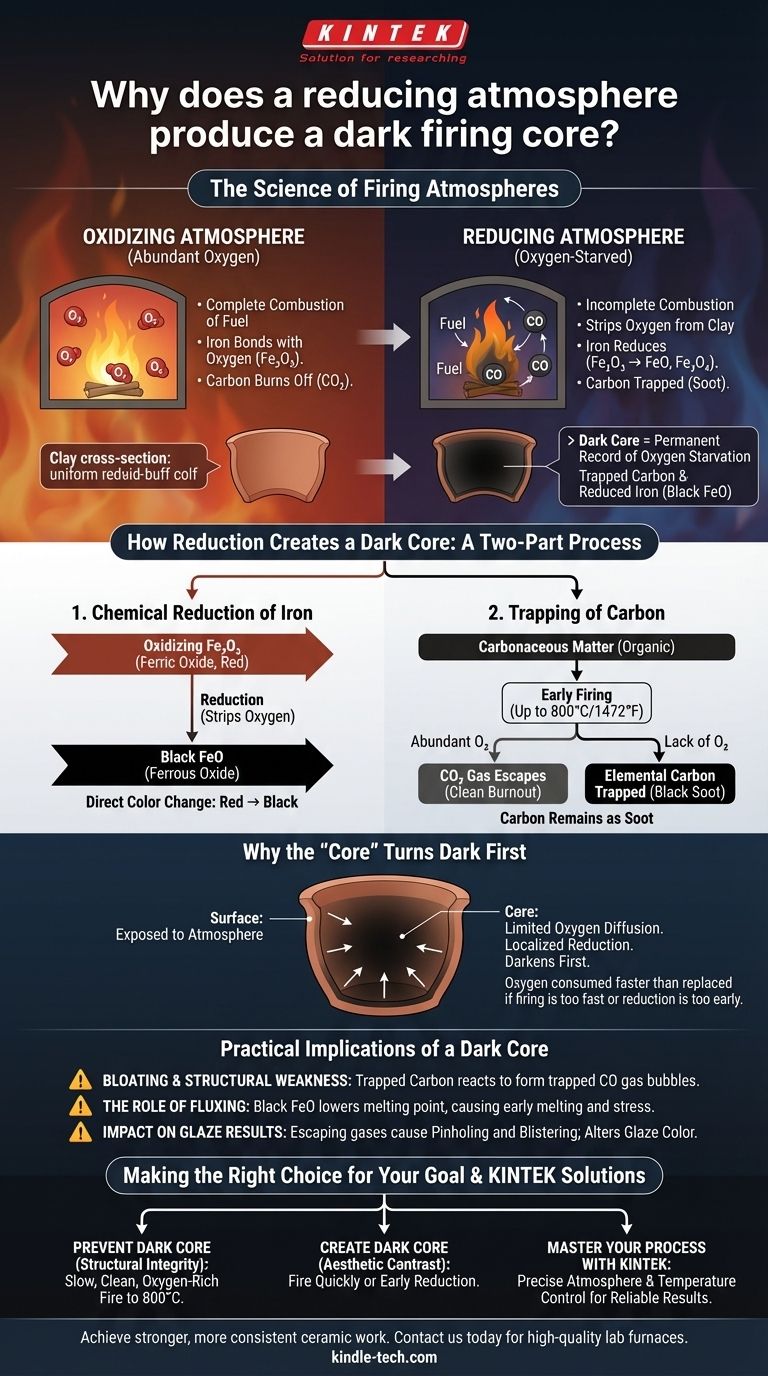
At its core, a reducing atmosphere produces a dark firing core because it lacks sufficient oxygen to burn out carbon impurities and to keep iron in its reddish, oxidized state. This oxygen-starved environment forces chemical reactions within the clay body that convert naturally occurring compounds into their darker forms, specifically black iron oxide and elemental carbon (soot).
The color of a ceramic core is a permanent record of the kiln's internal chemistry during firing. A dark core indicates that the center of the clay body did not have enough oxygen at a critical time, trapping unburnt carbon and creating chemically reduced, black-colored iron compounds.

The Chemistry of Firing: Oxidation vs. Reduction
To understand why a core turns dark, we must first understand the two fundamental types of kiln atmospheres. The balance between them is the single most important factor controlling the color of impurities in clay.
What Defines the Atmosphere?
The atmosphere inside a fuel-burning kiln is determined by the ratio of fuel to air. In an electric kiln, the atmosphere is naturally oxidizing unless combustible materials are introduced.
An oxidizing atmosphere has an abundance of oxygen. This allows for complete combustion of fuel and enables elements within the clay, like iron, to bond with oxygen.
