In short, nitrogen is used in sintering because it provides a cost-effective, relatively inert atmosphere that prevents the metal powder from oxidizing. This protective environment is essential for the individual particles to bond together properly and form a solid, dense part.
Nitrogen's primary role in sintering is to offer an economical solution for preventing oxidation. However, its tendency to react and form nitrides at high temperatures introduces a critical trade-off between enhancing mechanical properties and potentially reducing corrosion resistance.
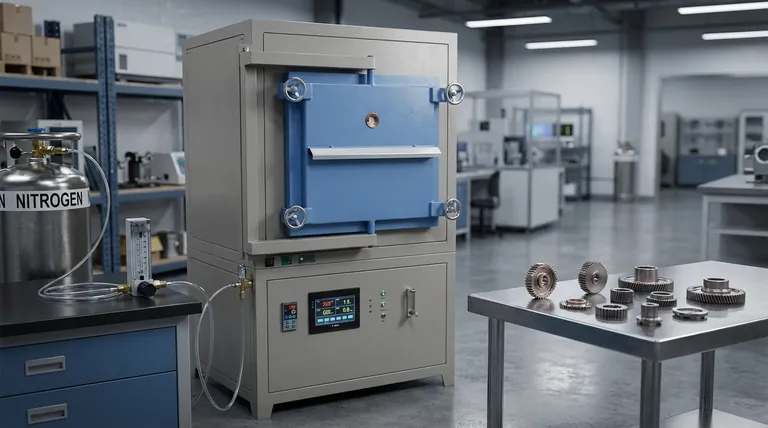

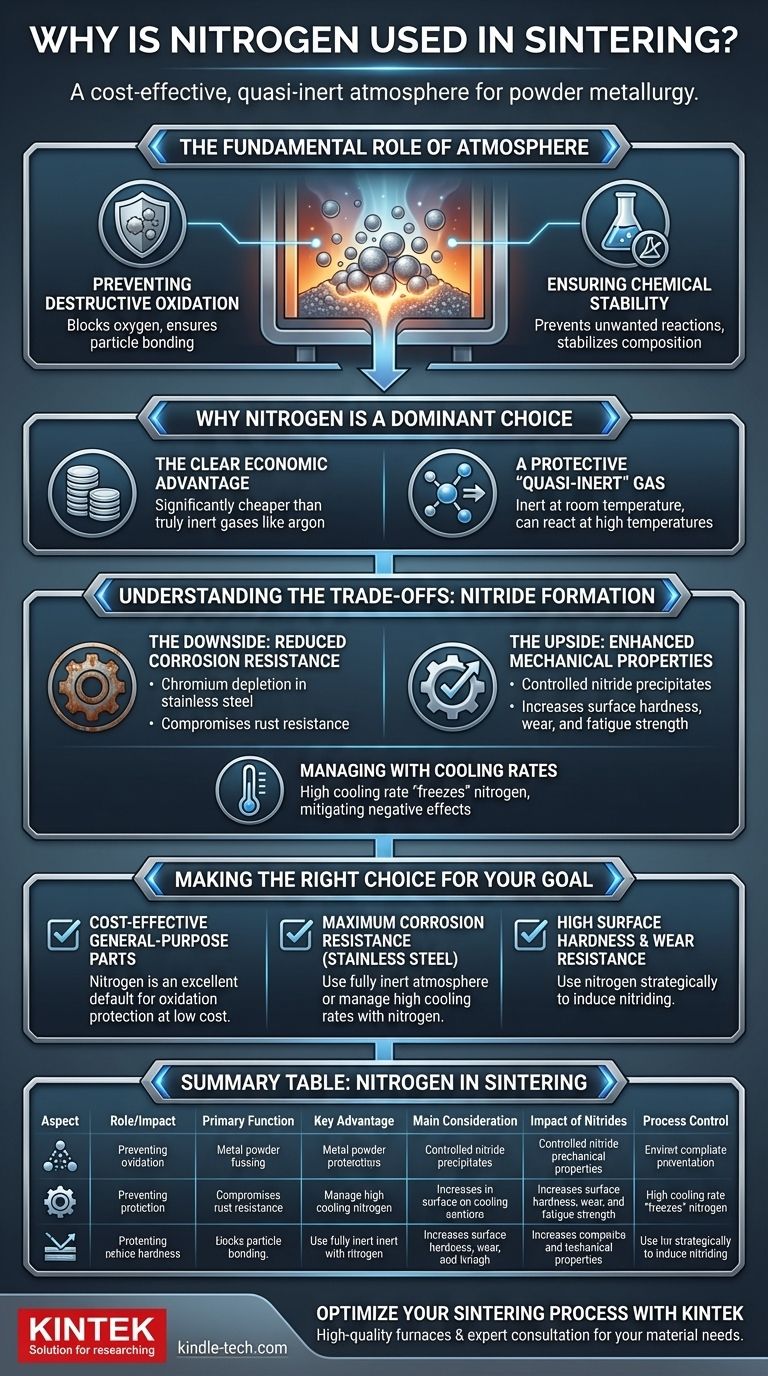
The Fundamental Role of Atmosphere in Sintering
Before focusing on nitrogen, it's crucial to understand why a controlled atmosphere is non-negotiable in the first place. The goal of sintering is to fuse metal powder particles together using heat, and the surrounding gas plays a pivotal role in this transformation.
