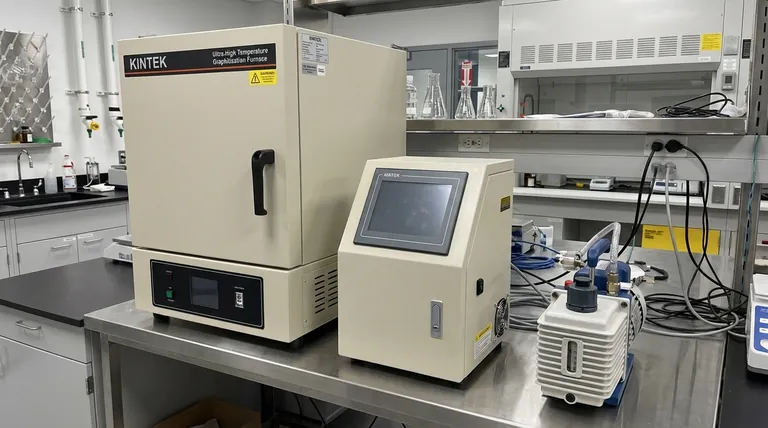
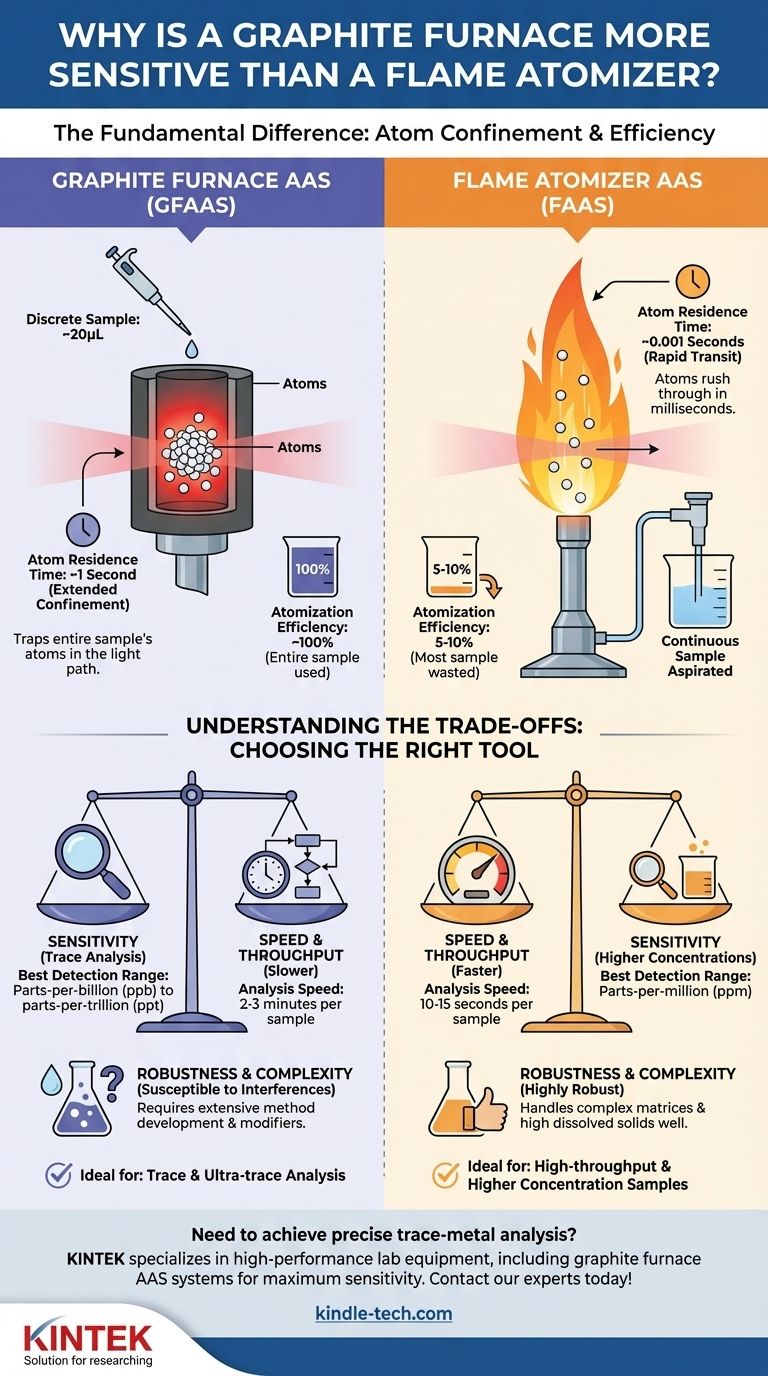
At its core, a graphite furnace is more sensitive than a flame atomizer because it is vastly more efficient at producing a dense, concentrated cloud of atoms and holding them in the instrument's light path for an extended period. A flame is a dynamic, high-velocity environment that wastes most of the sample and rushes atoms through the analysis zone in milliseconds, whereas a furnace traps the entire sample's atoms for a full second or more.
The fundamental difference in sensitivity is not about chemistry, but physics. Graphite Furnace AAS excels by maximizing two key factors: atom residence time and atomization efficiency, creating a stronger analytical signal from the same amount of sample.

