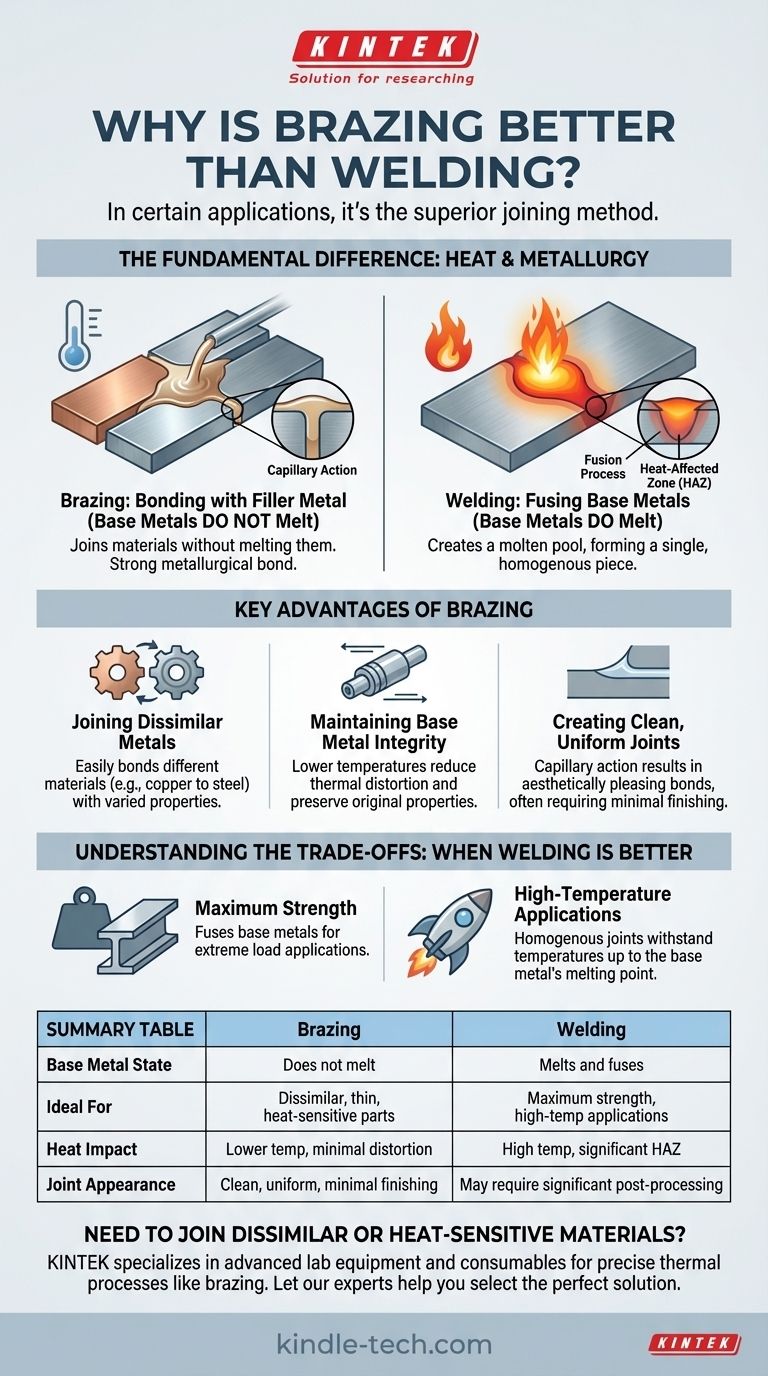
In certain applications, brazing is the superior joining method. It excels where welding would be impractical or damaging, particularly when joining dissimilar metals or heat-sensitive components. The process uses a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base materials, bonding them together without melting them, which is the fundamental difference from welding.
The choice between brazing and welding is not a matter of one being universally "better." The decision depends entirely on a single factor: whether or not the base metals can or should be melted. Brazing joins materials without melting them, while welding fuses them by melting them together.
