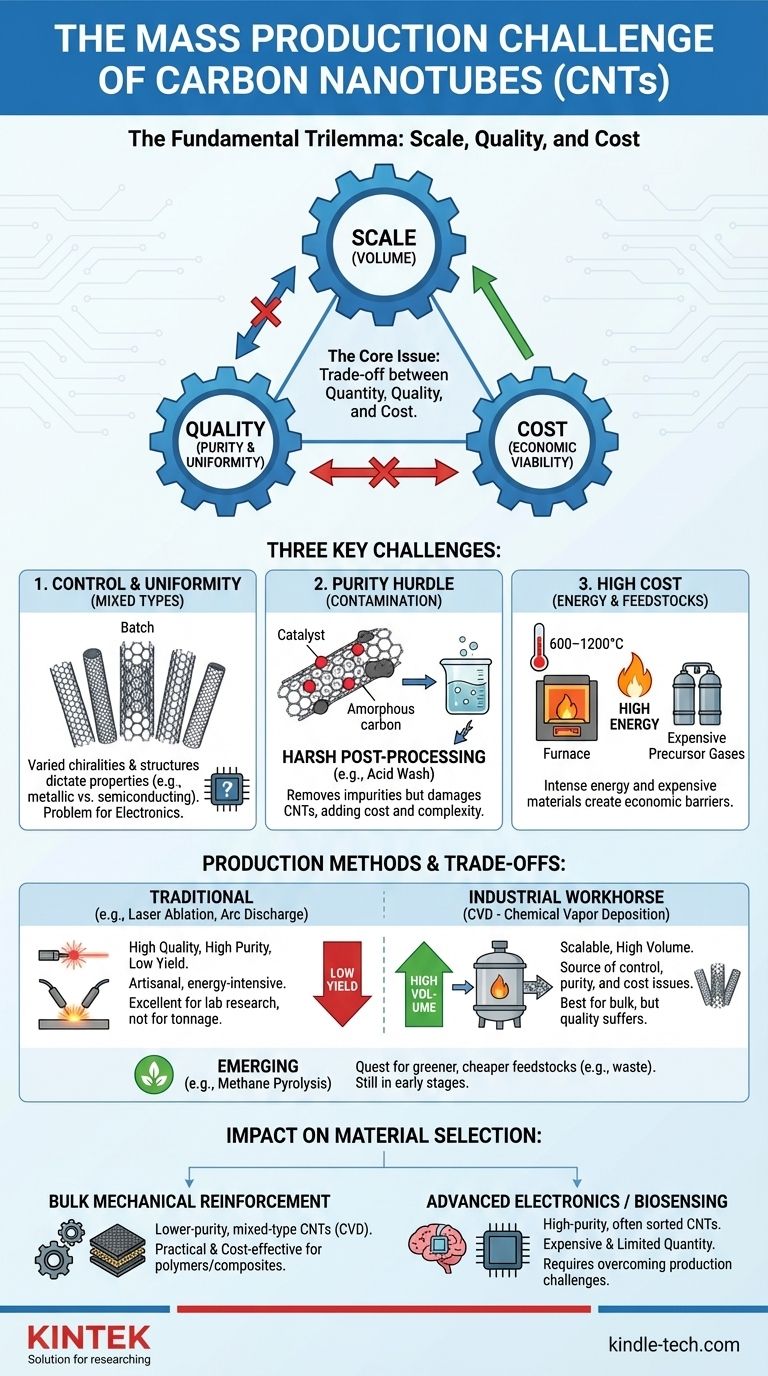
The fundamental challenge in mass-producing carbon nanotubes is not the inability to create large quantities, but the difficulty in controlling the quality and uniformity of those nanotubes at an industrial scale and an economically viable cost. While methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) can produce tons of material, the output is often a heterogeneous mix of different nanotube types contaminated with impurities, which is unsuitable for most high-performance applications.
The core issue is a persistent trade-off between quantity, quality, and cost. Current mass-production techniques excel at producing high quantities, but they do so at the expense of structural control and purity, creating significant downstream challenges for manufacturers.

The Core Challenge: The Trilemma of Scale, Quality, and Cost
To understand the difficulty of mass production, you must see it as a three-part problem. Achieving one goal, like high volume, often compromises another, like purity.
The Problem of Control and Uniformity
Current dominant methods, primarily Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), struggle to produce a uniform product. The process yields a mixture of nanotubes with varying diameters, lengths, and wall structures (single-walled vs. multi-walled).
