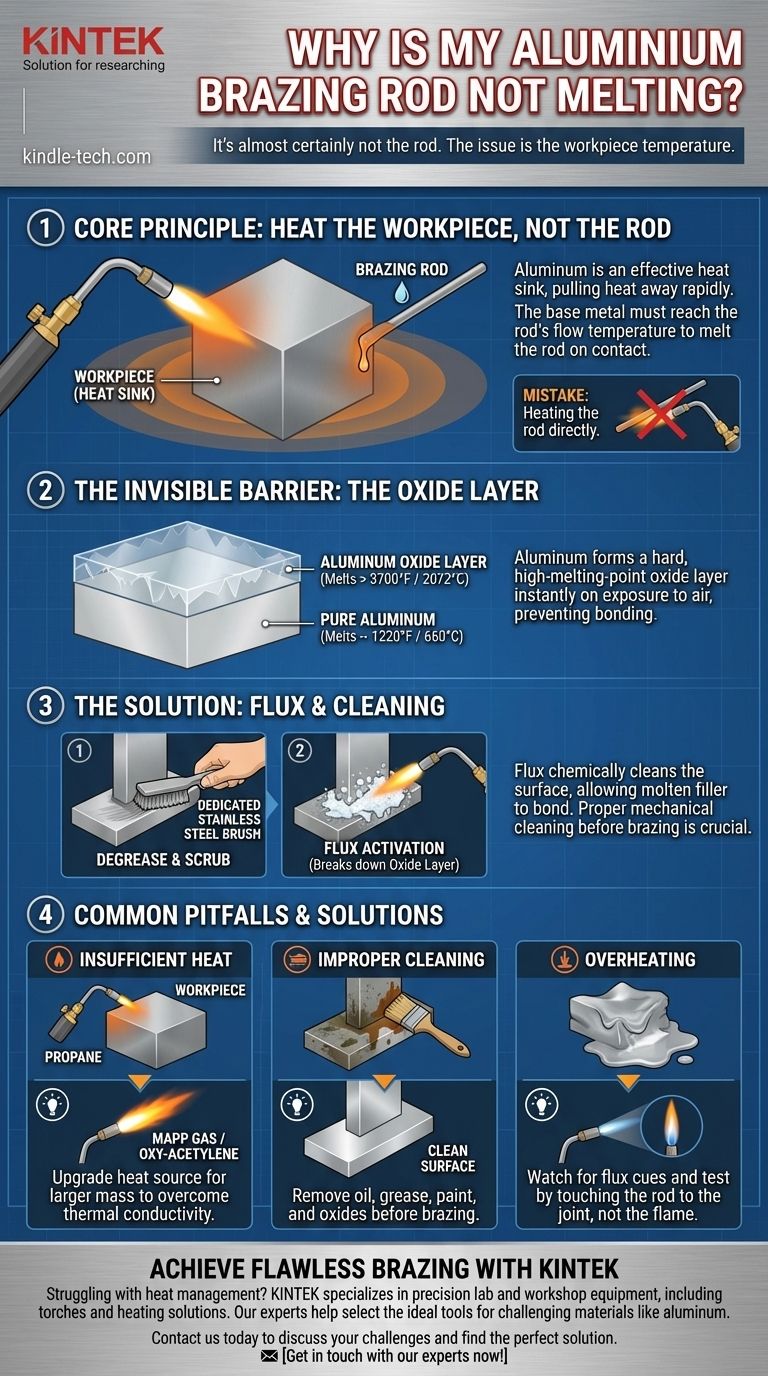
It's almost certainly not the rod. Your aluminum brazing rod isn't melting because the aluminum workpiece you are trying to braze is not hot enough. Aluminum is an incredibly effective heat sink, meaning it pulls heat away from the joint faster than your torch can supply it, a principle known as high thermal conductivity. You must heat the base metal until it is hot enough to melt the rod on contact.
The core mistake in aluminum brazing is heating the filler rod directly with the torch. Instead, you must heat the workpiece broadly and evenly. The base metal itself must reach the flow temperature of the rod, causing the rod to melt and flow into the joint when you touch it to the work.
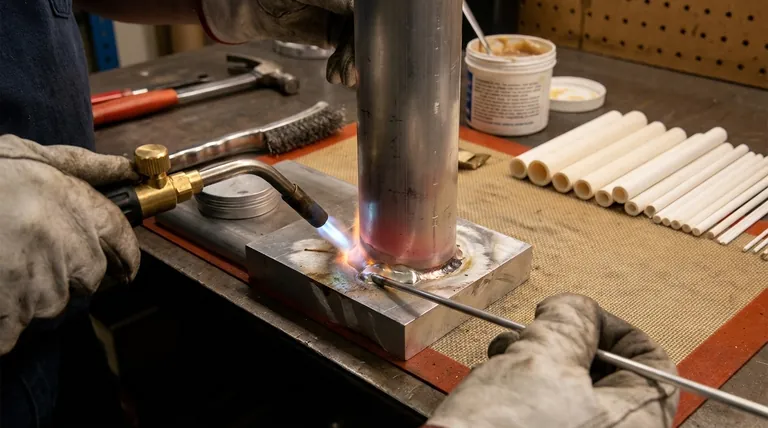

The Core Principle: Heat the Workpiece, Not the Rod
Understanding how aluminum behaves with heat is the key to a successful braze. Its properties are fundamentally different from steel, which trips up many people.