The Critical Factor: Atom Confinement
The primary goal of an atomizer in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is to convert a sample into free, ground-state atoms that can absorb light. The sensitivity of the measurement is directly proportional to how well the atomizer performs this task within the path of the light beam.
Atom Residence Time
This is the single most important concept. Residence time refers to the average duration an individual atom spends in the instrument's light path.
In a flame atomizer, the sample is continuously sprayed into a rapidly burning flame. The vertical gas velocity is high, meaning an atom is swept through the light path in a fraction of a second (typically ~10⁻³ seconds).
In a graphite furnace, the sample is vaporized inside a small, enclosed graphite tube. This tube is positioned so the light beam passes directly through it. The atoms are temporarily confined, increasing their residence time to a second or more—a 1000-fold increase over the flame.
Atom Density and Efficiency
This refers to how effectively the atomizer converts the liquid sample into a cloud of atoms.
A flame atomizer is remarkably inefficient. The nebulizer continuously aspirates the sample, but only 5-10% of it forms droplets fine enough to reach the flame. The rest goes to waste.
A graphite furnace, by contrast, is nearly 100% efficient. A small, discrete volume (e.g., 20 microliters) is pipetted directly into the furnace. The programmed heating cycle ensures that this entire sample volume is vaporized and atomized, creating a dense, concentrated cloud of atoms.
How Each Atomizer Process Works
Understanding the mechanical process of each technique makes the sensitivity difference intuitive.
The Flame Atomizer (FAAS) Process
A flame is a continuous, steady-state system. The sample is constantly being aspirated, nebulized, and burned. The instrument measures a stable, continuous absorbance signal as long as the sample is being introduced. This makes the measurement fast and repeatable.
The Graphite Furnace (GFAAS) Process
A graphite furnace is a discrete, transient system. The analysis occurs in a programmed sequence for each individual sample:
- Drying: The solvent is slowly evaporated at low temperature.
- Charring (Pyrolysis): The temperature is raised to burn off organic matrix components without vaporizing the analyte.
- Atomization: The temperature is rapidly ramped to >2000 °C, instantly creating the dense cloud of atoms for measurement. This produces a sharp, transient peak of absorbance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Superior sensitivity does not make the graphite furnace universally better. The choice of atomizer is a classic analytical trade-off between sensitivity and practicality.
Speed vs. Sensitivity
FAAS is fast. Once calibrated, a sample can be analyzed in 10-15 seconds. It is ideal for high-throughput labs analyzing many samples.
GFAAS is slow. A single analysis, with its drying, charring, and atomization steps, takes 2-3 minutes. This limits sample throughput significantly.
Concentration Range
FAAS is designed for higher concentrations, typically in the parts-per-million (ppm) range. Its lower sensitivity is actually an advantage here, preventing detector saturation.
GFAAS is designed for trace analysis, measuring in the parts-per-billion (ppb) or even parts-per-trillion (ppt) range. Trying to measure a ppm-level sample with GFAAS would require massive, often impractical, dilutions.
Robustness vs. Complexity
FAAS is highly robust. It can handle samples with high dissolved solids and complex matrices with relatively few chemical interferences.
GFAAS is far more susceptible to matrix interferences. The slower heating and confinement can lead to complex chemical interactions that suppress or enhance the signal, requiring more extensive method development and matrix modifiers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Choosing the correct technique requires you to match the tool to the analytical problem.
- If your primary focus is trace or ultra-trace analysis (ppb levels): GFAAS is the necessary choice due to its superior atom confinement and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening of samples with higher concentrations (ppm levels): FAAS provides the required speed, robustness, and appropriate working range.
- If you are dealing with complex sample matrices with high dissolved solids: FAAS is often the more robust and reliable starting point.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles of atomization allows you to select the most effective and efficient tool for your specific analytical challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Graphite Furnace AAS (GFAAS) | Flame Atomizer AAS (FAAS) |
|---|---|---|
| Atom Residence Time | ~1 second (longer confinement) | ~0.001 seconds (rapid transit) |
| Atomization Efficiency | ~100% (entire sample used) | 5-10% (most sample wasted) |
| Best Detection Range | Parts-per-billion (ppb) to parts-per-trillion (ppt) | Parts-per-million (ppm) |
| Analysis Speed | 2-3 minutes per sample (slower) | 10-15 seconds per sample (faster) |
| Ideal Use Case | Trace and ultra-trace analysis | High-throughput, higher concentration samples |
Need to achieve precise trace-metal analysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including graphite furnace AAS systems designed for maximum sensitivity and reliability. Whether you're analyzing environmental samples, pharmaceuticals, or advanced materials, our solutions help you detect even the smallest concentrations with confidence.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our AAS technology can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of the graphite material? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Heat
- What is the process of isostatic graphite manufacturing? Achieve Unmatched Material Uniformity and Performance
- How does a graphite furnace work? Achieve Extreme Temperatures in a Pure Environment
- What is the purpose of carbonization? Transform Organic Materials into Valuable Carbon Products
- What is the temperature of atomic absorption in graphite furnace? Mastering the Multi-Stage Heating Program
- What is the function of the graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat for Analysis & Materials Processing
- What is the basic principle of graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy? Achieve Ultra-Trace Element Detection
- What happens to graphite when heated? Unlock Its High-Temperature Potential or Risk Oxidation
