Even more critically, it produces a mix of different chiralities—the specific arrangement of carbon atoms. Chirality dictates a nanotube's electronic properties, determining whether it behaves like a metal or a semiconductor. For advanced electronics, this lack of control is a dealbreaker.
The Purity Hurdle: Catalyst Contamination
The CVD process relies on nanoparticle metal catalysts (like iron or nickel) from which the nanotubes grow. Unfortunately, these catalyst particles often become encapsulated in the carbon or remain mixed in the final product.
Removing these metallic and amorphous carbon impurities requires harsh post-processing steps, such as acid washes. These purification processes are not only expensive and complex but can also damage the nanotubes, compromising their structural integrity and desired properties.
The High Cost of Energy and Feedstocks
CVD reactors operate at extremely high temperatures (typically 600–1200°C) and require a continuous flow of specific hydrocarbon gases as a carbon source.
The energy consumption and the cost of these precursor materials make the entire process inherently expensive, presenting a significant economic barrier to true low-cost mass production.
A Look at Production Methods
The challenges are rooted in the physics and chemistry of the available production techniques. Each method comes with its own set of advantages and limitations.
Traditional Methods: High Quality, Low Yield
Methods like laser ablation and arc discharge can produce very high-quality, high-purity carbon nanotubes. However, they are extremely energy-intensive and operate on a small scale.
Think of these as artisanal methods. They are excellent for creating pristine samples for laboratory research but are simply not viable for producing materials by the ton.
The Industrial Workhorse: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the most scalable and widely used method for commercial CNT production today. In this process, a carbon-containing gas is introduced into a high-temperature reactor, where it decomposes on catalyst particles, causing nanotubes to grow.
While it is the best option for volume, CVD is the source of the control, purity, and cost challenges that currently define the limits of the industry.
Emerging Solutions: The Quest for Greener Production
New research is focused on overcoming CVD's limitations. Methods like methane pyrolysis (splitting methane into hydrogen and solid carbon) or using CO2 captured via molten salt electrolysis aim to use cheaper or waste feedstocks.
These "green" methods hope to reduce both the cost and the environmental impact of production, but they are still in early stages and not yet ready for widespread industrial scale-up.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Making a practical decision about using CNTs requires acknowledging the compromises inherent in their production.
High-Purity vs. High-Volume
There is a direct and unavoidable conflict between purity and production volume. The highest-purity nanotubes, essential for semiconductors or biomedical sensors, are produced in the smallest quantities at the highest cost.
Conversely, bulk CNTs used as additives in composites or polymers are produced in large volumes but have lower purity and a mix of structures. Their function is primarily mechanical reinforcement, where uniformity is less critical.
The Post-Processing Bottleneck
For many applications, the "raw" output from a CVD reactor is unusable. The material must then undergo extensive post-processing, including purification to remove catalysts and sorting to separate different types of nanotubes.
These extra steps add significant cost, introduce defects into the nanotubes, and represent a major bottleneck that hinders the smooth integration of CNTs into manufacturing supply chains.
How This Impacts Material Selection
Your choice of carbon nanotube material must be aligned with the realities of its production.
- If your primary focus is bulk mechanical reinforcement: Lower-purity, mixed-type CNTs from scalable CVD are a practical and cost-effective choice for enhancing polymers or composites.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics or biosensing: You must source high-purity, often sorted, nanotubes, acknowledging they will be expensive and available in limited quantities due to these production challenges.
Understanding these manufacturing constraints is the key to realistically assessing the true potential and cost of applying carbon nanotubes to your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Issue | Impact on Production |
|---|---|---|
| Control & Uniformity | Mixture of chiralities, diameters, and structures | Limits use in high-performance applications like electronics |
| Purity | Catalyst contamination (e.g., iron, nickel) | Requires costly, damaging post-processing (acid washes) |
| Cost | High energy consumption and expensive feedstocks | Barriers to economically viable industrial scale-up |
| Method Limitations | CVD scales volume but sacrifices quality; traditional methods lack scale | Trade-offs between quantity and quality persist |
Struggling to source the right carbon nanotubes for your application? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your research and production needs. Whether you're working with composites, electronics, or advanced materials, we understand the challenges of CNT uniformity and purity. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve better control and efficiency in your laboratory processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently



