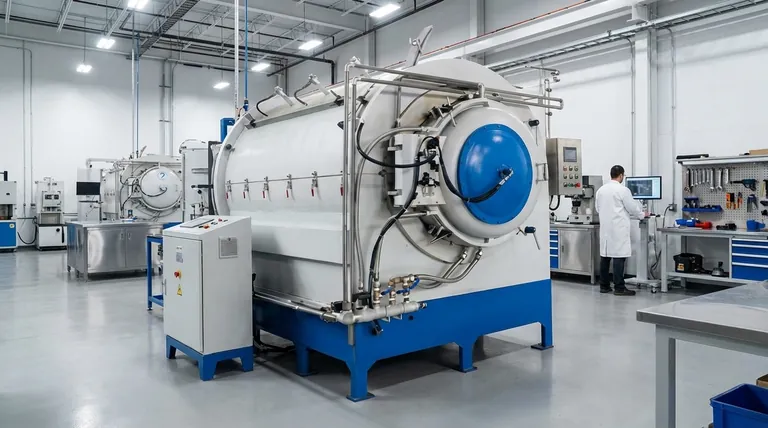

The Fundamental Difference: Heat and Metallurgy
The core distinction between these two processes dictates their respective strengths and weaknesses. Understanding this is key to selecting the correct method for your project.
Welding: Fusing the Base Metals
Welding works by creating a pool of molten material that includes both the base metals and, typically, a filler material. This pool cools to form a single, homogenous piece of metal.
This fusion process is what gives a properly executed weld its exceptional strength. The joint becomes an integral part of the parent materials.
Brazing: Bonding with a Filler Metal
Brazing introduces a filler metal with a lower melting point into a joint. Heat is applied to the base metals until they are hot enough to melt the filler, but not hot enough to melt themselves.
Through a process called capillary action, the molten filler is drawn into the tight-fitting space between the base parts, creating a strong metallurgical bond upon cooling. The integrity and properties of the base metals remain largely unchanged.
Key Advantages of Brazing
The lower-temperature, non-melting nature of brazing provides several distinct advantages in specific scenarios.
Joining Dissimilar Metals
This is arguably brazing's most significant advantage. Attempting to weld two different metals (like copper to steel) is often impossible due to their vastly different melting points, thermal expansion rates, and metallurgical properties.
Because brazing doesn't melt the base metals, it easily bypasses this issue, allowing you to form strong bonds between a wide variety of different materials.
Maintaining Base Metal Integrity
The intense, localized heat of welding can warp, distort, or weaken the base metals, especially on thin or precisely machined parts. This area of thermal damage is known as the Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ).
Brazing uses significantly lower temperatures and distributes heat more broadly. This dramatically reduces thermal distortion and preserves the original temper and metallurgical properties of the parent materials.
Creating Clean, Uniform Joints
The capillary action inherent to brazing pulls the filler metal through the entire joint, resulting in a very clean, uniform, and aesthetically pleasing bond. These joints often require little to no secondary finishing.
This makes brazing ideal for high-volume production where consistency and minimal post-processing are critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Welding Is the Better Choice
To be objective, it is critical to recognize the scenarios where brazing is not the right choice and welding's unique strengths are required.
The Need for Maximum Strength
While a properly brazed joint is very strong, it typically cannot match the absolute strength of a welded joint. By melting the base materials together, welding creates a single, continuous component.
For applications involving extreme loads or stresses where the joint must be as strong as or stronger than the parent material, welding is the appropriate choice.
High-Temperature Applications
The strength of a brazed joint is limited by the melting temperature of its filler metal. If the component's service temperature approaches that melting point, the joint will fail.
Welded joints, being homogenous with the parent metal, maintain their structural integrity up to the melting point of the base material itself, making them essential for high-temperature environments like engines and exhaust systems.
How to Choose Between Brazing and Welding
Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of your project, not by a general preference for one process over the other.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or heat-sensitive parts: Brazing is the superior choice because it avoids melting and potentially damaging the base materials.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum structural strength and high-temperature resistance: Welding is necessary because it fuses the base metals into a single, homogenous component.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with clean, repeatable aesthetics: Brazing often provides a more efficient process with less finishing work required.
By understanding this core metallurgical difference, you can confidently select the right process for your specific problem, ensuring a successful and reliable outcome.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Base Metal State | Does not melt | Melts and fuses |
| Ideal For | Dissimilar metals, thin sections, heat-sensitive parts | Maximum strength, high-temperature applications |
| Heat Impact | Lower temperature, minimal distortion | High temperature, significant Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) |
| Joint Appearance | Clean, uniform, minimal finishing | May require significant post-processing |
Need to Join Dissimilar or Heat-Sensitive Materials?
Choosing the right joining method is critical for the integrity and performance of your components. The brazing process is ideal for applications where preserving the base material's properties is paramount.
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise thermal processes like brazing. Whether you are in R&D, manufacturing, or quality control, we supply the reliable tools you need to achieve strong, clean, and consistent bonds.
Let our experts help you select the perfect solution for your laboratory's specific challenges.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project needs and ensure your joining process is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project



