A reducing atmosphere is oxygen-starved. This occurs when there is not enough air to completely burn the fuel, leading to an environment rich in unburnt fuel and carbon monoxide that actively seeks out oxygen from other sources—including the clay itself.
The Key Impurities in Clay
Nearly all natural clays contain two key impurities that are highly sensitive to the kiln atmosphere:
- Iron Oxides: Typically present as red iron oxide (ferric oxide, Fe₂O₃).
- Carbonaceous Matter: Residual organic material like decomposed plants and lignins.
How Reduction Creates a Dark Core
The formation of a dark core is a two-part process involving the transformation of both iron and carbon, driven by the lack of available oxygen inside the dense clay body.
The Chemical Reduction of Iron
In an oxygen-rich (oxidizing) fire, iron naturally forms ferric oxide (Fe₂O₃), which gives fired clay its characteristic warm red, orange, or buff color.
When the atmosphere becomes reducing, it is hungry for oxygen. It will strip oxygen atoms from the ferric oxide in the clay, "reducing" it to black iron oxide (ferrous oxide, FeO) or magnetite (Fe₃O₄). This is a direct color change from red/brown to black.
The Trapping of Carbon
During the early stages of firing (up to about 800°C / 1472°F), the organic matter in the clay must burn out. This requires plenty of oxygen to convert the carbon into carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas, which then escapes.
In a reducing atmosphere, there isn't enough oxygen to complete this process. Instead of burning away, the carbon remains trapped in the clay matrix as elemental carbon, which is essentially black soot.
Why the "Core" Turns Dark First
The outer surface of the pottery is directly exposed to the kiln atmosphere. The interior, or core, only gets oxygen that can slowly diffuse through the pores of the clay.
If the firing progresses too quickly or if the kiln is put into reduction too early, the oxygen in the core is consumed faster than it can be replaced. This creates a localized reducing environment inside the pot, even if the kiln atmosphere is oxidizing. The iron and carbon in the core are therefore reduced, turning dark, while the surface may re-oxidize later, creating a light-colored "sandwich" effect.
Understanding the Practical Implications
A dark core is not merely a cosmetic issue; it is often an indicator of structural problems and can have a significant impact on your final results.
Bloating and Structural Weakness
If carbon is not fully burned out before the clay body vitrifies (becomes glassy and non-porous), the trapped carbon can react with iron oxides at higher temperatures to produce carbon monoxide (CO) gas.
This gas, now trapped inside a sealed-off clay matrix, creates pressure and forms internal bubbles. This leads to bloating, deformation, and a structurally weak, brittle final product.
The Role of Fluxing
Black iron oxide (FeO) acts as a powerful flux, meaning it lowers the melting point of the clay around it. A dark core rich in FeO can begin to melt and become dense or glassy far sooner than the oxidized outer portion of the clay body, creating internal stress that can lead to cracking.
Impact on Glaze Results
Gases escaping from a dark core late in the firing process can bubble up through the molten glaze. This is a common cause of glaze defects like pinholing and blistering. The reduced state of the clay body beneath the glaze can also dramatically alter the final glaze color.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the atmosphere allows you to either prevent a dark core or create one for specific aesthetic effects. Your firing schedule is your primary tool.
- If your primary focus is preventing a dark core: Ensure a slow, clean, and oxygen-rich firing schedule up to at least 800°C (1472°F). This guarantees all carbonaceous matter has burned out before vitrification begins.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Avoiding a dark core is critical. A clean burnout period is the most important step for producing strong, stable ceramic ware.
- If your primary focus is achieving a dark core for aesthetic contrast: Fire more quickly through the early stages or introduce a reduction cycle early on to deliberately trap carbon and reduce the iron within the body.
By understanding the chemistry of reduction, you transform the firing process from an unpredictable ordeal into a controllable technique.
Summary Table:
| Cause of Dark Core | Effect on Ceramic |
|---|---|
| Reduction of Iron Oxide (Fe₂O₃ → FeO) | Creates black color |
| Trapping of Elemental Carbon (Soot) | Adds dark pigmentation |
| Localized Oxygen Starvation in Clay Body | Core darkens before surface |
Master your ceramic firing process with KINTEK. A dark firing core can indicate structural weakness and glaze defects. Whether your goal is to prevent this issue or harness it for artistic effect, precise control over your kiln's atmosphere is key. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and kilns that provide the reliable temperature and atmosphere control needed for perfect results. Let our experts help you choose the right equipment for your laboratory or studio. Contact us today to achieve stronger, more consistent ceramic work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product



