Aluminum's High Thermal Conductivity
Think of the aluminum part as a large sponge for heat. When you apply your torch to one spot, the metal rapidly spreads that thermal energy throughout its entire mass.
This means a small torch focused on the joint is often fighting a losing battle. The workpiece is constantly wicking the heat away, preventing the joint area from ever reaching the rod's melting temperature.
The "Flow" Temperature Misconception
Every brazing rod has a specific working temperature, often called its "flow temperature." This is the temperature the base metal must reach.
It is not enough to simply melt the rod in the flame. If you do this, the molten aluminum will just ball up and fall off, as the cooler workpiece gives it no reason to stick or flow. The workpiece must be hot enough to draw the filler metal into the joint via capillary action.
The Invisible Barrier: The Oxide Layer
Even if you get the temperature right, there is another critical factor at play: an invisible layer of aluminum oxide.
What is Aluminum Oxide?
The moment aluminum is exposed to air, it forms a very hard, transparent layer of aluminum oxide. This layer protects the metal but is a major problem for brazing.
This oxide layer has a melting point of over 3700°F (2072°C), while the aluminum underneath melts at around 1220°F (660°C). You would melt the workpiece into a puddle long before you could melt the oxide layer on its surface.
The Role of Flux
This is where flux becomes essential. Whether it's a separate paste or a core inside the brazing rod (a flux-cored rod), its job is to act as a powerful chemical cleaner.
As you heat the workpiece, the flux activates. It aggressively breaks down and removes the oxide layer, allowing the molten filler metal to bond directly with the pure, clean aluminum underneath. Without effective flux action, a proper bond is impossible.
Common Pitfalls and Technique Errors
If you're heating the workpiece and it's still not working, the issue likely lies in one of these common mistakes.
Insufficient Heat Source
Your torch may simply be underpowered for the job. A basic propane torch might be sufficient for a very thin piece of aluminum tubing, but it will fail against a thicker plate or block.
The mass of the metal dictates the heat required. For larger pieces, you need a hotter fuel like MAPP gas or even an oxy-acetylene setup to deliver enough BTUs to overcome the metal's thermal conductivity.
Improper Cleaning
Flux cannot work through oil, grease, paint, or heavy anodizing. The process must begin with perfectly clean metal.
First, degrease the area with a solvent like acetone or brake cleaner. Then, use a dedicated stainless steel brush to vigorously scrub the joint area. This mechanically breaks up the surface oxide and creates a clean, raw surface for the flux to work on. Using a brush that has been used on steel will contaminate the aluminum and ruin the braze.
Overheating the Workpiece
There is a fine line between heating the piece to the rod's flow temperature and melting the piece itself. This is the hardest part of the learning curve.
Watch the flux for visual cues; it will often turn watery or clear when the right temperature is near. You can also test by periodically touching the rod to the joint (away from the flame). If the workpiece is hot enough, the rod will melt and flow instantly. If it doesn't, pull it away and apply more heat.
A Practical Checklist for a Successful Braze
Apply these principles in order to solve the problem and achieve a strong, reliable joint.
- If your primary focus is a strong bond: Begin with rigorous cleaning. Degrease the part, then scrub the joint with a dedicated stainless steel brush immediately before brazing.
- If your primary focus is getting the rod to flow: Heat the workpiece broadly and evenly, focusing on the area around the joint, not the joint itself. Let the heat "soak" into the part.
- If your primary focus is avoiding failure on thicker parts: Ensure your heat source is adequate for the mass of the metal. If a propane torch isn't working after a minute, you likely need to upgrade to MAPP gas.
Master the heat in the workpiece, and you will master the art of aluminum brazing.
Summary Table:
| Common Problem | Primary Cause | Key Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Rod won't melt | Workpiece is too cold | Heat base metal broadly and evenly |
| Rod balls up, won't stick | Oxide layer prevents bonding | Use proper flux and clean with stainless steel brush |
| Process fails on thick parts | Torch is underpowered | Upgrade to MAPP gas or oxy-acetylene |
| Weak, failed joint | Insufficient cleaning before brazing | Degrease and scrub joint area immediately before heating |
Achieve flawless aluminum brazing results with the right equipment and expertise.
Struggling with heat management or joint failures? KINTEK specializes in precision lab and workshop equipment, including torches and heating solutions perfect for challenging materials like aluminum. Our experts can help you select the ideal tools for your specific application, ensuring strong, reliable bonds every time.
Contact us today to discuss your brazing challenges and find the perfect solution for your laboratory or workshop needs.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Precision Machined Yttrium Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Rod for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Rod for High Temperature Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
People Also Ask
- What is the process of alumina tube manufacturing? From Powder to High-Performance Ceramic
- How high temperature can ceramic withstand? A Guide to Extreme Heat Performance
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity
- What is the advantage of ceramic over metal? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits



















