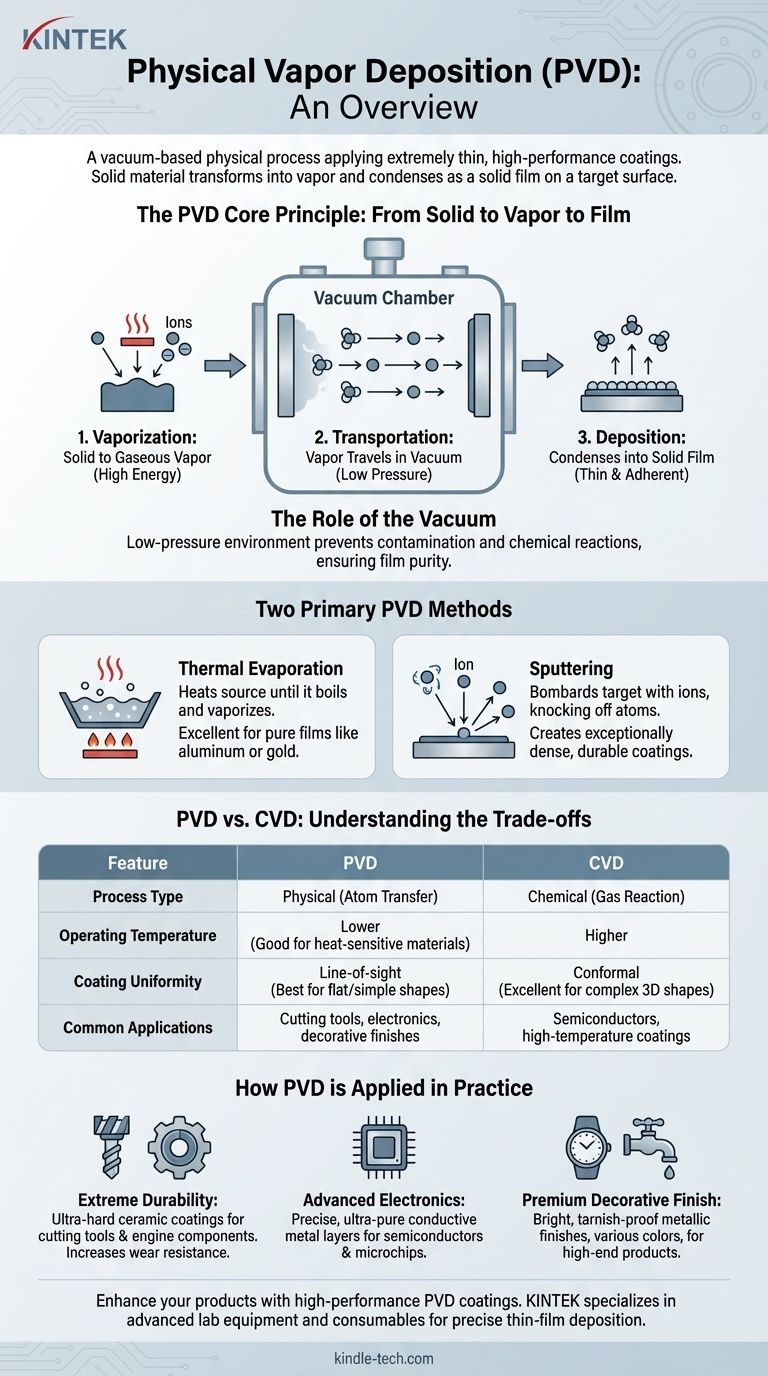
In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a family of vacuum-based processes used to apply extremely thin, high-performance coatings to a vast range of objects. It works by physically transforming a solid coating material into a vapor, which then travels through a vacuum chamber and condenses atom by atom onto a target surface, forming a solid film.
The critical takeaway is that PVD is fundamentally a physical process, not a chemical one. Think of it as "spray painting" with individual atoms in a vacuum, allowing for precise control over the coating's properties like hardness, durability, and color.