Preventing Destructive Oxidation
The primary enemy of successful sintering is oxygen. At high temperatures, metal powders will rapidly react with any available oxygen to form oxide layers on their surfaces.
These layers act as a barrier, preventing the metal-to-metal contact required for particles to bond, which would result in a weak, brittle, or completely failed part.
Ensuring Chemical Stability
A controlled atmosphere ensures that the chemical composition of the material remains stable. It prevents unwanted reactions that could alter the final properties of the component.
Why Nitrogen is a Dominant Choice
While other gases like hydrogen or argon can be used, nitrogen holds a prominent place in the industry for several practical reasons.
The Clear Economic Advantage
Nitrogen is significantly less expensive than truly inert gases like argon. For high-volume industrial applications, this cost difference is a major driver in its widespread adoption.
A Protective "Quasi-Inert" Gas
At room temperature, nitrogen is highly inert. In the intense heat of a sintering furnace, however, it can become reactive with certain metals.
This "quasi-inert" behavior is key. It's inert enough to prevent oxidation but active enough to sometimes be used to the engineer's advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Nitride Formation
The most important technical consideration when using nitrogen is its tendency to react with metals at high temperatures to form compounds called nitrides. This reaction is a double-edged sword.
The Downside: Reduced Corrosion Resistance
For materials like stainless steel, the formation of certain nitrides (specifically chromium nitrides) can be detrimental. This process can deplete the chromium needed to form the protective passive layer that gives stainless steel its corrosion resistance.
The result can be a part with good mechanical strength but a compromised ability to resist rust and corrosion.
The Upside: Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Conversely, for other applications, this "nitriding" effect is intentional. For some steel alloys, the controlled formation of fine nitride precipitates within the material's structure can significantly increase surface hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength.
In these cases, nitrogen is not just a protective atmosphere but an active alloying agent that contributes directly to the final material properties.
Managing Nitrides with Cooling Rates
Engineers can control the impact of nitriding through the cooling process. Using a high cooling rate after sintering can help "freeze" the nitrogen in the material's structure before it has time to form the large, detrimental nitride precipitates that harm corrosion resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering atmosphere depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of general-purpose parts: Nitrogen is an excellent default choice, offering superior protection from oxidation at a low cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum corrosion resistance in stainless steels: You must either use a more inert atmosphere (like pure hydrogen or argon) or carefully manage high cooling rates when using nitrogen to suppress nitride formation.
- If your primary focus is achieving high surface hardness and wear resistance: Nitrogen can be used strategically as an active gas to intentionally induce nitriding and enhance the part's mechanical properties.
Ultimately, mastering your sintering process means treating the atmospheric gas not as a simple blanket, but as a critical ingredient in your material's final recipe.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Nitrogen in Sintering |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents oxidation of metal powders during high-temperature heating. |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective compared to fully inert gases like argon. |
| Main Consideration | Can react with certain metals (e.g., stainless steel) to form nitrides. |
| Impact of Nitrides | Potential Downside: Reduces corrosion resistance. Potential Upside: Enhances hardness and wear resistance. |
| Process Control | Cooling rates can be managed to mitigate negative effects of nitride formation. |
Optimize Your Sintering Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right sintering atmosphere is critical to achieving the desired mechanical properties and corrosion resistance in your metal parts. Whether you need a cost-effective nitrogen solution or a fully inert atmosphere for specialized alloys, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's needs.
We provide:
- High-quality sintering furnaces with precise atmosphere control.
- Expert consultation to help you select the optimal gas and process parameters for your specific material and application.
Let's enhance your material's performance together. Contact our experts today to discuss your sintering requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2



