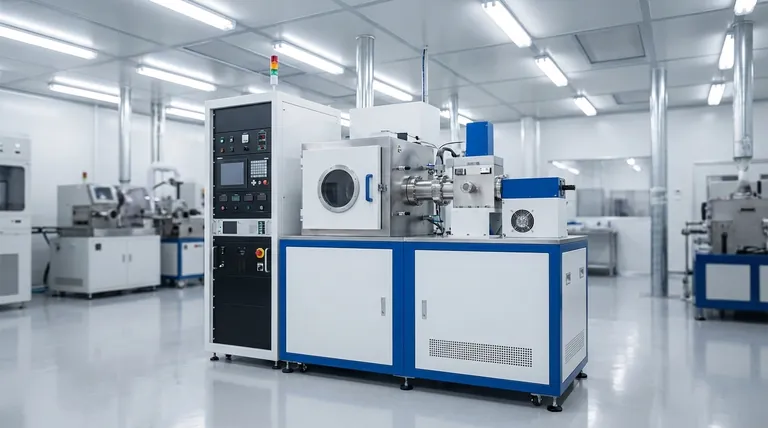

The Core Principle: From Solid to Vapor to Film
How PVD Works
The PVD process can be broken down into three fundamental steps that occur inside a vacuum chamber.
First is vaporization, where a solid source material (known as the "target") is converted into a gaseous vapor. This is achieved using high energy.
Second is transportation. The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line through the low-pressure vacuum environment from the source to the object being coated (the "substrate").
Third is deposition. Upon reaching the substrate, the vapor condenses back into a solid state, forming a thin, dense, and highly adherent film.
The Role of the Vacuum
Operating in a vacuum is non-negotiable for PVD. The low-pressure environment ensures that the vaporized atoms do not collide with air particles, such as oxygen or nitrogen, on their way to the substrate.
This prevents contamination and chemical reactions, ensuring the deposited film is pure and has the desired properties.
The Two Primary PVD Methods
While there are many variations of PVD, the two most common methods are thermal evaporation and sputtering. Each uses a different technique to create the initial vapor.
Thermal Evaporation
This method involves heating the source material in the vacuum chamber until it effectively boils and vaporizes.
The resulting vapor rises, travels through the chamber, and condenses on the cooler substrate, much like steam condensing on a cold mirror. This technique is excellent for depositing very pure films of materials like aluminum or gold.
Sputtering
Sputtering is a more energetic process. Instead of heat, a target is bombarded with high-energy ions (typically from an inert gas like argon).
This atomic-scale bombardment is like a microscopic sandblaster, physically knocking atoms off the target's surface. These ejected atoms then travel and deposit onto the substrate, creating an exceptionally dense and durable coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. CVD
To fully appreciate PVD, it's helpful to contrast it with its main alternative, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Physical vs. Chemical Process
The most significant difference is in the name. PVD is physical; it simply moves existing atoms from a source to a substrate. CVD is chemical; it introduces precursor gases that react on the substrate's surface to create an entirely new solid material.
Operating Temperature
PVD processes can often be performed at much lower temperatures than CVD. This makes PVD ideal for coating heat-sensitive materials, such as plastics or certain metal alloys, that would be damaged or warped by high-heat CVD processes.
Line-of-Sight vs. Conformal Coating
Because PVD atoms travel in a straight line, it is considered a line-of-sight process. It is excellent for coating flat or outwardly curved surfaces but struggles to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with hidden surfaces.
CVD gases, by contrast, can flow around objects and react on all exposed surfaces, creating a more uniform or "conformal" coating on intricate geometries.
How PVD is Applied in Practice
The choice to use PVD is driven by the need to engineer a surface with specific properties that the underlying material does not possess.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability: PVD is used to apply ultra-hard ceramic coatings to cutting tools, drills, and engine components to drastically increase their wear resistance and lifespan.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics: PVD is critical for depositing the precise, ultra-pure conductive metal layers that form the circuitry in semiconductors and microchips.
- If your primary focus is a premium decorative finish: PVD creates the bright, tarnish-proof metallic finishes found on high-end watches, faucets, and door hardware, offering a wide range of colors from gold to black.
Ultimately, PVD is a cornerstone technology for engineering surfaces at the atomic level, enabling performance and properties unattainable by other means.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (atom transfer) | Chemical (gas reaction) |
| Operating Temperature | Lower (ideal for heat-sensitive materials) | Higher |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight (best for flat/simple shapes) | Conformal (excellent for complex 3D shapes) |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, electronics, decorative finishes | Semiconductors, high-temperature coatings |
Ready to enhance your products with high-performance PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thin-film deposition. Whether you're developing cutting tools, electronic components, or decorative finishes, our solutions deliver superior hardness, durability, and purity. Contact us today to discuss how our PVD expertise can meet your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of PECVD? Understanding the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition


















